Full Stack Developers possess in-depth coding expertise and can build complex applications from scratch, managing both front-end and back-end development efficiently. Citizen Developers leverage low-code or no-code platforms, enabling faster, more accessible app creation for non-technical users but with limitations in customization and scalability. Choosing between the two depends on project complexity, resource availability, and the need for speed versus control in software development.
Table of Comparison
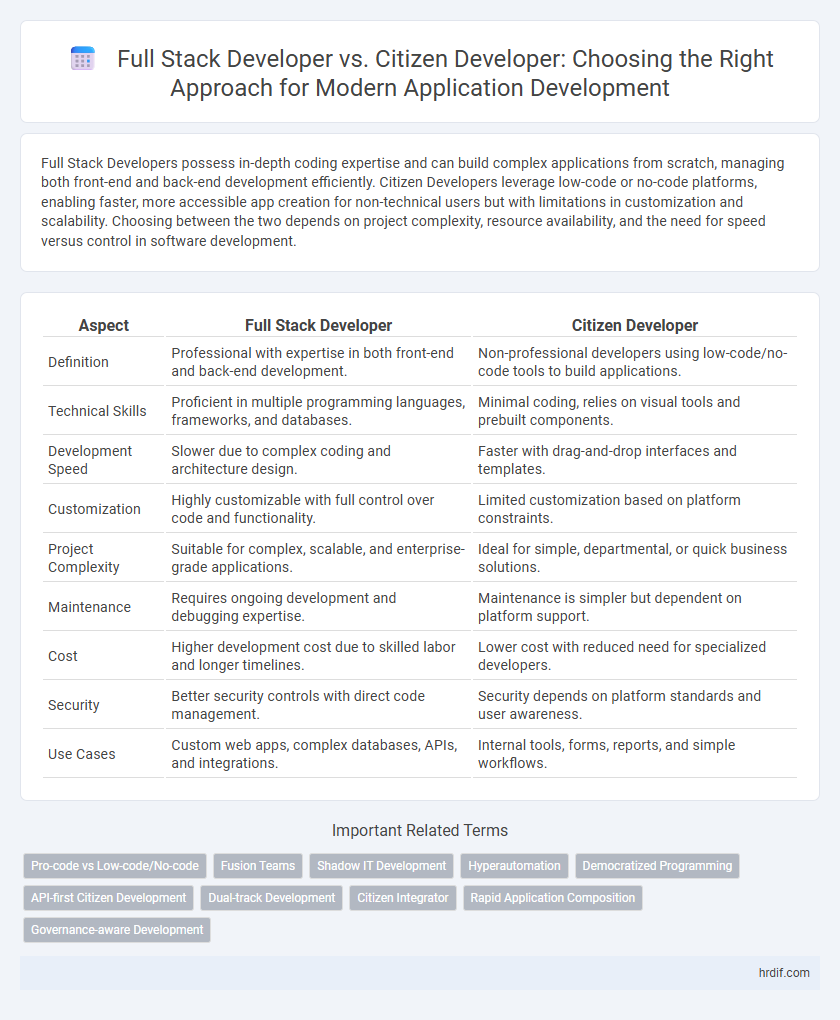
| Aspect | Full Stack Developer | Citizen Developer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Professional with expertise in both front-end and back-end development. | Non-professional developers using low-code/no-code tools to build applications. |
| Technical Skills | Proficient in multiple programming languages, frameworks, and databases. | Minimal coding, relies on visual tools and prebuilt components. |
| Development Speed | Slower due to complex coding and architecture design. | Faster with drag-and-drop interfaces and templates. |
| Customization | Highly customizable with full control over code and functionality. | Limited customization based on platform constraints. |
| Project Complexity | Suitable for complex, scalable, and enterprise-grade applications. | Ideal for simple, departmental, or quick business solutions. |
| Maintenance | Requires ongoing development and debugging expertise. | Maintenance is simpler but dependent on platform support. |
| Cost | Higher development cost due to skilled labor and longer timelines. | Lower cost with reduced need for specialized developers. |
| Security | Better security controls with direct code management. | Security depends on platform standards and user awareness. |
| Use Cases | Custom web apps, complex databases, APIs, and integrations. | Internal tools, forms, reports, and simple workflows. |
Understanding Full Stack Developers
Full Stack Developers possess comprehensive expertise in front-end and back-end technologies, enabling them to design, build, and maintain entire applications independently. Their proficiency in programming languages, databases, APIs, and UI/UX best practices ensures scalable and efficient software solutions. Organizations rely on Full Stack Developers for complex development projects requiring deep technical knowledge and integration skills.
