Certification provides formal recognition of specialized skills and knowledge, often required by industries to validate professional expertise. Microcredentials offer targeted, flexible learning opportunities that quickly update competencies, making them ideal for adapting to evolving job market demands. Both serve career advancement, but certifications carry more weight for long-term professional credibility, while microcredentials enhance specific skill sets efficiently.
Table of Comparison
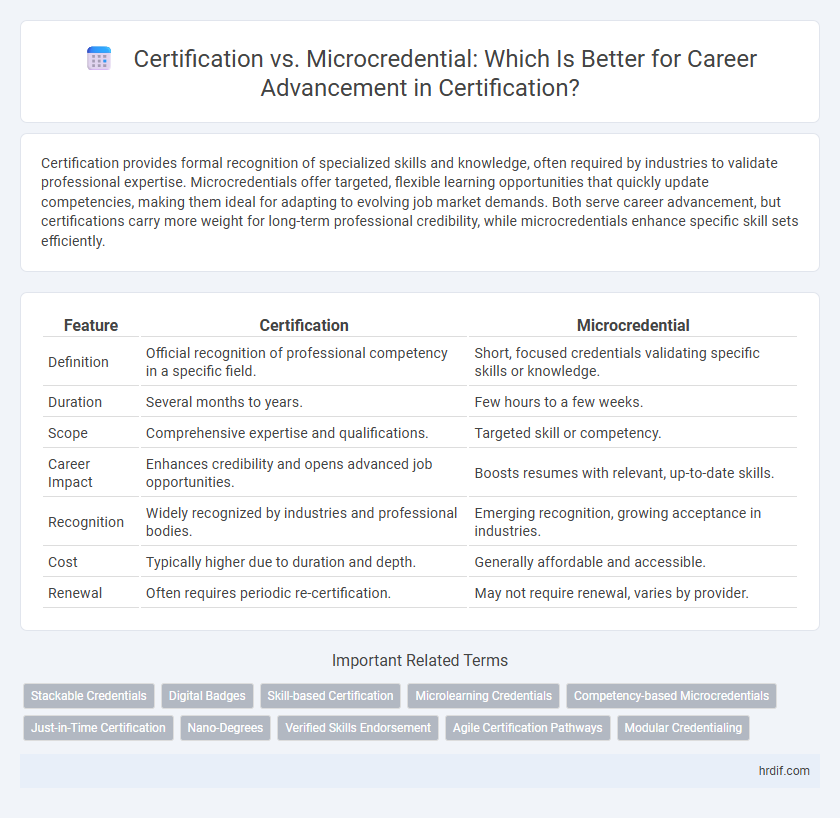
| Feature | Certification | Microcredential |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official recognition of professional competency in a specific field. | Short, focused credentials validating specific skills or knowledge. |
| Duration | Several months to years. | Few hours to a few weeks. |
| Scope | Comprehensive expertise and qualifications. | Targeted skill or competency. |
| Career Impact | Enhances credibility and opens advanced job opportunities. | Boosts resumes with relevant, up-to-date skills. |
| Recognition | Widely recognized by industries and professional bodies. | Emerging recognition, growing acceptance in industries. |
| Cost | Typically higher due to duration and depth. | Generally affordable and accessible. |
| Renewal | Often requires periodic re-certification. | May not require renewal, varies by provider. |
Understanding Certifications and Microcredentials
Certifications demonstrate mastery of industry-recognized standards and often require passing rigorous exams, making them valuable for verifying professional expertise. Microcredentials focus on specific skills or competencies and offer flexible, bite-sized learning modules that align with emerging job market demands. Both serve as important tools for career advancement, with certifications providing comprehensive validation and microcredentials enabling targeted skill development.
Key Differences Between Certifications and Microcredentials
Certifications typically require passing comprehensive exams and demonstrate mastery in a specific professional area, often recognized by industry-standard organizations. Microcredentials focus on targeted skills or competencies, are shorter in duration, and provide flexible, stackable learning options tailored to evolving career needs. While certifications offer formal validation of expertise, microcredentials enable continuous skill development and adaptability in rapidly changing job markets.
Evaluating Industry Recognition: Certification vs Microcredential
Certification often holds greater industry recognition due to its rigorous standards and comprehensive validation of skills, making it highly valued by employers for career advancement. Microcredentials offer targeted, skill-specific proof of competence that can quickly adapt to emerging industry needs but may lack the widespread acknowledgment of traditional certifications. Evaluating industry recognition requires assessing employer preferences, the credential issuer's reputation, and alignment with professional standards.
Time and Cost Investment: What to Expect
Certification programs generally require a higher time commitment and financial investment, often spanning several months with fees ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars. Microcredentials offer more flexibility, typically completed within weeks at a lower cost, making them accessible for professionals seeking quick skill validation. Both certifications and microcredentials enhance career advancement but differ significantly in their time and cost investment.
Skill Depth and Breadth: Which Offers More?
Certification typically provides deeper expertise in a specific field, demonstrating comprehensive skill mastery and adherence to industry standards. Microcredentials offer broader skill sets by covering diverse, often emerging competencies that complement traditional knowledge. Professionals aiming for career advancement benefit from certifications when prioritizing specialized roles, while microcredentials enhance adaptability and interdisciplinary capabilities.
