A traditional CV provides a linear overview of a candidate's work history and education, often limiting the insight into specific skills and competencies. In contrast, a skill graph visually maps interconnected abilities, experiences, and achievements, offering a dynamic and comprehensive profile tailored for application processes. Leveraging skill graphs enhances talent matching and highlights relevant expertise beyond standard resume formats.
Table of Comparison
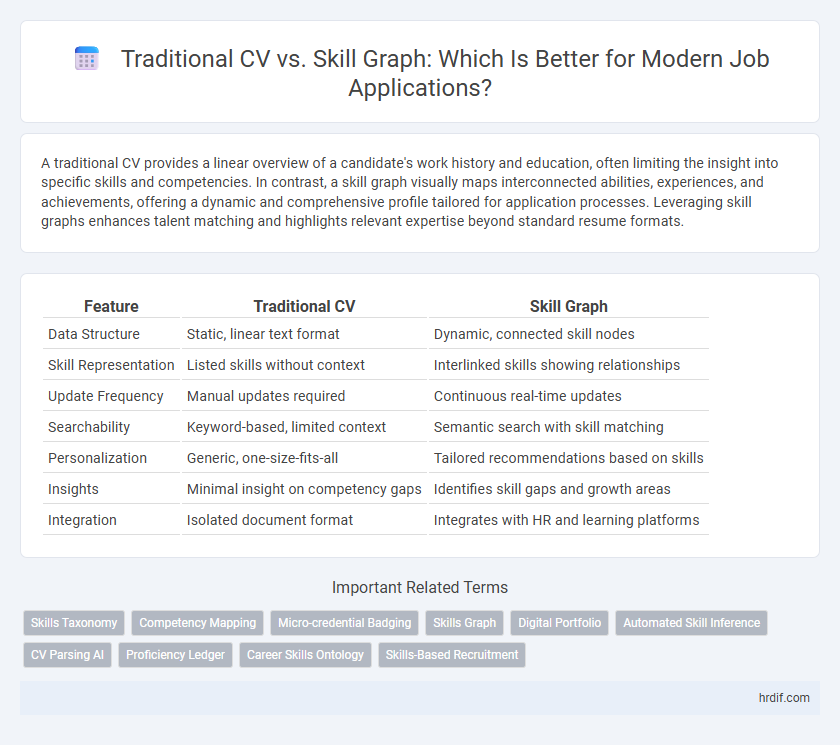
| Feature | Traditional CV | Skill Graph |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Static, linear text format | Dynamic, connected skill nodes |
| Skill Representation | Listed skills without context | Interlinked skills showing relationships |
| Update Frequency | Manual updates required | Continuous real-time updates |
| Searchability | Keyword-based, limited context | Semantic search with skill matching |
| Personalization | Generic, one-size-fits-all | Tailored recommendations based on skills |
| Insights | Minimal insight on competency gaps | Identifies skill gaps and growth areas |
| Integration | Isolated document format | Integrates with HR and learning platforms |
Understanding Traditional CVs: Overview and Structure
Traditional CVs typically include a structured format with sections such as personal information, work experience, education, skills, and certifications. This linear presentation emphasizes chronological job history and formal qualifications but often lacks detailed insights into specific skill sets and competencies. Understanding the limitations of traditional CVs is crucial for recognizing the need for skill-based evaluation methods like skill graphs that provide a more dynamic and comprehensive profile.
What Is a Skill Graph? Definition and Components
A Skill Graph is a dynamic data structure that maps an individual's skills, competencies, and experiences, connecting them with relevant job roles and industry requirements. It integrates components such as skill nodes, proficiency levels, endorsements, and contextual relationships to provide a comprehensive and adaptable profile beyond static information found in traditional CVs. Unlike traditional resumes, Skill Graphs enable personalized job matching and continuous skill development by leveraging semantic connections and real-time updates.
