Public speaking demands strong vocal projection, body language, and real-time audience engagement, making it ideal for creating a personal connection and immediate feedback. Digital speaking relies on technology and multimedia tools to reach a broader audience, emphasizing clear visuals, concise messaging, and adaptability across various devices. Both forms require tailored communication skills to effectively convey messages and influence listeners in their respective environments.
Table of Comparison
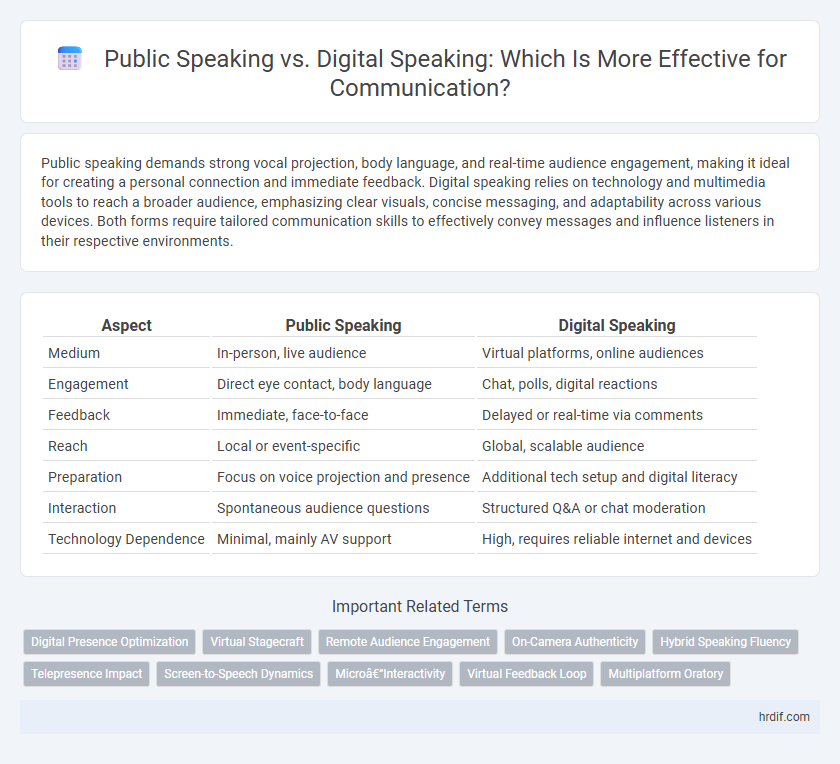
| Aspect | Public Speaking | Digital Speaking |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | In-person, live audience | Virtual platforms, online audiences |
| Engagement | Direct eye contact, body language | Chat, polls, digital reactions |
| Feedback | Immediate, face-to-face | Delayed or real-time via comments |
| Reach | Local or event-specific | Global, scalable audience |
| Preparation | Focus on voice projection and presence | Additional tech setup and digital literacy |
| Interaction | Spontaneous audience questions | Structured Q&A or chat moderation |
| Technology Dependence | Minimal, mainly AV support | High, requires reliable internet and devices |
Definition and Scope: Public Speaking vs Digital Speaking
Public speaking involves delivering a live speech to a physical audience, emphasizing verbal and non-verbal cues such as body language and vocal tone in real-time. Digital speaking encompasses communication through virtual platforms, integrating multimedia elements like slides, videos, and interactive tools to engage remote or online audiences. The scope of public speaking is limited to face-to-face interaction, while digital speaking expands reach globally through technology-driven channels.
Key Skills Required for Each Communication Mode
Public speaking demands strong verbal clarity, confident body language, and the ability to engage a live audience through vocal tone and physical presence. Digital speaking requires proficiency with technology platforms, clear visual communication via video, and skills in managing virtual interaction dynamics such as screen sharing and chat responsiveness. Both modes emphasize storytelling and adaptability, but digital speaking further requires technical literacy and concise messaging suited for online attention spans.
Audience Engagement: Face-to-Face vs Virtual Platforms
Public speaking fosters direct audience engagement through nonverbal cues and immediate feedback, enhancing connection and trust. Digital speaking relies on interactive tools like polls and chat features to maintain audience attention but may face challenges in conveying emotions effectively. Understanding these dynamics is essential for tailoring communication strategies to maximize impact across both face-to-face and virtual platforms.
Overcoming Challenges: Stage Fright vs Screen Anxiety
Overcoming challenges in public speaking often involves managing stage fright, which can trigger intense fear due to physical presence and eye contact with a live audience. In contrast, digital speaking requires strategies to combat screen anxiety, where speakers may feel isolated or distracted by technical issues and lack of immediate feedback. Effective communication in both formats depends on building confidence through preparation, practice, and mastering engagement techniques tailored to the medium.
Nonverbal Cues: Body Language vs Digital Presence
Public speaking relies heavily on body language, including gestures, posture, and facial expressions, which convey confidence and engage the audience effectively. Digital speaking demands a strong digital presence, using vocal tone, camera eye contact, and background setup to compensate for the lack of physical cues. Both forms require mastery of nonverbal communication tailored to their specific environments to enhance message clarity and audience connection.
