Employees typically offer deeper job engagement due to their long-term commitment and alignment with company culture, fostering greater loyalty and productivity. Fractional talent provides flexibility and specialized skills for specific projects but may lack the continuous dedication and integration that full-time employees bring. Balancing these workforce options helps organizations maximize efficiency while maintaining strong employee engagement.
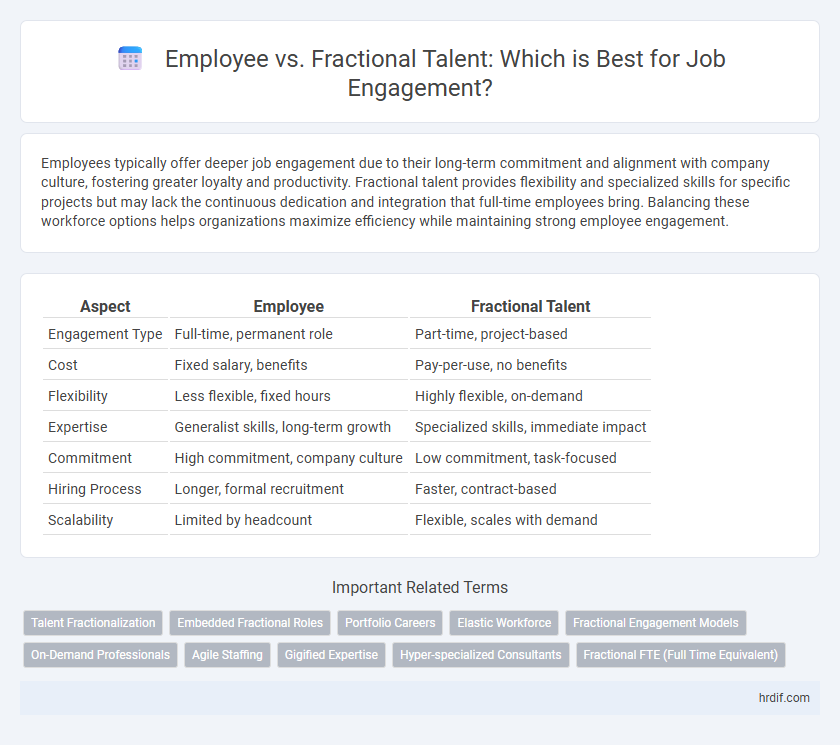
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Employee | Fractional Talent |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement Type | Full-time, permanent role | Part-time, project-based |
| Cost | Fixed salary, benefits | Pay-per-use, no benefits |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fixed hours | Highly flexible, on-demand |
| Expertise | Generalist skills, long-term growth | Specialized skills, immediate impact |
| Commitment | High commitment, company culture | Low commitment, task-focused |
| Hiring Process | Longer, formal recruitment | Faster, contract-based |
| Scalability | Limited by headcount | Flexible, scales with demand |
Understanding Employee and Fractional Talent Roles
Employee roles typically involve long-term commitments with responsibilities that align closely with company culture, fostering continuity and deep organizational knowledge. Fractional talent offers specialized skills on a part-time or project basis, enabling flexible engagement without the overhead of full-time employment. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses optimize workforce strategies by balancing consistency and expertise for varying operational needs.
Core Differences Between Employees and Fractional Talent
Employees typically maintain long-term commitments within a single organization, receiving consistent benefits, comprehensive training, and career development support. Fractional talent, conversely, works on a part-time or project basis for multiple clients, offering specialized skills without the obligations of full-time employment. Core differences include employment duration, level of organizational integration, compensation structure, and flexibility in work arrangements.
Flexibility: Employees vs Fractional Talent
Employees typically offer consistent availability and deep organizational integration, providing long-term stability and a clear understanding of company culture. Fractional talent excels in flexibility, allowing businesses to scale skills on-demand without long-term commitment, often bringing specialized expertise for specific projects. This flexibility makes fractional talent ideal for dynamic workloads and rapid adaptation to changing business needs.
Cost Implications in Hiring Models
Hiring a full-time employee involves consistent salary, benefits, and overhead costs, which can significantly impact long-term budgeting. Fractional talent offers cost advantages by providing specialized skills on an as-needed basis without the expenses related to full-time employment. This flexible hiring model reduces financial risk and optimizes resource allocation for project-specific or seasonal demands.
Engagement Levels: Full-Time Staff vs Fractional Professionals
Full-time employees typically exhibit higher engagement levels due to consistent involvement and stronger organizational commitment, which fosters deeper company culture integration. Fractional professionals, while offering specialized expertise and flexibility, may experience lower engagement because of limited hours and less direct interaction with teams. Organizations balancing both models must tailor management strategies to maximize engagement, leveraging the strengths of each workforce type for optimal job performance.
