Group projects often rely on fixed roles and linear workflows, which can slow down adaptation and innovation. Agile pods emphasize small, cross-functional teams that promote continuous feedback and rapid iteration, enhancing collaboration efficiency. This dynamic structure fosters accountability and flexibility, optimizing productivity in evolving project environments.
Table of Comparison
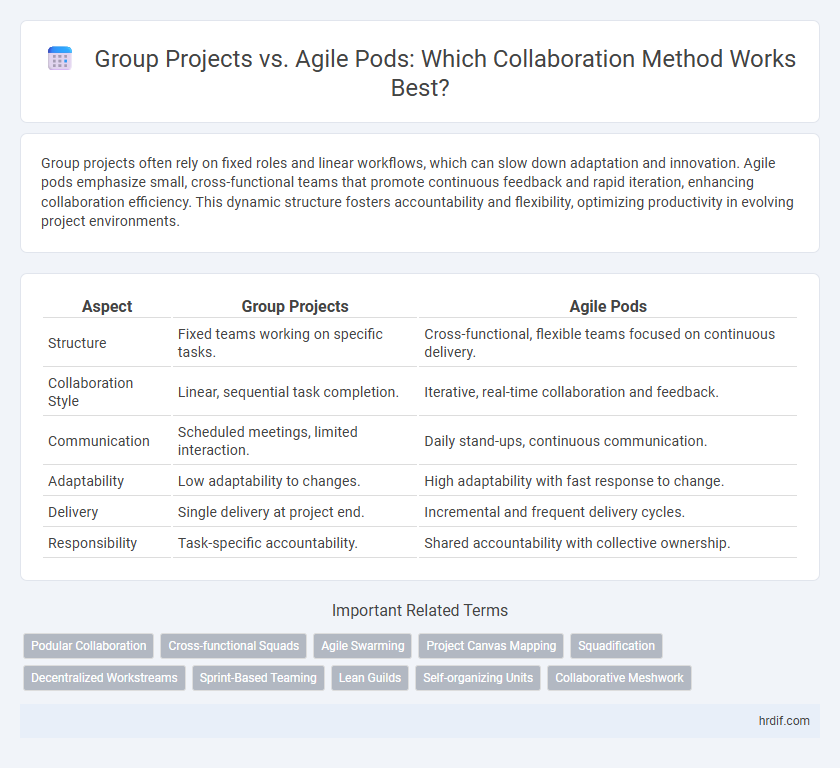
| Aspect | Group Projects | Agile Pods |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Fixed teams working on specific tasks. | Cross-functional, flexible teams focused on continuous delivery. |
| Collaboration Style | Linear, sequential task completion. | Iterative, real-time collaboration and feedback. |
| Communication | Scheduled meetings, limited interaction. | Daily stand-ups, continuous communication. |
| Adaptability | Low adaptability to changes. | High adaptability with fast response to change. |
| Delivery | Single delivery at project end. | Incremental and frequent delivery cycles. |
| Responsibility | Task-specific accountability. | Shared accountability with collective ownership. |
Understanding Group Projects: Traditional Collaboration Models
Traditional group projects in collaboration rely on predefined roles and linear workflows, often leading to rigid structures and slower adaptation to changes. These models emphasize clear hierarchies, scheduled meetings, and deliverables tied to strict timelines, which can limit flexibility and responsiveness. Understanding group projects highlights the challenges of coordination and communication in dynamic environments compared to more iterative and self-organizing frameworks like Agile pods.
What Are Agile Pods? Defining Modern Team Structures
Agile pods are small, cross-functional teams designed to operate autonomously, enabling faster decision-making and enhanced collaboration compared to traditional group projects. Each pod combines diverse skill sets focused on specific project goals, fostering adaptability and continuous improvement within modern team structures. This approach optimizes workflow efficiency by breaking down silos and encouraging shared responsibility, making Agile pods a preferred model for dynamic project environments.
Key Differences Between Group Projects and Agile Pods
Group projects typically follow a linear workflow with defined roles and a fixed timeline, emphasizing individual accountability and sequential task completion. Agile pods operate using iterative cycles, cross-functional teams, and continuous feedback loops, fostering adaptability and collective ownership of outcomes. Key differences include Agile pods' emphasis on flexibility, real-time collaboration, and responsiveness to change compared to the structured, milestone-driven approach of group projects.
Strengths of Group Projects in Workplace Settings
Group projects in workplace settings excel at fostering diverse skill integration by bringing together members with varied expertise to tackle complex tasks. They provide structured roles and clear deadlines that enhance accountability and ensure focused effort throughout the project lifecycle. The collaborative environment promotes knowledge sharing and strengthens team cohesion, which can lead to innovative solutions and improved overall performance.
The Advantages of Agile Pods for Dynamic Teams
Agile pods enhance collaboration by fostering cross-functional teamwork within small, self-managing units, enabling faster decision-making and adaptability compared to traditional group projects. These pods leverage iterative workflows, continuous feedback, and transparent communication tools, which optimize productivity and responsiveness in dynamic environments. Emphasizing autonomy and shared ownership, agile pods reduce bottlenecks and improve alignment with shifting project goals and product requirements.
