Application Developers offer deep customization and control by writing complex code tailored to specific business needs, ensuring high scalability and integration capabilities. Low-code/No-code Developers accelerate development with intuitive visual interfaces and pre-built components, enabling faster deployment and easier maintenance for non-technical users or rapid prototyping. Choosing between these approaches depends on the project's complexity, timeline, and resource availability, balancing flexibility with speed.
Table of Comparison
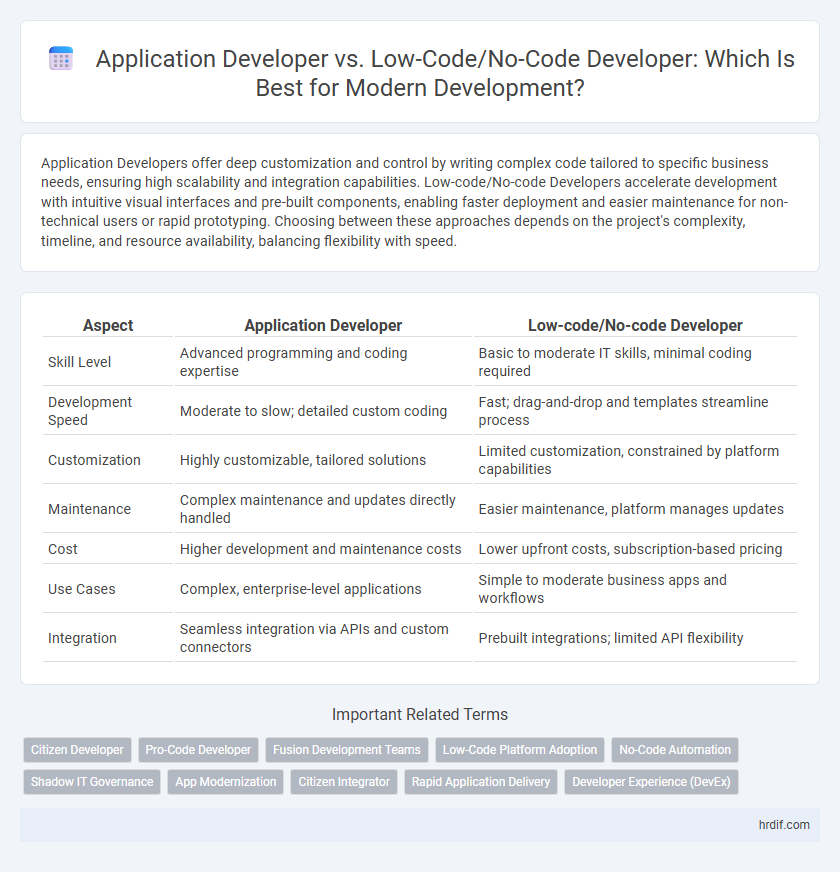
| Aspect | Application Developer | Low-code/No-code Developer |
|---|---|---|
| Skill Level | Advanced programming and coding expertise | Basic to moderate IT skills, minimal coding required |
| Development Speed | Moderate to slow; detailed custom coding | Fast; drag-and-drop and templates streamline process |
| Customization | Highly customizable, tailored solutions | Limited customization, constrained by platform capabilities |
| Maintenance | Complex maintenance and updates directly handled | Easier maintenance, platform manages updates |
| Cost | Higher development and maintenance costs | Lower upfront costs, subscription-based pricing |
| Use Cases | Complex, enterprise-level applications | Simple to moderate business apps and workflows |
| Integration | Seamless integration via APIs and custom connectors | Prebuilt integrations; limited API flexibility |
Introduction: The Evolving Landscape of Application Development
Application development has rapidly transformed with the rise of low-code/no-code platforms, enabling faster deployment and reducing the need for extensive coding expertise. Traditional application developers focus on complex, customized solutions using programming languages like Java, Python, or C#, while low-code/no-code developers leverage visual interfaces and pre-built components to accelerate workflows. This evolution democratizes development, empowering business users to create functional applications without deep technical knowledge, reshaping the software development lifecycle.
Defining Application Developers and Low-code/No-code Developers
Application Developers are skilled professionals who write, test, and maintain custom software programs using traditional programming languages like Java, Python, or C#. Low-code/No-code Developers utilize platforms that enable rapid application development through visual interfaces and pre-built components, requiring minimal or no coding knowledge. These platforms empower business users and developers to create functional applications faster, bridging the gap between technical expertise and business needs.
Core Skills: Traditional Coding vs Low-code/No-code Platforms
Application developers require strong skills in traditional coding languages such as Java, Python, and C# to build complex, custom software solutions from scratch. Low-code/no-code developers primarily leverage platforms like Microsoft Power Apps, OutSystems, or Mendix to rapidly create applications through visual interfaces and pre-built components with minimal hand-coding. Mastery of APIs and integration tools remains essential for both roles, but low-code/no-code development emphasizes speed and accessibility over deep programming expertise.
Learning Curve and Accessibility
Application developers encounter a steeper learning curve due to their need to master complex programming languages and development frameworks, while low-code/no-code developers benefit from intuitive platforms designed to boost accessibility and speed. Low-code/no-code environments enable users with limited technical backgrounds to create functional applications rapidly, promoting democratization of software development across businesses. This accessibility significantly reduces onboarding time and expands development participation beyond traditional coding experts.
Speed of Development and Deployment
Application Developers typically require extensive coding skills and longer development cycles, which can delay deployment. Low-code/No-code Developers leverage visual interfaces and pre-built components, significantly accelerating the speed of development and deployment. This rapid approach enables faster iteration and quicker time-to-market, especially for simple to moderately complex applications.
