Teamwork emphasizes structured roles where each member contributes specific expertise to achieve a common goal efficiently. Swarming involves rapid, collective attention from multiple team members to address urgent tasks or issues, maximizing quick problem-solving. Choosing between teamwork and swarming depends on the nature of the collaboration, with teamwork fostering sustained productivity and swarming enabling immediate response.
Table of Comparison
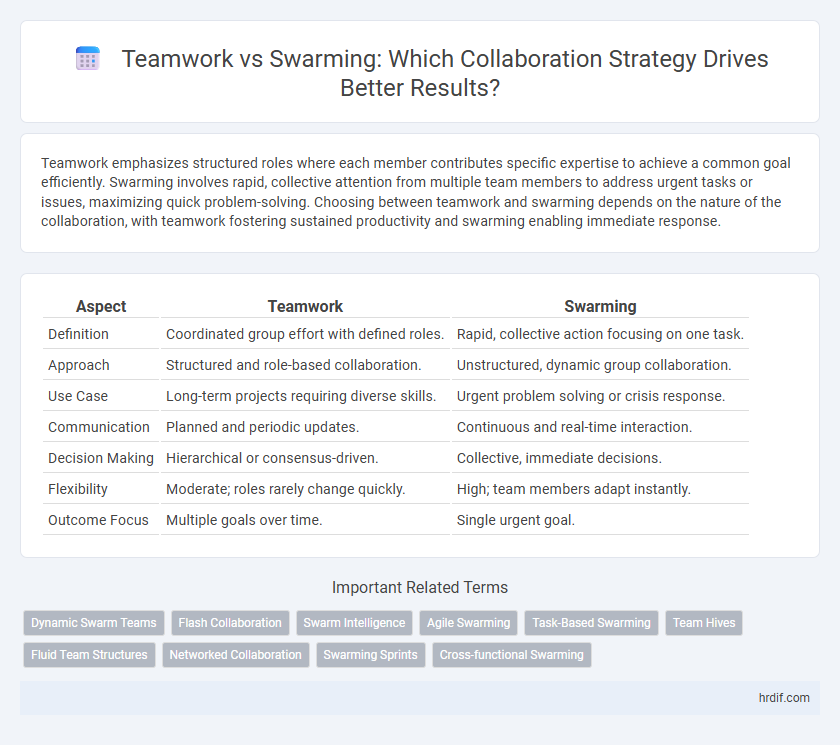
| Aspect | Teamwork | Swarming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coordinated group effort with defined roles. | Rapid, collective action focusing on one task. |
| Approach | Structured and role-based collaboration. | Unstructured, dynamic group collaboration. |
| Use Case | Long-term projects requiring diverse skills. | Urgent problem solving or crisis response. |
| Communication | Planned and periodic updates. | Continuous and real-time interaction. |
| Decision Making | Hierarchical or consensus-driven. | Collective, immediate decisions. |
| Flexibility | Moderate; roles rarely change quickly. | High; team members adapt instantly. |
| Outcome Focus | Multiple goals over time. | Single urgent goal. |
Understanding Teamwork: Definition and Principles
Teamwork involves a structured group of individuals working collectively towards common goals, emphasizing clear roles, consistent communication, and mutual accountability. It is grounded in principles such as trust, collaboration, and shared responsibility, ensuring efficient task delegation and goal alignment. Understanding teamwork enhances organizational productivity by fostering cohesive interactions and sustained cooperation among team members.
What is Swarming? An Emerging Collaboration Approach
Swarming is an emerging collaboration approach where team members rapidly converge on a task or problem, working collectively in real-time to achieve faster resolution. Unlike traditional teamwork that often follows predefined roles and sequential processes, swarming emphasizes dynamic participation and immediate resource pooling. This method enhances agility, promotes shared ownership, and accelerates problem-solving in complex or high-priority projects.
Key Differences Between Teamwork and Swarming
Teamwork involves coordinated efforts with defined roles and sequential task completion, enhancing efficiency through specialization and structured communication. Swarming emphasizes real-time, collective problem-solving where all members simultaneously engage to address urgent issues, fostering rapid adaptability and shared ownership. The key differences lie in the static versus dynamic role allocation and the linear versus simultaneous task execution models.
When to Use Teamwork vs Swarming
Teamwork excels in structured projects requiring clear roles, long-term coordination, and progressive task completion, maximizing efficiency through defined responsibilities. Swarming is ideal for urgent, complex issues needing rapid problem-solving and collective focus, leveraging real-time collaboration to swiftly address bottlenecks. Choosing between teamwork and swarming depends on project urgency, task clarity, and the need for either sustained collaboration or immediate, concentrated effort.
Advantages of Teamwork in the Workplace
Teamwork in the workplace fosters clear role definition and consistent communication, leading to improved accountability and specialized skill development. It promotes a collaborative environment where employees build trust and long-term working relationships, enhancing overall productivity. Structured teamwork also enables efficient project management by aligning individual strengths with specific tasks, resulting in higher quality outcomes.