Collaboration Efficiency: Comparing Group Projects and Agile Pods
Group projects often face challenges with uneven task distribution and communication delays, reducing collaboration efficiency. Agile pods enhance productivity by fostering continuous feedback, real-time adjustments, and autonomous teamwork within small, cross-functional units. Empirical studies show Agile pods increase project completion speed by up to 30% compared to traditional group projects due to streamlined communication and accountability.
Accountability and Roles: Clarity in Group vs Agile Structures
Group projects often struggle with accountability due to unclear role definitions, leading to overlapping responsibilities or gaps in task ownership. Agile pods emphasize well-defined roles such as Scrum Master, Product Owner, and cross-functional team members, fostering transparent accountability and streamlined collaboration. This clarity in Agile structures enhances individual responsibility and accelerates project progress compared to traditional group project models.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Team Collaboration
Agile pods enhance flexibility and adaptability in team collaboration by enabling cross-functional members to rapidly respond to evolving project needs and priorities. Unlike traditional group projects with fixed roles and linear processes, Agile pods emphasize iterative development and continuous feedback, fostering a dynamic and resilient workflow. This approach accelerates decision-making and innovation, making teams more effective in managing change and delivering results.
Impact on Career Growth: Skills Learned in Each Model
Group projects typically emphasize teamwork, time management, and communication skills, providing a foundation for collaborative work but often limited in adaptability to changing project requirements. Agile pods enhance career growth by fostering dynamic skill sets such as iterative problem-solving, cross-functional expertise, and rapid feedback incorporation, which are critical in modern, fast-paced work environments. Professionals experienced in agile pods often demonstrate greater proficiency in leadership, technical versatility, and resilience, directly contributing to accelerated career advancement opportunities.
Choosing the Right Collaborative Approach for Your Organization
Selecting the ideal collaborative approach hinges on organizational goals and team dynamics; group projects suit clearly defined, linear tasks, while Agile pods excel in iterative, fast-paced environments emphasizing adaptability and cross-functional expertise. Agile pods foster continuous feedback loops and rapid problem-solving, enhancing innovation and responsiveness, whereas group projects provide structure and accountability through predefined roles and milestones. Organizations prioritizing speed, flexibility, and customer-centric development benefit from Agile pods, whereas those requiring detailed planning and sequential execution may find traditional group projects more effective.
Related Important Terms
Podular Collaboration
Podular collaboration in Agile Pods enhances team efficiency by fostering cross-functional expertise and continuous feedback loops, leading to faster problem-solving and innovation. Compared to traditional group projects, Agile Pods promote autonomous decision-making and adaptive workflows, optimizing collaboration in dynamic environments.
Cross-functional Squads
Cross-functional squads in Agile Pods enhance collaboration by integrating diverse skill sets within small, self-organizing teams focused on iterative progress and continuous feedback. Group projects often lack this dynamic adaptability and efficiency, as they typically involve hierarchical structures and less frequent interdepartmental communication.
Agile Swarming
Agile swarming optimizes collaboration by enabling cross-functional teams to quickly converge on high-priority tasks, unlike traditional group projects that often follow rigid roles and sequential workflows. This dynamic approach accelerates problem-solving and enhances team responsiveness, driving efficient project delivery and adaptive innovation.
Project Canvas Mapping
Project Canvas Mapping enhances collaboration by providing clear visual frameworks for both group projects and Agile pods, enabling teams to define roles, objectives, and deliverables effectively. Agile pods leverage the dynamic adaptability of Project Canvas to streamline iterative workflows, while group projects benefit from its structured overview to manage diverse tasks and dependencies efficiently.
Squadification
Group projects often face challenges with coordination and accountability, while Agile Pods utilize squadification to enhance collaboration by creating small, cross-functional teams focused on specific goals. Squadification promotes autonomy, faster decision-making, and continuous feedback loops, driving higher productivity and innovation in collaborative environments.
Decentralized Workstreams
Group projects often rely on centralized decision-making and defined roles, which can limit flexibility in decentralized workstreams. Agile pods embrace decentralized collaboration by empowering cross-functional teams with autonomy, enabling faster adaptation and iterative progress across distributed environments.
Sprint-Based Teaming
Sprint-based teaming in Agile pods promotes continuous collaboration through iterative development cycles, enabling real-time feedback and rapid adjustments; group projects typically follow a linear timeline with predefined roles and less flexibility. Agile pods enhance productivity and adaptability by fostering cross-functional expertise and autonomous decision-making within short sprints, contrasting with the traditional group project's often siloed and rigid structure.
Lean Guilds
Lean Guilds enhance collaboration by integrating Agile Pods' adaptive workflows with the focused expertise found in Group Projects, fostering continuous improvement and rapid iteration. This hybrid approach streamlines communication, maximizes resource efficiency, and drives innovation through collective ownership and specialized skill-sharing.
Self-organizing Units
Agile pods function as self-organizing units that enhance collaboration by enabling teams to quickly adapt, distribute responsibilities dynamically, and maintain continuous communication without rigid hierarchies. In contrast, traditional group projects often rely on preset roles and linear workflows, limiting flexibility and responsiveness in fast-paced environments.
Collaborative Meshwork
Collaborative Meshwork enhances collaboration by integrating Group Projects and Agile Pods, allowing dynamic interaction and adaptive workflows that leverage diverse expertise across teams. This approach facilitates seamless knowledge sharing and continuous feedback, optimizing productivity and innovation in complex, interdependent tasks.
Group Projects vs Agile Pods for collaboration. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com