Skill Specialization and Access
Employees offer consistent availability and deep organizational knowledge, ensuring skill specialization aligned with company culture and long-term goals. Fractional talent provides access to highly specialized skills on demand, enabling businesses to engage experts for specific projects without full-time commitment. This flexibility allows companies to optimize workforce costs while leveraging niche expertise not always available in-house.
Scalability and Business Needs
Employees provide consistent roles with deep organizational knowledge, ensuring long-term scalability aligned with evolving business needs. Fractional talent offers flexible, project-specific skills, enabling rapid scaling during peak demand or specialized initiatives without long-term commitments. Balancing full-time employees and fractional talent optimizes workforce agility and cost efficiency for dynamic business growth.
Cultural Integration and Team Dynamics
Employees often achieve stronger cultural integration and cohesive team dynamics due to their continuous presence and deeper involvement in organizational values and workflows. Fractional talent may excel in specialized tasks but can face challenges aligning fully with company culture and maintaining sustained interpersonal relationships. Effective team dynamics rely heavily on consistent communication and shared experiences, which are more naturally fostered by full-time employees than by part-time or project-based talent.
Long-Term Commitment: Employees vs Fractional Talent
Employees typically demonstrate higher long-term commitment through deep organizational knowledge and stronger cultural alignment, fostering sustained productivity and loyalty. Fractional talent offers flexibility and specialized skills but often lacks the continuous engagement and institutional memory that employees provide. Companies seeking consistent growth and internal development benefit more from the stability of dedicated employees than from temporary fractional professionals.
Choosing the Right Talent Model for Your Business
Selecting between full-time employees and fractional talent depends on your business's workload consistency and budget constraints. Full-time employees offer long-term commitment and in-depth company knowledge, while fractional talent provides flexible, specialized expertise without the overhead of permanent hires. Evaluating project scope, operational needs, and cost-effectiveness helps determine the optimal talent model to maximize productivity and agility.
Related Important Terms
Talent Fractionalization
Talent fractionalization enables companies to engage specialized experts on a part-time basis, maximizing skill utilization without the overhead of full-time employees. Fractional talent offers flexible scalability and targeted project expertise, contrasting with traditional employees who provide continuous, comprehensive roles.
Embedded Fractional Roles
Embedded fractional roles offer businesses flexible access to specialized skills without the long-term commitment of full-time employees, optimizing resource allocation and project-specific expertise. This approach enhances agility and cost-efficiency while maintaining deep integration within the company's operations.
Portfolio Careers
Portfolio careers leverage fractional talent by combining multiple specialized roles, offering businesses flexible, scalable expertise without the commitment of full-time employee contracts. This approach enhances agility and innovation compared to traditional employee models that often limit job engagement to singular, long-term positions.
Elastic Workforce
Elastic workforce models leverage fractional talent to provide businesses with flexible, scalable employee engagement options, optimizing resource allocation and reducing overhead costs. Employees offer continuity and deeper organizational knowledge, while fractional talent delivers specialized skills on demand, enhancing agility in dynamic market conditions.
Fractional Engagement Models
Fractional engagement models enable organizations to access specialized skills on a project-by-project basis, offering flexibility and cost-efficiency compared to traditional full-time employee commitments. These models optimize workforce agility by allowing companies to scale talent precisely according to business needs without the overhead of permanent employment.
On-Demand Professionals
On-demand professionals offer businesses flexible access to specialized skills without long-term commitments, optimizing project-based job engagement and reducing overhead costs compared to traditional full-time employees. This model enhances agility by aligning talent deployment precisely with fluctuating workloads, ensuring efficiency and scalability in workforce management.
Agile Staffing
Agile staffing leverages fractional talent to provide businesses with flexible, project-specific expertise, enabling rapid adaptation to changing market demands without the long-term commitments associated with traditional employees. Fractional talent offers specialized skills on a part-time or contract basis, optimizing workforce agility and cost-efficiency compared to full-time employees.
Gigified Expertise
Employees offer consistent, long-term commitment and deep organizational knowledge, while fractional talent provides flexible, gigified expertise tailored for specific projects or skill gaps. Embracing gigified fractional talent enables businesses to rapidly access specialized skills without the overhead of full-time employment, optimizing workforce agility and cost-efficiency.
Hyper-specialized Consultants
Hyper-specialized consultants offer targeted expertise and flexibility that traditional employees often lack, enabling businesses to address complex challenges with precision and agility. Fractional talent provides scalable, project-based engagement, maximizing efficiency while minimizing overhead costs compared to full-time employee commitments.
Fractional FTE (Full Time Equivalent)
Fractional FTEs provide businesses with flexible, cost-efficient access to specialized skills for specific projects without the commitment of full-time employment, optimizing resource allocation and scalability. Unlike traditional employees, fractional talent allows companies to engage expert professionals on a part-time basis, enhancing productivity while minimizing overhead and benefits expenses.
Employee vs Fractional Talent for job engagement. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com