Certificates represent formal recognition of mastery in a broad subject area, offering comprehensive validation of skills, while microcredentials focus on specific competencies, enabling targeted upskilling. Choosing between a certificate and a microcredential depends on the desired depth and scope of the learning outcome, with certificates providing extensive knowledge and microcredentials facilitating quick, flexible skill acquisition. Both serve as valuable tools for professional development, but microcredentials offer a more agile approach to meeting immediate industry demands.
Table of Comparison
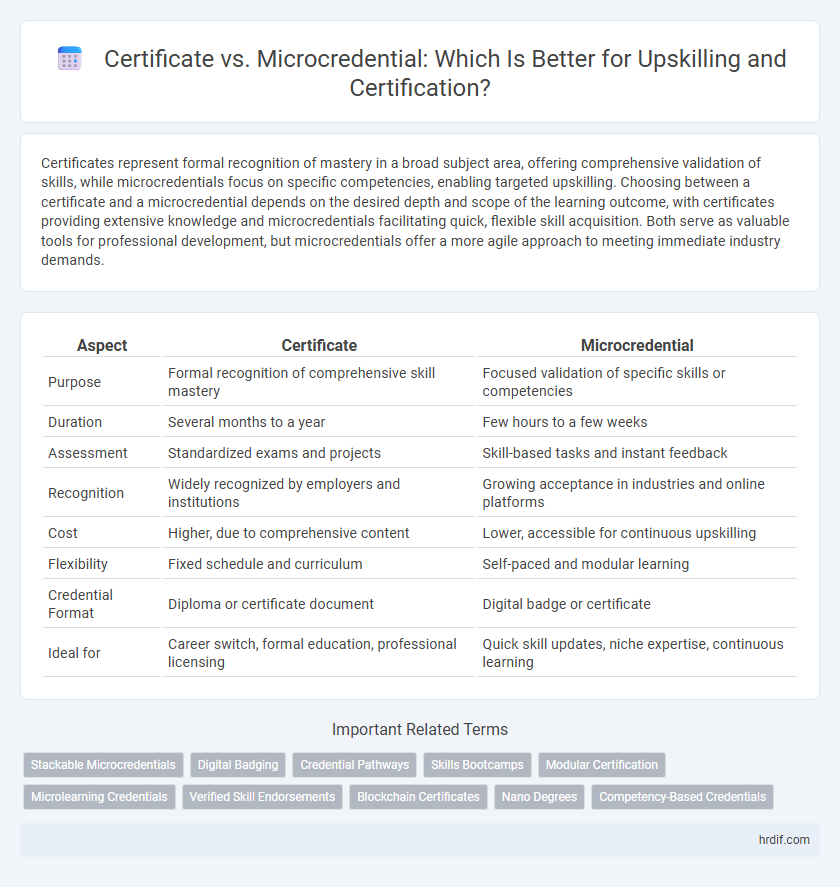
| Aspect | Certificate | Microcredential |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Formal recognition of comprehensive skill mastery | Focused validation of specific skills or competencies |
| Duration | Several months to a year | Few hours to a few weeks |
| Assessment | Standardized exams and projects | Skill-based tasks and instant feedback |
| Recognition | Widely recognized by employers and institutions | Growing acceptance in industries and online platforms |
| Cost | Higher, due to comprehensive content | Lower, accessible for continuous upskilling |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedule and curriculum | Self-paced and modular learning |
| Credential Format | Diploma or certificate document | Digital badge or certificate |
| Ideal for | Career switch, formal education, professional licensing | Quick skill updates, niche expertise, continuous learning |
Understanding Certificates and Microcredentials
Certificates and microcredentials serve as formal recognitions of skills acquired through targeted learning, but they differ significantly in scope and duration. Certificates typically represent comprehensive knowledge and skills in a broader subject area, often requiring extended coursework, while microcredentials focus on specific competencies or skills gained through shorter, more flexible learning modules. Both play vital roles in upskilling, with certificates offering in-depth expertise and microcredentials providing agile, skill-focused validation aligned with fast-evolving industry needs.
Key Differences Between Certificates and Microcredentials
Certificates typically represent comprehensive, formal recognition of mastering a subject, often requiring completion of multiple courses or a program. Microcredentials are more focused, modular achievements validating specific skills or competencies and designed for flexible, rapid upskilling. Certificates tend to carry broader academic or professional weight, while microcredentials offer targeted, stackable learning aligned with specific industry needs.
Duration and Time Commitment
Microcredentials typically require a shorter duration and lower time commitment, often ranging from a few hours to several weeks, making them ideal for rapid upskilling and targeted skill acquisition. Certificates usually involve a more extensive time investment, often spanning several months to a year, providing comprehensive knowledge and deeper expertise in a specific field. The choice between the two depends on the learner's availability and the depth of skills desired for professional development.
Industry Recognition and Credibility
Certificates provide formal recognition from accredited institutions, often aligning with standardized industry requirements and enhancing professional credibility. Microcredentials offer targeted skill validation endorsed by industry partners, enabling rapid demonstration of specialized competencies relevant to evolving job roles. Both forms signal industry recognition, but certificates typically carry greater weight for long-term career advancement due to their comprehensive assessment and institutional backing.
Cost Comparison: Certificate vs Microcredential
Certificates often require a higher financial investment, with costs ranging from several hundred to thousands of dollars depending on the institution and program length. Microcredentials typically offer a more affordable alternative, costing between $100 and $500, while providing targeted skill development for immediate application. Budget-conscious learners prioritize microcredentials for cost-effective upskilling that delivers specialized competencies without the extended commitment of a full certificate program.