Flexibility and Customization Capabilities
Application Developers offer extensive flexibility and customization capabilities by coding applications from scratch, enabling tailored solutions to complex business needs. Low-code/No-code Developers utilize visual interfaces and pre-built components, accelerating development but often limiting deep customization and adaptability for unique requirements. Choosing between them depends on project complexity, time constraints, and the need for precise control over application features.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Application developers possess deep coding expertise and can build complex, custom solutions, making them highly sought after for advanced technical roles and leadership positions. Low-code/no-code developers enable faster prototyping and deployment but often face limitations in scalability and customization, which can restrict long-term career growth in more specialized or senior development roles. Career advancement for application developers typically includes paths like software architect, technical lead, or engineering manager, whereas low-code/no-code developers may advance toward process automation specialists or citizen developer coordinators.
Industry Demand and Job Market Trends
Application developers remain in high demand due to their expertise in complex coding and software architecture, essential for custom, scalable solutions in industries like finance and healthcare. Low-code/no-code developers are gaining traction for rapid application development, especially in startups and small to medium enterprises seeking cost-effective and agile solutions. Job market trends indicate a growing preference for hybrid skills, where developers proficient in both traditional coding and low-code platforms command a competitive edge.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
Application developers bring deep coding expertise, enabling complex customization and robust integration within development teams. Low-code/no-code developers accelerate project timelines by creating functional prototypes and applications with minimal coding, fostering collaboration across cross-functional teams including business analysts and designers. Balancing traditional developers with low-code/no-code contributors enhances team dynamics by combining technical proficiency with rapid iterative development.
Choosing Your Path: Which Developer Role Fits You?
Application developers require strong programming skills in languages like Java, Python, or C#, enabling them to build complex, custom software solutions with extensive control over functionality and performance. Low-code/no-code developers leverage platforms such as OutSystems, Mendix, or Microsoft Power Apps, which allow rapid application development through visual interfaces and prebuilt components, ideal for business users or those with limited coding experience. Selecting your path depends on your technical expertise, project complexity, and desired development speed, with traditional application development suited for intricate, scalable systems and low-code/no-code platforms perfect for fast, iterative deployments.
Related Important Terms
Citizen Developer
Citizen developers leverage low-code/no-code platforms to rapidly create applications without extensive traditional programming knowledge, democratizing software development within organizations. Application developers, in contrast, utilize advanced coding skills to build complex, customizable solutions, but citizen developers accelerate innovation by enabling non-technical users to address business needs through intuitive development tools.
Pro-Code Developer
Pro-code developers possess advanced programming skills and deep technical knowledge, enabling them to create highly customized, scalable, and complex applications tailored to specific business requirements. They excel in environments requiring integration with diverse systems and intricate logic, areas where low-code/no-code platforms often face limitations in flexibility and extensibility.
Fusion Development Teams
Fusion Development Teams integrate Application Developers and Low-code/No-code Developers to accelerate project delivery by combining deep coding expertise with rapid visual development tools. This collaboration enhances innovation and scalability while reducing time-to-market and operational costs in software development.
Low-Code Platform Adoption
Low-code/no-code developers accelerate digital transformation by enabling faster application delivery through visual interfaces and pre-built components, reducing dependency on traditional coding skills. Adoption of low-code platforms boosts organizational agility and scalability, with Gartner predicting that by 2025, 70% of new applications will be developed using low-code or no-code tools.
No-Code Automation
No-code automation empowers developers to streamline application development by using visual interfaces and pre-built components, significantly reducing the need for traditional coding expertise. While application developers offer deep customization and complex logic implementation, no-code developers accelerate time-to-market and enable non-technical users to create functional workflows efficiently.
Shadow IT Governance
Application Developers possess deep coding expertise enabling complex, scalable software solutions, while Low-code/No-code Developers accelerate deployment through visual interfaces, often increasing Shadow IT risks due to decentralized app creation. Effective Shadow IT governance requires integrating low-code/no-code platforms into centralized IT policies, ensuring compliance, security, and maintainability without stifling innovation.
App Modernization
Application developers leverage extensive coding skills and frameworks to build and modernize complex, scalable applications, ensuring high customization and integration capabilities critical for legacy system modernization. Low-code/no-code developers accelerate app modernization by using visual development platforms that enable rapid prototyping and deployment, reducing time to market while empowering non-technical users to participate in development processes.
Citizen Integrator
Application developers leverage advanced coding skills and custom frameworks to build complex software solutions, whereas low-code/no-code developers empower citizen integrators to create functional applications through visual interfaces and pre-built components, significantly accelerating development cycles and reducing dependency on traditional IT resources. The rise of citizen integrators fosters inclusive innovation by enabling users with business domain expertise to actively participate in digital transformation without extensive coding knowledge.
Rapid Application Delivery
Application developers leverage traditional coding skills to create highly customized software solutions, ensuring flexibility and control over complex functionalities; low-code/no-code developers accelerate rapid application delivery by using visual development platforms that minimize manual coding, enabling faster deployment and iteration. Both approaches optimize development timelines but cater to different project complexity levels and resource availability.
Developer Experience (DevEx)
Application Developers typically engage in complex coding environments requiring advanced programming skills, offering deep customization and control but demanding extensive debugging and maintenance efforts. Low-code/No-code Developers enhance Developer Experience (DevEx) by enabling faster prototyping and deployment through visual interfaces, reducing technical barriers while potentially limiting flexibility and scalability for complex applications.
Application Developer vs Low-code/No-code Developer for Development. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com