Defining the Citizen Developer Role
Citizen developers are non-professional programmers who use low-code or no-code platforms to create applications, enabling faster development cycles and reducing dependency on IT departments. Full stack developers possess comprehensive technical expertise across front-end and back-end technologies, allowing them to build complex, scalable applications from scratch. Defining the citizen developer role highlights their contribution to democratizing software development by empowering business users to solve problems independently while full stack developers focus on advanced coding and system architecture.
Skill Set Comparison: Full Stack vs Citizen Developers
Full Stack Developers possess comprehensive expertise in front-end, back-end, databases, and server management, enabling end-to-end application development and complex problem solving. Citizen Developers typically have limited coding knowledge but leverage low-code or no-code platforms to create functional business applications rapidly. The skill set gap involves advanced programming languages, full software lifecycle understanding for Full Stack Developers versus platform-specific tool proficiency and business process insight for Citizen Developers.
Project Complexity and Suitability
Full Stack Developers excel in handling complex projects requiring advanced coding skills and deep technical expertise across multiple layers of software architecture. Citizen Developers are suited for simpler, low-code or no-code solutions, enabling faster prototyping and deployment without extensive programming knowledge. Project suitability depends on complexity: high-complexity enterprise applications demand Full Stack Developers, while straightforward business automation benefits from Citizen Developers.
Speed and Agility in Development
Full Stack Developers leverage comprehensive coding expertise to build complex applications with high customization, often requiring longer development cycles but enabling robust functionality. Citizen Developers use low-code or no-code platforms to accelerate development speed and enhance agility, empowering non-technical users to create applications quickly with limited customization. The balance between Full Stack Developers and Citizen Developers hinges on project complexity and the need for rapid iteration versus deep technical control.
Cost Implications for Businesses
Full Stack Developers typically demand higher salaries due to their advanced coding expertise, increasing development costs for businesses. Citizen Developers, leveraging low-code or no-code platforms, reduce expenses by minimizing the need for specialized programming skills and enabling faster prototyping. However, reliance on Citizen Developers may incur hidden costs from limited customization and potential scalability challenges in complex projects.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Full Stack Developers typically hold deeper expertise in secure coding practices, enabling robust implementations of security protocols and compliance standards such as GDPR and HIPAA within the development lifecycle. Citizen Developers, while accelerating application deployment through low-code platforms, may introduce higher risks of security vulnerabilities and compliance breaches due to limited technical knowledge and oversight. Integrating governance frameworks and automated compliance tools is essential to mitigate security risks when leveraging citizen development alongside full stack development.
Scalability and Maintenance Perspectives
Full Stack Developers deliver robust, scalable applications by leveraging comprehensive coding expertise, ensuring maintainable architecture and efficient debugging processes. Citizen Developers often create rapid, less complex solutions with limited scalability and maintenance potential due to their reliance on low-code or no-code platforms. For enterprise-grade projects requiring long-term scalability and systematic updates, Full Stack Developers provide superior control over code quality and application lifecycle management.
Career Pathways and Growth Opportunities
Full Stack Developers benefit from deep expertise in multiple programming languages and frameworks, enabling diverse project roles and leadership positions within software engineering teams. Citizen Developers leverage no-code/low-code platforms, accelerating app delivery with business-centric tools but face limitations in scalability and customization, influencing career growth mostly within business analysis and solution design. The career trajectory for Full Stack Developers offers broader advancement into technical architecture and development management, while Citizen Developers often transition into hybrid roles that bridge technical skills and business strategy.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Full stack developers bring deep technical expertise in coding, system architecture, and software integration, making them ideal for complex, scalable projects requiring custom solutions. Citizen developers leverage low-code/no-code platforms to create applications quickly with minimal IT support, enabling faster delivery and empowering business units to solve specific problems independently. Organizations should assess project complexity, resource availability, and long-term maintenance needs to determine whether full stack or citizen development best aligns with their strategic goals.