Adapting Messages for Live and Digital Audiences
Adapting messages for live and digital audiences requires understanding the distinct attention spans and engagement methods in each setting. Public speaking demands dynamic body language and vocal variation to maintain connection, while digital speaking relies on clear visuals, concise language, and interactive elements to overcome screen distractions. Tailoring content to the platform enhances clarity, retention, and audience interaction across both communication formats.
Technology’s Impact on Communication Effectiveness
Technology has transformed communication effectiveness by enabling digital speaking to reach global audiences instantly, enhancing interaction through multimedia tools and real-time feedback. Public speaking remains vital for personal connection and nonverbal cues, but digital platforms expand accessibility and engagement through features like chat, polls, and virtual reality. Integrating traditional public speaking techniques with digital tools optimizes message clarity and audience retention in modern communication environments.
Career Opportunities in Public and Digital Speaking
Public speaking offers career opportunities in corporate training, motivational speaking, and event hosting, leveraging in-person audience engagement skills. Digital speaking expands these opportunities to include webinars, virtual conferences, and online course creation, capitalizing on global reach and multimedia integration. Mastery of both formats enhances marketability and adaptability in the evolving communication landscape.
Measuring Success: Feedback and Analytics
Measuring success in public speaking relies heavily on immediate audience feedback such as facial expressions and verbal reactions, allowing speakers to adjust their delivery in real-time. Digital speaking leverages advanced analytics tools that track viewer engagement, click-through rates, and demographic data, providing detailed insights beyond physical audience interaction. Effective communication strategies integrate both qualitative feedback and quantitative analytics to enhance speaker performance and content impact.
Future Trends in Workplace Communication
Public speaking remains essential for face-to-face workplace communication, fostering immediate feedback and emotional connection, while digital speaking leverages virtual platforms, enabling remote collaboration and global reach. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid communication models that integrate advanced video conferencing tools, augmented reality, and AI-driven speech analytics to enhance engagement and inclusivity. Proficiency in both public speaking and digital communication tools is projected to become a critical skill set for future workforce effectiveness and leadership.
Related Important Terms
Digital Presence Optimization
Digital speaking leverages multimedia tools and real-time audience interaction to enhance communication effectiveness and engagement, optimizing digital presence through strategic content delivery and platform-specific customization. Public speaking emphasizes verbal and non-verbal cues in physical settings, while digital presence optimization prioritizes search algorithms, audience analytics, and multimedia integration to expand reach and influence online.
Virtual Stagecraft
Public speaking demands mastery of physical presence, vocal projection, and audience interaction, while digital speaking emphasizes virtual stagecraft, including camera engagement, background setup, and digital body language to maintain connection through screens. Effective communication in virtual settings relies on optimizing lighting, sound quality, and eye contact techniques to create a compelling digital presence that resonates with remote audiences.
Remote Audience Engagement
Public speaking relies on direct voice modulation and body language to capture audience attention, while digital speaking demands strategic use of visual aids and interactive tools to maintain remote audience engagement. Effective remote communication integrates clear speech with technology-driven engagement techniques such as polls, Q&A sessions, and real-time feedback to overcome physical distance barriers.
On-Camera Authenticity
On-camera authenticity in digital speaking requires mastering non-verbal cues, vocal modulation, and eye contact within a confined frame to build audience trust effectively. Unlike public speaking's dynamic physical presence, digital communication demands heightened self-awareness and adaptability to create genuine connections through virtual platforms.
Hybrid Speaking Fluency
Hybrid speaking fluency enhances communication effectiveness by blending the engaging presence of public speaking with the adaptability of digital platforms, allowing speakers to connect seamlessly with diverse audiences. Mastery in both face-to-face articulation and virtual interaction tools creates a dynamic communication skill set tailored for modern hybrid environments.
Telepresence Impact
Telepresence technology revolutionizes communication by enabling digital speaking to simulate in-person public speaking experiences through high-definition video, spatial audio, and real-time interaction. This advancement enhances engagement, emotional connection, and audience responsiveness, bridging the gap between traditional public speaking and virtual communication platforms.
Screen-to-Speech Dynamics
Public speaking relies heavily on body language, vocal projection, and real-time audience interaction to convey messages effectively, whereas digital speaking emphasizes screen presence, clarity of speech, and engagement through virtual tools like visuals and chat interactions to maintain attention. Mastering screen-to-speech dynamics involves optimizing microphone quality, managing visual aids, and adapting tone to bridge the gap between physical absence and impactful communication.
Micro–Interactivity
Public speaking relies on direct audience engagement through gestures and vocal modulation, fostering immediate micro-interactivity that enhances message retention. Digital speaking integrates interactive tools such as polls and chat functions, enabling real-time feedback and personalized communication that drives deeper audience participation.
Virtual Feedback Loop
Public speaking relies heavily on immediate audience reactions like facial expressions and body language to gauge engagement, whereas digital speaking utilizes virtual feedback loops through real-time chat, polls, and reaction icons to measure audience response and adjust delivery dynamically. This integration of instant digital feedback enhances speaker adaptability and interaction in remote communication environments.
Multiplatform Oratory
Public speaking demands mastery of vocal tone, body language, and immediate audience engagement, while digital speaking requires adapting content for virtual platforms through concise messaging and interactive multimedia. Multiplatform oratory integrates traditional oration techniques with digital tools to enhance communication effectiveness across in-person, livestream, and social media channels.
Public Speaking vs Digital Speaking for communication. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com