Certification in online learning typically signifies formal recognition of skill mastery awarded by an accredited institution, while a verified certificate confirms the learner's identity and course completion through identity verification processes. Choosing between certification and a verified certificate depends on whether the emphasis is on credential legitimacy or proof of individual participation. Employers often prioritize certifications for their authoritative value, whereas verified certificates ensure authenticity in self-paced online education.
Table of Comparison
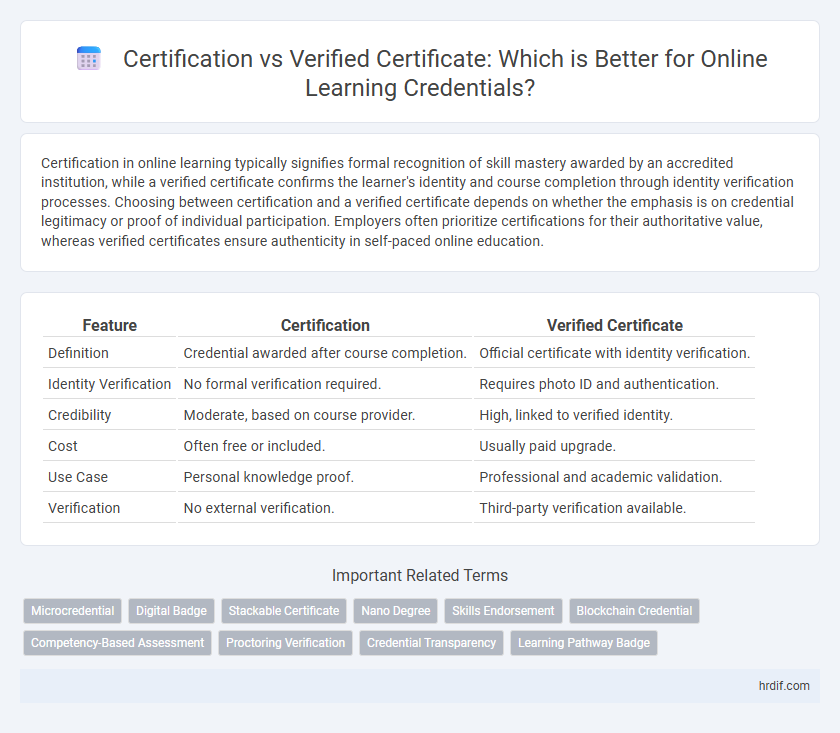
| Feature | Certification | Verified Certificate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Credential awarded after course completion. | Official certificate with identity verification. |
| Identity Verification | No formal verification required. | Requires photo ID and authentication. |
| Credibility | Moderate, based on course provider. | High, linked to verified identity. |
| Cost | Often free or included. | Usually paid upgrade. |
| Use Case | Personal knowledge proof. | Professional and academic validation. |
| Verification | No external verification. | Third-party verification available. |
Understanding Certifications in Online Learning
Certification in online learning typically represents a formal recognition of course completion that may require passing assessments to demonstrate mastery of the subject matter. Verified certificates, offered by many platforms, involve identity verification steps such as photo ID submission to ensure the authenticity of the learner's achievement. Understanding the difference between standard certifications and verified certificates helps learners choose credentials that best meet their professional and educational validation needs.
What is a Verified Certificate?
A Verified Certificate is an official document issued by online learning platforms like Coursera or edX that confirms a learner's identity and successful completion of a course through identity verification processes, such as photo ID and webcam checks. Unlike a standard certificate, which may be awarded without stringent verification, a Verified Certificate holds more credibility for employers and academic institutions because it authenticates the learner's achievements. This type of certification enhances the value of online education by ensuring that the certificate holder truly completed the course work.
Key Differences Between Certification and Verified Certificate
Certification demonstrates comprehensive skill mastery often obtained through rigorous assessments and recognized by industry standards, while a verified certificate confirms identity verification and course completion without guaranteeing full proficiency. Certifications typically require passing formal exams and may involve ongoing renewal, whereas verified certificates are awarded after finishing course requirements and verifying learner identity via government ID or webcam. Employers frequently value certifications higher for job qualifications due to their depth and credibility compared to verified certificates that mainly prove participation.
Value of Certification for Career Advancement
Certification from accredited institutions demonstrates mastery of skills, enhancing credibility in competitive job markets and increasing opportunities for promotions. Verified certificates provide proof of course completion with identity confirmation, adding a layer of trust but often carry less weight than full certifications in career advancement. Employers prioritize certifications that reflect comprehensive knowledge and practical expertise when making hiring and salary decisions.
The Role of Verified Certificates in Skill Validation
Verified certificates play a crucial role in skill validation by providing authenticated proof of course completion tied directly to the learner's identity, enhancing credibility with employers. Unlike standard certificates, verified certificates utilize identity verification processes such as photo ID and secure login, ensuring the legitimacy of the skills demonstrated. Employers increasingly rely on verified certificates from reputable platforms as reliable indicators of validated expertise in targeted professional skills.