Benefits of Swarming for Rapid Problem-Solving
Swarming enhances rapid problem-solving by enabling cross-functional experts to converge instantly on complex issues, accelerating decision-making and reducing resolution time. This collaborative approach fosters real-time knowledge sharing and diverse perspectives, which improve solution quality and adaptability. Swarming minimizes communication barriers and streamlines workflows, delivering faster outcomes compared to traditional teamwork models.
Challenges Faced in Teamwork Collaboration
Teamwork collaboration often faces challenges such as communication breakdowns, unequal participation, and conflicts over roles or responsibilities, which can hinder project progress. Misalignment of goals and varying commitment levels among team members frequently lead to reduced efficiency and morale. Addressing these issues requires clear communication channels, defined roles, and continuous feedback mechanisms to foster effective collaboration.
Common Obstacles in Swarming Environments
Swarming environments often face common obstacles such as communication overload, role ambiguity, and coordination challenges due to the dynamic and spontaneous nature of team interactions. Unlike traditional teamwork, swarming requires rapid adaptability and continuous information sharing, which can lead to bottlenecks if not managed effectively. Addressing these obstacles involves implementing clear protocols, real-time collaboration tools, and fostering a culture of trust to ensure seamless coordination and productivity.
Building a Collaborative Culture: Integrating Both Methods
Integrating teamwork and swarming fosters a dynamic collaborative culture by balancing structured roles with agile problem-solving. Teamwork provides clear responsibilities and long-term coordination, while swarming accelerates issue resolution through rapid, focused collaboration. Combining these methods enhances adaptability and drives continuous innovation within organizations.
Future Trends: Evolving Collaboration Models in Careers
Future collaboration models emphasize a shift from traditional teamwork to dynamic swarming techniques that enhance real-time problem-solving and innovation. Swarming leverages flexible, cross-functional groups that rapidly assemble and disband around tasks, optimizing agility in fast-paced career environments. This evolution reflects growing demands for adaptive collaboration frameworks driven by digital transformation and the rise of remote work.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Swarm Teams
Dynamic swarm teams enhance collaboration by enabling rapid, flexible response to evolving tasks through autonomous, skill-based member engagement, outperforming traditional teamwork structures that rely on fixed roles and hierarchical coordination. These swarm teams leverage real-time data and continuous communication to optimize resource allocation and problem-solving efficiency in complex, fast-paced environments.
Flash Collaboration
Flash collaboration leverages rapid swarming techniques where team members quickly converge on an issue, enabling real-time problem solving and accelerated decision-making. This dynamic approach contrasts with traditional teamwork by emphasizing immediate, flexible task allocation and continuous information flow to enhance overall productivity.
Swarm Intelligence
Swarm intelligence leverages decentralized, self-organizing systems inspired by natural behaviors of social insects to enhance collaboration efficiency and adaptability in problem-solving scenarios. Unlike traditional teamwork, which relies on structured roles and hierarchy, swarming promotes dynamic interaction and real-time information sharing among agents, leading to faster consensus and innovation.
Agile Swarming
Agile swarming enhances collaboration by enabling cross-functional team members to converge rapidly on high-priority tasks, accelerating problem-solving and reducing cycle times compared to traditional teamwork structures. This dynamic approach fosters real-time communication and collective ownership, driving continuous improvement and maximizing delivery efficiency in Agile environments.
Task-Based Swarming
Task-based swarming enhances collaboration by mobilizing a focused group of experts to address specific tasks swiftly, improving problem resolution and efficiency compared to traditional teamwork. Unlike teamwork that follows predefined roles and processes, swarming adapts dynamically to task demands, enabling rapid knowledge sharing and real-time coordination.
Team Hives
Team Hives leverage the strength of teamwork by organizing members into specialized units that focus on distinct tasks, enhancing overall efficiency and clarity of roles. Unlike swarming, which involves simultaneous group action on a single task, Team Hives maintain structured collaboration to optimize productivity and sustain long-term project goals.
Fluid Team Structures
Fluid team structures enable organizations to rapidly shift from traditional teamwork, where roles and responsibilities are fixed, to swarming, which involves dynamic, real-time collaboration among diverse experts converging on a problem. This adaptability enhances innovation and problem-solving efficiency by leveraging collective intelligence and minimizing delays inherent in rigid team hierarchies.
Networked Collaboration
Teamwork traditionally involves structured roles and sequential task completion, while swarming leverages immediate, simultaneous engagement from multiple collaborators to solve problems dynamically. Networked collaboration enhances swarming by enabling real-time information sharing and fluid resource allocation across decentralized teams.
Swarming Sprints
Swarming sprints accelerate problem-solving by mobilizing all team members simultaneously to focus on a single issue, ensuring faster resolution and enhanced agility compared to traditional teamwork approaches that often segment tasks sequentially. This collaborative intensity leverages collective expertise in real-time, driving innovation and improving project outcomes through concentrated effort and immediate feedback loops.
Cross-functional Swarming
Cross-functional swarming enhances collaboration by rapidly assembling diverse expertise to address complex challenges in real-time, surpassing traditional teamwork's sequential approach. This dynamic method accelerates problem-solving and innovation through intensified, simultaneous contributions from all relevant functions.
Teamwork vs Swarming for collaboration. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com