Related Important Terms
Pro-code vs Low-code/No-code
Full Stack Developers leverage pro-code expertise to build complex, scalable applications with full control over software architecture and customization, utilizing programming languages like JavaScript, Python, and frameworks such as React or Django. Citizen Developers employ low-code/no-code platforms like Microsoft Power Apps or OutSystems, enabling rapid application development through visual interfaces and pre-built components, accelerating delivery while reducing dependency on traditional coding skills.
Fusion Teams
Full Stack Developers bring deep technical expertise in both front-end and back-end development, enabling complex application creation within Fusion Teams, while Citizen Developers leverage low-code/no-code platforms to rapidly build solutions, enhancing agility and reducing backlog. Combining these roles in Fusion Teams accelerates innovation, optimizes resource utilization, and bridges the gap between IT and business stakeholders.
Shadow IT Development
Full Stack Developers possess comprehensive expertise in multiple programming languages and frameworks, enabling them to build robust, scalable applications from front-end to back-end. Citizen Developers, often business users with limited coding skills, contribute to Shadow IT Development by creating unofficial solutions that can introduce security risks and integration challenges within enterprise environments.
Hyperautomation
Full Stack Developers leverage comprehensive coding skills across multiple layers of software development to create scalable and robust applications, essential for implementing complex hyperautomation workflows. Citizen Developers, using low-code or no-code platforms, accelerate hyperautomation by enabling rapid application creation and automation of routine tasks without deep programming knowledge, fostering greater collaboration between IT and business units.
Democratized Programming
Full Stack Developers possess comprehensive coding expertise across front-end and back-end technologies, enabling complex application development, while Citizen Developers leverage low-code or no-code platforms to create solutions without deep technical skills, accelerating democratized programming and empowering business units to address specific needs more rapidly. This shift toward citizen development fosters increased collaboration, reduces IT backlogs, and promotes agile innovation by broadening participation beyond traditional developer roles.
API-first Citizen Development
API-first Citizen Development empowers non-technical users to build scalable applications by leveraging pre-built APIs, accelerating innovation without deep coding skills. Full Stack Developers offer comprehensive control over both front-end and back-end, but API-first approaches democratize development, enabling faster prototyping and integration across platforms.
Dual-track Development
Full Stack Developers offer comprehensive coding expertise across front-end and back-end systems, enabling robust, customizable solutions essential for dual-track development frameworks. Citizen Developers enhance agility by leveraging low-code platforms to rapidly prototype and iterate, complementing professional developers and accelerating overall delivery cycles.
Citizen Integrator
Citizen Integrators bridge the gap between business needs and IT by enabling non-technical users to create and manage applications through low-code or no-code platforms, enhancing agility in development cycles. Full Stack Developers offer deep technical expertise across frontend and backend technologies, but Citizen Integrators accelerate digital transformation by empowering domain experts to innovate independently without extensive coding knowledge.
Rapid Application Composition
Full Stack Developers leverage extensive coding expertise to build complex applications from scratch, enabling precise control over functionality and customization, whereas Citizen Developers utilize low-code or no-code platforms for rapid application composition, accelerating deployment and reducing dependency on IT teams. The rise of citizen development empowers organizations to quickly address business needs with scalable solutions, while Full Stack Developers ensure robust, maintainable, and scalable application architectures.
Governance-aware Development
Full Stack Developers offer comprehensive coding expertise enabling governance-aware development through rigorous security protocols, code reviews, and compliance checks embedded in the software lifecycle. Citizen Developers accelerate innovation by building low-code/no-code applications, but require robust governance frameworks to mitigate risks, ensure data integrity, and maintain alignment with organizational policies.
Full Stack Developer vs Citizen Developer for Development Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com