Employer Perspectives: Certification vs Verified Certificate
Employers often prioritize verified certificates over general certificates due to the additional credibility provided by identity verification, ensuring the candidate's authenticity. Verified certificates typically include proctored exams and photo ID confirmation, which employers recognize as a stronger indicator of genuine skill acquisition. This distinction enhances trust in the candidate's qualifications during recruitment and performance evaluation.
Cost and Accessibility of Certification Types
Certification for online learning typically involves a fee that grants a recognized credential, offering better career value and industry acceptance. Verified certificates often require identity validation and incur higher costs, but they enhance credibility and reduce fraud risks. Free or low-cost certificates lack verification, making them more accessible but sometimes less trusted by employers.
Recognized Institutions Offering Certifications and Verified Certificates
Recognized institutions offering certifications for online learning typically provide formal credentials that validate a learner's skills and knowledge upon successful course completion, often required by employers and industry professionals. Verified certificates include identity verification processes, such as photo ID checks and proctored exams, ensuring the authenticity of the certificate holder's achievements. Both certification and verified certificates from accredited providers enhance credibility, but verified certificates add an extra layer of trust by confirming the learner's identity and performance under secure conditions.
Use Cases: When to Choose Certification or Verified Certificate
Certification is ideal for learners seeking formal recognition in professional fields where accredited credentials are required for career advancement or regulatory compliance. Verified certificates suit individuals who want to demonstrate course completion and mastery without pursuing full accreditation, often used for skill enhancement or personal development. Organizations often opt for certification when hiring to ensure standardized expertise, while verified certificates support continuing education and resume building.
Making the Right Choice for Your Career Path
Choosing between a certification and a verified certificate for online learning depends on your career goals and industry standards. Certifications often hold more weight with employers due to rigorous assessment and industry recognition, while verified certificates primarily attest to course completion and personal development. Prioritize certifications when aiming for career advancement or specialized roles, as they demonstrate validated expertise and commitment to professional growth.
Related Important Terms
Microcredential
Microcredentials provide verified certificates that validate specific skills through rigorous assessment, whereas traditional certification may offer generalized acknowledgment without detailed verification. Verified certificates in microcredential programs enhance credibility by linking learner identity to demonstrated competencies, supporting employer trust and professional advancement.
Digital Badge
Certification in online learning typically signifies formal recognition of course completion and mastery, whereas a Verified Certificate includes identity verification and often carries greater credibility. Digital Badges enhance both by providing a shareable, verifiable digital credential embedded with metadata confirming skills, achievements, and issuing authority.
Stackable Certificate
Stackable certificates offer flexible pathways by allowing learners to accumulate verified certificates that build toward a comprehensive certification in online learning. Verified certificates provide authentication of individual course completion, while stackable certificates integrate multiple verified credentials to demonstrate advanced expertise and professional growth.
Nano Degree
A Nanodegree certification demonstrates mastery of skills through project-based assessments and industry-relevant curriculum, offering greater credibility than a verified certificate, which primarily confirms identity and course completion. Employers often prefer Nanodegree certifications for their comprehensive validation of practical expertise and job-ready competencies.
Skills Endorsement
Certification in online learning validates a learner's mastery of skills through rigorous assessments, providing recognized credentials valued by employers and industry standards. Verified certificates enhance this credibility by incorporating identity verification and proctored exams, offering stronger skills endorsement and reducing fraud risks compared to standard completion certificates.
Blockchain Credential
Blockchain credentials offer enhanced security and tamper-proof verification compared to traditional certificates, ensuring authenticity and ownership for online learning achievements. Verified certificates utilize blockchain technology to provide immutable records, enabling employers and institutions to efficiently validate qualifications without relying on intermediaries.
Competency-Based Assessment
Certification in online learning typically validates mastery through competency-based assessments that measure practical skills and knowledge application, ensuring learners meet industry standards. Verified certificates add a layer of identity authentication, linking the certification directly to the individual's verified identity, enhancing credibility and trustworthiness for employers.
Proctoring Verification
Certification requires a verified certificate that includes proctoring verification to ensure the authenticity of the learner's identity and exam integrity. Proctoring verification uses tools such as biometric authentication and live monitoring, which distinguishes verified certificates from non-proctored ones by preventing fraud and validating the learner's mastery.
Credential Transparency
Certification provides formal recognition of skill mastery through rigorous assessment, ensuring employer trust and industry alignment, while Verified certificates confirm identity and course completion but may lack comprehensive validation of competency. Credential transparency increases trust by clearly differentiating the depth of evaluation behind certifications versus verified certificates, enabling learners and employers to make informed decisions.
Learning Pathway Badge
Certification provides formal recognition that validates comprehensive mastery in a subject, often requiring successful completion of multiple courses within a learning pathway, while a Verified Certificate typically confirms individual course completion with identity verification. Earning a Learning Pathway Badge integrates these credentials, highlighting progress and achievements across a curated sequence of courses to showcase specialized expertise and commitment to continuous learning.
Certification vs Verified certificate for online learning Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com