Hierarchical collaboration relies on a clear chain of command and defined roles, streamlining decision-making through top-down authority. Holacracy distributes authority across self-managing teams, fostering agility and innovation by empowering individuals at every level. Choosing between these models depends on organizational goals, with hierarchical structures suiting stability and Holacracy enhancing adaptability and employee engagement.
Table of Comparison
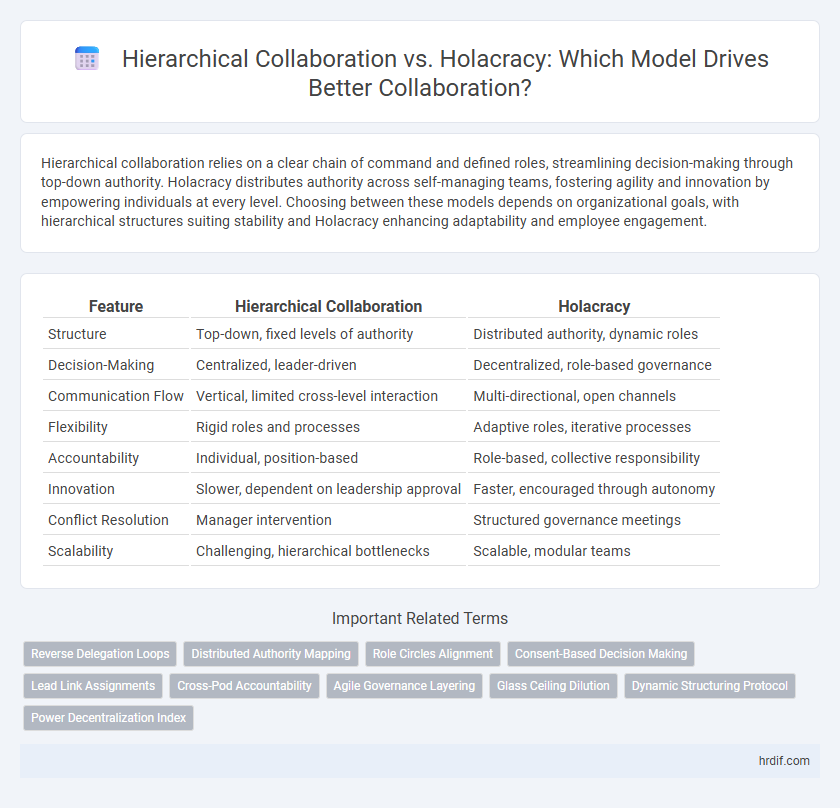
| Feature | Hierarchical Collaboration | Holacracy |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Top-down, fixed levels of authority | Distributed authority, dynamic roles |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, leader-driven | Decentralized, role-based governance |
| Communication Flow | Vertical, limited cross-level interaction | Multi-directional, open channels |
| Flexibility | Rigid roles and processes | Adaptive roles, iterative processes |
| Accountability | Individual, position-based | Role-based, collective responsibility |
| Innovation | Slower, dependent on leadership approval | Faster, encouraged through autonomy |
| Conflict Resolution | Manager intervention | Structured governance meetings |
| Scalability | Challenging, hierarchical bottlenecks | Scalable, modular teams |
Understanding Hierarchical Collaboration
Hierarchical collaboration organizes teams through defined roles and top-down decision-making, ensuring clear authority and accountability. This structure streamlines communication by establishing a chain of command, which can accelerate decision approval but may limit creativity and flexibility. Understanding hierarchical collaboration highlights its effectiveness in stable environments requiring consistent processes and clear leadership.
What is Holacracy?
Holacracy is a decentralized management system that replaces traditional hierarchical structures with distributed authority and self-organizing teams. It emphasizes clear roles, transparent governance, and dynamic processes to enhance agility and employee autonomy. Unlike hierarchical collaboration, Holacracy fosters innovation by empowering individuals to make decisions within defined circles without relying on top-down directives.
Structural Differences: Hierarchy vs. Holacracy
Hierarchical collaboration relies on a top-down structure with clearly defined roles and decision-making authority concentrated at higher management levels, facilitating control and predictable workflows. Holacracy distributes authority across self-organizing teams, using dynamic roles and governance meetings to enable flexibility and rapid adaptation. This structural difference affects communication patterns, accountability, and the agility of collaboration within organizations.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Hierarchical collaboration relies on a top-down decision-making process where authority and accountability are clearly defined within organizational levels, enabling quick execution but potentially limiting innovation and employee autonomy. In contrast, holacracy distributes decision-making across self-organizing teams, fostering transparency and collective responsibility while requiring comprehensive communication and alignment among roles. Understanding these differences is crucial for organizations aiming to balance agility with structured oversight in collaborative environments.
Communication Flow in Each Model
Hierarchical collaboration features top-down communication where information flows through established chains of command, often leading to slower decision-making and potential information bottlenecks. Holacracy promotes decentralized communication with dynamic roles and direct peer-to-peer interaction, enabling faster information exchange and adaptive workflows. This decentralized communication flow in holacracy enhances transparency and responsiveness compared to the rigid, structured pathways inherent in hierarchical models.
Employee Autonomy and Empowerment
Hierarchical collaboration often limits employee autonomy by concentrating decision-making authority at upper management levels, which can hinder empowerment and slow responsiveness. Holacracy distributes authority across self-managing teams, fostering greater employee autonomy and enabling faster, more agile decision-making. Organizations adopting holacratic structures report increased innovation and engagement by empowering employees to take ownership of their roles and collaborate dynamically.