Flexibility and Accessibility for Learners
Certifications provide structured, in-depth validation of skills often recognized across industries, while microcredentials offer shorter, focused learning experiences tailored for quick skill acquisition. Microcredentials deliver greater flexibility and accessibility by enabling learners to complete modules at their own pace, often online, making them ideal for working professionals seeking immediate application. This adaptability supports continuous career advancement by allowing targeted skill updates without the extensive time commitment associated with traditional certifications.
The Role of Certifications in Traditional Career Paths
Certifications play a pivotal role in traditional career paths by validating specialized skills and industry knowledge, often required for job promotions and salary increases. Unlike microcredentials, which target specific competencies and emerging fields, certifications provide comprehensive training recognized by employers across established professions such as IT, healthcare, and finance. Their standardized assessment criteria and broad acceptance enhance career credibility and open doors to leadership roles within conventional organizational hierarchies.
Microcredentials for Emerging and Tech-Focused Roles
Microcredentials offer targeted skill validation essential for emerging and tech-focused roles, providing learners with industry-recognized expertise in specific technologies like AI, data analytics, and cybersecurity. Unlike traditional certifications that cover broad knowledge areas, microcredentials emphasize hands-on competencies and timely relevancy, making them ideal for rapid career advancement in fast-evolving tech sectors. Employers increasingly value microcredentials for their ability to demonstrate up-to-date skills aligned with current industry demands, enhancing candidate competitiveness in the job market.
Employer Perspectives: Hiring with Certifications vs Microcredentials
Employers increasingly value certifications for their standardized validation of skills and industry-recognized benchmarks, often perceiving them as more reliable indicators of candidate competence. Microcredentials are gaining traction for demonstrating specialized, up-to-date expertise and agility in niche areas, appealing to roles requiring continuous learning. Hiring decisions frequently balance certifications' comprehensive credibility against microcredentials' flexibility, depending on job requirements and sector demands.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Career Goals
Certification provides formal validation of expertise in a specific field, often recognized by industry standards and employers. Microcredentials offer targeted, flexible learning modules that demonstrate specialized skills and can be stacked to build comprehensive knowledge. Selecting between certification and microcredentials depends on your career goals, desired recognition, and the depth of competency required in your profession.
Related Important Terms
Stackable Credentials
Stackable credentials, including certifications and microcredentials, offer flexible pathways for career advancement by allowing professionals to accumulate specialized skills recognized by industry employers. Certifications provide comprehensive validation of expertise in a specific field, while microcredentials deliver targeted, modular learning experiences that can be combined to build a broader qualification portfolio.
Digital Badges
Digital badges serve as verifiable microcredentials that showcase specific skills and competencies, offering more flexible and targeted proof of expertise compared to traditional certifications. These badges enable professionals to quickly demonstrate career-relevant achievements and continuously update their qualifications in rapidly evolving industries.
Skill-based Certification
Skill-based certification provides verifiable proof of proficiency in specific competencies, often aligning directly with industry standards and employer expectations, enhancing career advancement opportunities more effectively than microcredentials. Unlike microcredentials, which may cover narrower or emerging topics, skill-based certifications typically offer broader recognition and credibility, making them valuable for long-term professional growth and job market competitiveness.
Microlearning Credentials
Microlearning credentials offer targeted skill development through short, focused modules, making them highly adaptable for rapid career advancement. Unlike traditional certifications, microcredentials provide employers with evidence of specific competencies aligned with evolving industry demands.
Competency-based Microcredentials
Competency-based microcredentials offer targeted skill validation that aligns closely with industry demands, making them highly effective for rapid career advancement compared to traditional certifications. These microcredentials emphasize demonstrable expertise in specific competencies, providing flexible, stackable learning paths that enhance employability and professional growth.
Just-in-Time Certification
Just-in-Time Certification offers targeted, timely skill validation tailored to immediate job requirements, contrasting with traditional certifications that often cover broader, less agile content. Microcredentials emphasize modular learning paths but may lack the comprehensive recognition and depth essential for significant career advancement compared to Just-in-Time Certification.
Nano-Degrees
Nano-degrees offer targeted skill sets that align with emerging industry demands, providing a faster and more flexible alternative to traditional certifications for career advancement. Unlike broad certifications, nano-degrees emphasize practical, project-based learning, enhancing job readiness and specialized expertise in key professional sectors.
Verified Skills Endorsement
Certification provides a comprehensive validation of expertise and industry standards, while microcredentials offer targeted Verified Skills Endorsement in specific areas to quickly showcase competencies. Employers increasingly value microcredentials for their precise skill verification, accelerating career advancement through focused professional recognition.
Agile Certification Pathways
Agile Certification pathways, such as PMI-ACP and SAFe Agilist, offer comprehensive validation of expertise, providing industry-recognized credentials that enhance career advancement opportunities. Microcredentials focus on specific Agile skills or tools, enabling targeted skill enhancement but may lack the broader recognition and career impact of full Agile Certifications.
Modular Credentialing
Modular credentialing offers flexible, stackable learning units that build specialized skills aligned with industry demands, making it a strategic choice for career advancement compared to traditional certifications. Microcredentials provide targeted proof of competency in specific areas, while certifications typically represent comprehensive knowledge, allowing professionals to tailor their development through modular pathways.
Certification vs Microcredential for career advancement Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com