Flexibility and Learning Formats
Certificates typically require completion of a structured curriculum over several months, offering less flexibility compared to microcredentials. Microcredentials provide modular learning formats that allow learners to acquire specific skills at their own pace, often through online or hybrid delivery methods. This adaptability makes microcredentials ideal for professionals seeking targeted upskilling without committing to lengthy programs.
Skills Coverage and Depth of Study
Certificates typically offer comprehensive skills coverage with an emphasis on in-depth study, preparing learners for specialized roles or advanced knowledge areas. Microcredentials focus on narrow, targeted skills development, allowing for quick acquisition and validation of specific competencies. Both pathways enhance employability, but certificates provide broader expertise while microcredentials deliver precise, skill-specific mastery for upskilling.
Career Impact and Advancement Opportunities
Certificates and microcredentials both enhance career impact and advancement opportunities, but certificates often provide broader recognition across industries, supporting significant role changes or promotions. Microcredentials, with their focus on specific skills and shorter completion times, offer targeted upskilling that meets immediate job market demands and niche expertise. Employers increasingly value microcredentials for demonstrating up-to-date competencies, while certificates remain vital for validating comprehensive knowledge and formal qualifications.
Choosing the Right Credential for Your Career Goals
Certificates often represent comprehensive, credentialed programs that validate mastery in a broad skill area, while microcredentials focus on specific competencies or skill sets for targeted upskilling. Choosing the right credential depends on career goals, industry demands, and time commitment; certificates suit those seeking in-depth knowledge and formal recognition, whereas microcredentials provide flexible, quick skill enhancements aligned with specialized roles. Prioritize credentials that are recognized by employers in your field and map closely to the skills required for your desired career advancement.
Future Trends in Upskilling: Certificates and Microcredentials
Future trends in upskilling highlight a growing preference for microcredentials due to their modular, skill-specific nature and rapid validation process, making them ideal for adapting to fast-changing job markets. Certificates remain valuable for comprehensive knowledge validation and are often recognized by industries requiring standardized qualifications. The convergence of digital platforms and employer partnerships is expanding the credibility and accessibility of both certificates and microcredentials, driving personalized learning pathways and continuous professional development.
Related Important Terms
Stackable Microcredentials
Stackable microcredentials offer flexible, modular learning paths that allow professionals to accumulate specialized skills and build toward full certification in their field. Unlike traditional certificates, these microcredentials are designed for continuous upskilling, enabling targeted skill acquisition aligned with industry demands.
Digital Badging
Digital badging enhances microcredentials by providing verifiable, portable evidence of skills acquired, making them more flexible and stackable compared to traditional certificates. Microcredentials with digital badges allow learners to showcase specific competencies in real-time, accelerating career growth and continuous upskilling in rapidly evolving industries.
Credential Pathways
Certificate programs provide comprehensive training and validation through established academic or professional standards, creating a formal credential pathway recognized by employers and institutions. Microcredentials offer focused, skill-specific recognition with flexible, stackable pathways that enhance career agility and continuous upskilling in rapidly evolving industries.
Skills Bootcamps
Skills Bootcamps provide targeted training through microcredentials that emphasize specific skills, offering flexibility and quicker upskilling compared to traditional certificates which cover broader knowledge areas. Microcredentials from Skills Bootcamps are often industry-recognized, enabling learners to demonstrate proficiency in high-demand competencies within a shorter timeframe.
Modular Certification
Modular certification breaks down traditional certificates into smaller, focused units, allowing learners to accumulate microcredentials that target specific skills for rapid upskilling. These microcredentials provide flexible, stackable credentials that employers increasingly recognize as proof of specialized competencies.
Microlearning Credentials
Microlearning credentials provide targeted skill validation through short, focused learning segments, making them ideal for continuous upskilling in fast-evolving industries. Unlike traditional certificates, microcredentials emphasize mastery of specific competencies, enabling learners to quickly adapt and demonstrate expertise in niche areas.
Verified Skill Endorsements
Certificates provide comprehensive learning recognition with formal accreditation from educational institutions, while microcredentials offer verified skill endorsements focused on specific competencies, enabling targeted upskilling with immediate applicability in professional settings. Verified skill endorsements in microcredentials enhance credibility by validating practical expertise through assessments and digital badges, making them highly valuable for employers seeking demonstrable skills.
Blockchain Certificates
Blockchain certificates provide comprehensive validation of in-depth skills and knowledge, often recognized by industry and academia, while microcredentials offer targeted, bite-sized learning achievements designed for rapid upskilling in specific blockchain technologies. Employers increasingly value blockchain microcredentials for their flexibility and relevance in fast-evolving sectors, whereas certificates establish foundational expertise and credibility in blockchain development and applications.
Nano Degrees
Nano degrees provide targeted, skill-specific education with flexible, online formats, making them ideal for rapid upskilling compared to traditional certificates that often require longer commitments and broader coursework. These microcredentials are recognized by industry leaders for their practical focus on in-demand skills, enhancing employability and career advancement in specialized fields.
Competency-Based Credentials
Certificate programs and microcredentials both serve competency-based credentials for upskilling, but microcredentials offer more targeted validation of specific skills and are often shorter, more flexible, and stackable. Certificates typically represent broader knowledge acquisition over a longer period, making microcredentials more agile for rapidly evolving job market demands.
Certificate vs Microcredential for upskilling. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com