Cross-functional teams bring together members from different departments to leverage diverse expertise, fostering innovation and comprehensive problem-solving. Liquid teams offer dynamic, flexible structures where members flow between projects based on skills and needs, enhancing adaptability and rapid response. Both models boost collaboration, but liquid teams excel in fast-changing environments, while cross-functional teams provide stability and deep, consistent knowledge sharing.
Table of Comparison
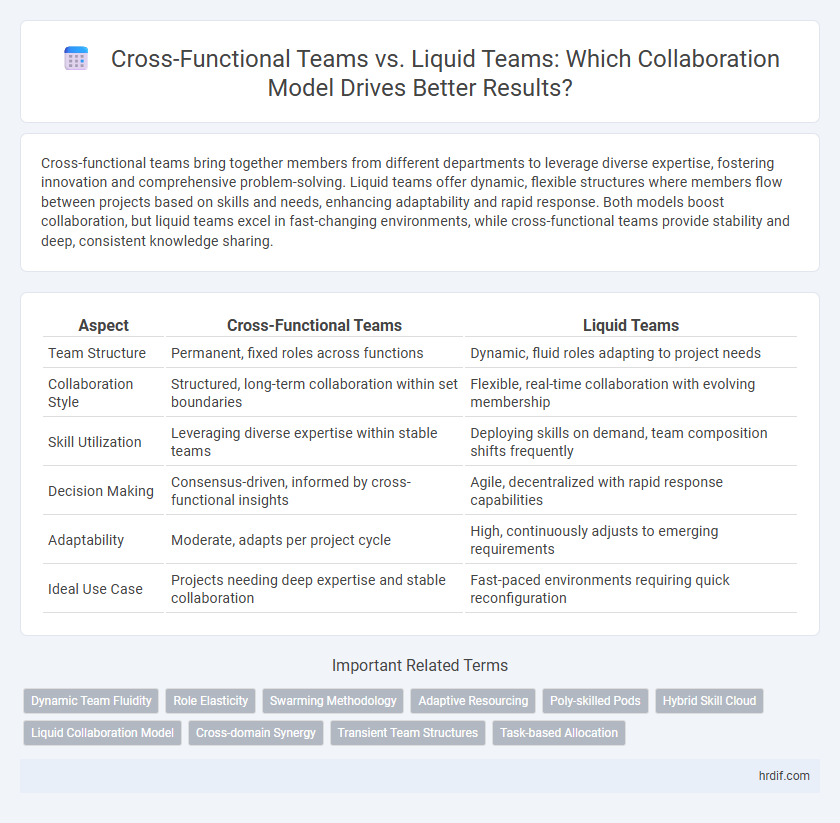
| Aspect | Cross-Functional Teams | Liquid Teams |
|---|---|---|
| Team Structure | Permanent, fixed roles across functions | Dynamic, fluid roles adapting to project needs |
| Collaboration Style | Structured, long-term collaboration within set boundaries | Flexible, real-time collaboration with evolving membership |
| Skill Utilization | Leveraging diverse expertise within stable teams | Deploying skills on demand, team composition shifts frequently |
| Decision Making | Consensus-driven, informed by cross-functional insights | Agile, decentralized with rapid response capabilities |
| Adaptability | Moderate, adapts per project cycle | High, continuously adjusts to emerging requirements |
| Ideal Use Case | Projects needing deep expertise and stable collaboration | Fast-paced environments requiring quick reconfiguration |
Defining Cross-Functional Teams: Structure and Purpose
Cross-functional teams consist of members from diverse departments working together to achieve shared goals, enhancing innovation and problem-solving through varied expertise. These teams are structured with clearly defined roles and responsibilities, fostering accountability and streamlined communication across functional boundaries. Their purpose centers on leveraging multidisciplinary perspectives to address complex challenges and drive organizational success.
Understanding Liquid Teams: Flexibility and Dynamics
Liquid teams emphasize adaptability and dynamic membership, allowing professionals from different departments to join and leave projects as needed, enhancing responsiveness to changing goals. Unlike static cross-functional teams, liquid teams dissolve and re-form based on project demands, promoting flexibility in roles and expertise. This fluid structure supports innovative collaboration by leveraging diverse skills in a timely and efficient manner.
Core Differences Between Cross-Functional and Liquid Teams
Cross-functional teams consist of specialists from different departments working together temporarily to achieve specific project goals, emphasizing diverse skill sets within a structured format. Liquid teams offer dynamic, flexible collaboration where members flow between projects based on expertise and availability, adapting quickly to shifting priorities. Core differences include rigidity versus adaptability, fixed roles against fluid contributions, and defined tenure compared to continuous team evolution.
Key Collaboration Benefits of Cross-Functional Teams
Cross-functional teams enhance collaboration by integrating diverse expertise from various departments, fostering innovative problem-solving and broader perspectives. These teams improve communication flow and accelerate decision-making processes by breaking down organizational silos. The collective knowledge and varied skills in cross-functional teams drive higher productivity and more effective project outcomes compared to liquid teams.
Advantages of Liquid Teams in Agile Work Environments
Liquid teams provide unmatched flexibility by allowing members to seamlessly shift roles based on project needs, enhancing adaptability in Agile work environments. Their fluid structure accelerates decision-making and innovation, as expertise is dynamically allocated without rigid boundaries. This approach reduces bottlenecks and fosters continuous collaboration, driving higher productivity and faster delivery of value in Agile projects.