Leadership Roles: Traditional vs. Distributed
Leadership roles in hierarchical collaboration rely on a clear chain of command with defined authority and responsibility centralized at the top, ensuring streamlined decision-making but potentially limiting employee autonomy. In contrast, holacracy distributes leadership across self-organizing teams, empowering individuals to take on multiple roles and make decisions collectively, enhancing agility and innovation. This distributed leadership model fosters accountability at all levels, creating a dynamic collaboration environment where roles evolve based on expertise and project needs.
Collaboration Efficiency and Innovation
Hierarchical collaboration centralizes decision-making, which can streamline processes but often limits cross-functional innovation and slows adaptation to change. Holacracy promotes distributed authority and autonomous teams, enhancing collaboration efficiency through rapid communication and fostering a culture of continuous innovation. Organizations adopting holacracy report increased agility and creative problem-solving compared to traditional hierarchical structures.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Hierarchical collaboration often faces challenges in slow decision-making and limited innovation due to rigid chains of command and top-down communication. Holacracy can encounter limitations with role ambiguity and increased complexity in coordination, leading to potential confusion and inefficiency in fast-paced environments. Both approaches require careful adaptation to organizational culture and clear guidelines to mitigate their respective drawbacks.
Choosing the Right Collaboration Model for Your Organization
Choosing the right collaboration model depends on your organization's structure and goals, with hierarchical collaboration offering clear roles, decision-making authority, and accountability paths, ideal for organizations valuing stability and control. Holacracy, characterized by decentralized decision-making and self-organizing teams, fosters agility, innovation, and employee empowerment, suited for dynamic environments requiring quick adaptation. Evaluating factors like organizational size, culture, and complexity can guide the selection between hierarchical collaboration and holacracy for optimal performance and engagement.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Delegation Loops
Hierarchical collaboration often struggles with reverse delegation loops, where tasks are passed back upward due to unclear authority, causing delays and inefficiencies. Holacracy eliminates these loops by distributing authority across self-managed teams, ensuring decisions are made at the appropriate level and accelerating collaboration.
Distributed Authority Mapping
Distributed Authority Mapping in hierarchical collaboration centralizes decision-making within defined roles and levels of a traditional organizational chart, ensuring clear accountability but potentially limiting agility. Holacracy distributes authority dynamically across self-organizing teams, enabling flexible, role-based governance that adapts to evolving tasks and promotes greater autonomy.
Role Circles Alignment
Hierarchical collaboration relies on clearly defined roles within a top-down structure, ensuring role circles are aligned through formal reporting lines and centralized decision-making, which enhances accountability but may limit flexibility. Holacracy distributes authority across self-organizing role circles that dynamically align through transparent governance processes, promoting adaptability and real-time role adjustments to better meet evolving organizational needs.
Consent-Based Decision Making
Hierarchical collaboration relies on top-down decision-making where authority is concentrated, often limiting team input, whereas holacracy emphasizes consent-based decision making that distributes authority across roles to foster collective responsibility and agile responses. Consent-based decision making in holacracy removes veto power but requires objections to be reasoned and integrative, optimizing collaboration by ensuring all voices influence decisions without paralysis.
Lead Link Assignments
Lead Link assignments in Hierarchical Collaboration centralize decision-making and clarify accountability within defined roles, ensuring streamlined command chains for efficient project management. In Holacracy, Lead Link roles dynamically connect multiple circles, distributing authority and fostering autonomous teamwork through flexible role assignments and transparent governance processes.
Cross-Pod Accountability
Hierarchical collaboration often struggles with cross-pod accountability due to rigid reporting lines and limited communication channels, resulting in siloed decision-making and slower problem resolution. Holacracy enhances cross-pod accountability by distributing authority across autonomous teams, enabling swift collaboration, transparent responsibility sharing, and adaptive workflows that improve organizational agility.
Agile Governance Layering
Hierarchical collaboration relies on top-down decision-making and clearly defined roles, which can slow responsiveness but maintain control, while holacracy promotes distributed authority and self-management, enhancing agility and adaptability through dynamic role definitions. Agile governance layering integrates these models by combining strategic oversight from hierarchical structures with operational flexibility from holacracy, enabling scalable, responsive collaboration within complex organizations.
Glass Ceiling Dilution
Hierarchical collaboration often reinforces rigid Glass Ceiling structures by concentrating decision-making power at the top, limiting upward mobility and innovation. Holacracy dissolves traditional Glass Ceilings by distributing authority across self-organizing teams, fostering inclusivity and enhancing transparent collaboration.
Dynamic Structuring Protocol
Hierarchical Collaboration relies on fixed roles and top-down decision-making, which can limit adaptability and responsiveness in fast-changing environments. Holacracy's Dynamic Structuring Protocol enables distributed authority and fluid role definitions, promoting agility and decentralized collaboration for more effective innovation and problem-solving.
Power Decentralization Index
Hierarchical collaboration typically features low Power Decentralization Index values due to centralized decision-making concentrated at top management levels, limiting employee autonomy. Holacracy demonstrates a high Power Decentralization Index by distributing authority through self-managing teams, promoting transparency and empowering frontline contributors to drive organizational adaptation.
Hierarchical Collaboration vs Holacracy for collaboration. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com