Challenges in Managing Cross-Functional Teams
Cross-functional teams face challenges such as conflicting priorities, communication barriers, and skill gaps that hinder seamless collaboration. Managing diverse expertise requires aligning goals and fostering mutual trust to avoid inefficiencies and interpersonal conflicts. Unlike liquid teams, which emphasize fluid roles and rapid adaptability, cross-functional teams often struggle with rigid structures and slower decision-making processes.
Overcoming Obstacles Faced by Liquid Teams
Liquid teams enhance flexibility by dynamically reconfiguring members across projects, yet they encounter challenges such as ambiguous roles and fluctuating team cohesion. Overcoming obstacles for liquid teams requires implementing clear communication protocols and robust knowledge-sharing platforms to ensure continuity and alignment despite constant member changes. Establishing standardized onboarding processes and leveraging collaborative technology mitigates disruptions and fosters seamless integration within liquid team structures.
Impact on Innovation: Cross-Functional vs Liquid Teams
Cross-functional teams drive innovation by integrating diverse expertise, fostering creative problem-solving through structured collaboration across departments. Liquid teams enhance innovation with their agility and dynamic reconfiguration, enabling rapid adaptation to emerging challenges and seamless knowledge sharing in real-time. Both models boost innovation; cross-functional teams offer stability and depth, while liquid teams provide flexibility and speed in collaborative innovation processes.
Choosing the Right Team Model for Your Organization
Cross-functional teams bring together specialists from diverse departments to leverage specific expertise on structured projects, enhancing innovation and problem-solving through clear role definitions and steady collaboration. Liquid teams offer a flexible, dynamic approach where members shift fluidly between projects based on evolving organizational needs, promoting adaptability and rapid response to market changes. Selecting the appropriate team model depends on factors such as organizational agility, project complexity, and the need for specialized knowledge versus flexibility in resource allocation.
Best Practices for Effective Team Collaboration
Cross-functional teams leverage diverse expertise from different departments to foster innovation and problem-solving, emphasizing clear communication and role clarity for effective collaboration. Liquid teams prioritize adaptability and dynamic membership, allowing rapid reconfiguration based on project needs, which enhances responsiveness but requires robust knowledge-sharing systems to prevent information silos. Best practices include establishing transparent goals, utilizing collaborative tools for real-time information exchange, and promoting a culture of trust and continuous feedback to maximize team performance regardless of structure.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Team Fluidity
Cross-functional teams bring together diverse expertise from distinct departments to solve complex problems, enhancing innovation through structured collaboration. Liquid teams emphasize dynamic team fluidity by allowing members to move fluidly between projects, adapting quickly to changing priorities and fostering agile, real-time collaboration.
Role Elasticity
Cross-functional teams leverage fixed roles within diverse expertise to enhance collaboration, while liquid teams emphasize role elasticity, allowing members to dynamically shift responsibilities based on project needs and skills. Role elasticity in liquid teams fosters agility and innovation by enabling seamless adaptation to changing tasks and priorities.
Swarming Methodology
Cross-functional teams integrate diverse expertise within stable groups, enabling consistent knowledge sharing, while liquid teams dynamically form around tasks using swarming methodology to rapidly address complex problems with agile collaboration. Swarming emphasizes real-time communication and collective problem-solving, optimizing responsiveness and innovation in fluid project environments.
Adaptive Resourcing
Cross-functional teams combine diverse expertise within fixed roles to enhance collaboration, while liquid teams prioritize adaptive resourcing by dynamically assembling talent across departments based on project needs. Adaptive resourcing in liquid teams maximizes agility and resource efficiency, enabling rapid response to evolving business challenges.
Poly-skilled Pods
Cross-functional teams consist of members with distinct expertise working together on specific projects, while liquid teams emphasize fluid roles and dynamic collaboration across functions, fostering agility. Poly-skilled pods integrate multi-disciplinary skills within small units, enhancing adaptability and seamless knowledge sharing to optimize innovation and project execution.
Hybrid Skill Cloud
Cross-functional teams bring diverse expertise from fixed departments to solve complex projects, while liquid teams leverage a hybrid skill cloud by dynamically assembling specialized talents across the organization, enhancing flexibility and innovation. The hybrid skill cloud enables seamless knowledge sharing and agile resource allocation, optimizing collaboration efficiency in rapidly changing environments.
Liquid Collaboration Model
Liquid teams promote dynamic collaboration by enabling fluid membership and role changes based on project needs, enhancing flexibility and innovation beyond the static structure of cross-functional teams. This model leverages real-time resource allocation and skill-based task assignments to optimize team performance and accelerate decision-making processes.
Cross-domain Synergy
Cross-functional teams bring together experts from diverse departments to foster cross-domain synergy, enhancing problem-solving and innovation by leveraging varied skill sets. Liquid teams, characterized by flexible and dynamic membership, optimize collaboration by adapting roles fluidly, yet cross-functional teams maintain stronger domain-specific continuity for sustained strategic alignment.
Transient Team Structures
Cross-functional teams bring together members from diverse functional areas to achieve specific project goals, fostering deep expertise and structured collaboration, while liquid teams offer flexible, transient team structures that dynamically assemble and disband based on immediate business needs, enhancing adaptability and rapid response to changing environments. Emphasizing transient team structures, liquid teams optimize collaboration by seamlessly integrating talent across organizational boundaries, promoting innovation through real-time resource fluidity.
Task-based Allocation
Cross-functional teams bring together members with diverse expertise to work collaboratively on shared goals, enabling comprehensive problem-solving through permanent role allocation. Liquid teams offer dynamic, task-based allocation where specialists are flexibly assigned to projects as needed, enhancing agility and responsiveness in rapidly changing environments.
Cross-functional teams vs Liquid teams for collaboration. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com