Comparing Data Representation: Chronology vs Competency
Traditional CVs organize applicant information chronologically, listing work experience and education in a linear timeline, which highlights career progression but often overlooks skill depth and relevance. Skill Graphs represent competencies as interconnected nodes, demonstrating relationships between abilities, projects, and achievements, enabling a more dynamic and holistic view of a candidate's expertise. This competency-based data representation facilitates tailored applicant matching and deeper insights for recruiters beyond simple timelines.
Highlighting Strengths: Achievements vs Capabilities
Traditional CVs emphasize achievements by listing past roles, awards, and measurable outcomes, showcasing concrete results. Skill Graphs highlight capabilities through interconnected skills and competencies, illustrating how expertise applies across various tasks and projects. This dynamic representation enables employers to assess adaptability and potential beyond static accomplishments.
Applicant Tracking Systems: Compatibility and Effectiveness
Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) often struggle with parsing Traditional CVs due to inconsistent formatting and keyword reliance, which can lead to qualified candidates being overlooked. Skill Graphs provide structured, standardized data that enhances ATS compatibility by enabling precise skill matching and relationship mapping between qualifications and job requirements. This results in improved applicant screening efficiency and higher accuracy in identifying suitable candidates.
Customization: Tailoring Applications to Job Descriptions
Traditional CVs offer limited customization, often requiring manual adjustments to highlight relevant experiences for each job application. Skill Graphs enable dynamic tailoring by mapping skills directly to specific job descriptions, enhancing precision and relevance. This technology streamlines the application process, improving alignment with employer requirements and increasing the chances of candidate selection.
Visual Appeal: Layout Differences and First Impressions
Traditional CVs feature linear layouts with distinct sections that guide recruiters through chronological work history, often limiting visual engagement. Skill graphs utilize dynamic visual elements like charts or nodes to highlight competencies, creating an interactive and impactful first impression. Enhanced visual appeal in skill graphs increases applicant visibility by clearly mapping skills to job requirements, improving recruiter retention and interest.
Industry Adoption: Where Each Approach Excels
Traditional CVs remain widely adopted in industries such as finance and law where formal education, certifications, and chronological work history are critical for evaluating candidates. Skill graphs excel in tech and creative sectors by providing dynamic, detailed mappings of competencies and project experiences that align with rapidly evolving job requirements. Companies leveraging AI-powered recruitment tools increasingly prefer skill graphs for their ability to uncover transferable skills and predict candidate success beyond standard resume formats.
Highlights and Limitations: Pros and Cons of Both Methods
Traditional CVs provide a straightforward overview of an applicant's work history and education, offering quick, easily scannable insights for recruiters but often lack detailed context about skills and their interconnections. Skill Graphs enable a dynamic representation of an applicant's competencies and their relationships, enhancing precision in matching job requirements but may require more sophisticated analysis tools and time to interpret. While CVs excel in simplicity and familiarity, Skill Graphs deliver richer, data-driven insights critical for complex roles demanding specific skill sets.
Future Trends: Shaping the Future of Job Applications
Skill Graphs leverage AI-driven data integration to provide dynamic, real-time updates on candidates' capabilities, surpassing the static nature of Traditional CVs. Future job applications will increasingly prioritize granular skill mappings and contextual relevance over chronological work history. This shift enables more precise matching between applicants and evolving industry demands, streamlining recruitment and enhancing workforce agility.
Related Important Terms
Skills Taxonomy
Traditional CVs often present skills in an unstructured format, limiting the ability to systematically analyze and match competencies, whereas Skill Graphs leverage a hierarchical Skills Taxonomy to categorize and interrelate skills for enhanced precision in talent identification. Implementing Skills Taxonomy within Skill Graphs enables dynamic mapping of candidate capabilities to job requirements, improving recruitment efficiency and promoting data-driven decision-making in talent acquisition.
Competency Mapping
Traditional CVs often provide a static snapshot of qualifications that lack detailed competency mapping, whereas Skill Graphs dynamically represent interconnected skills, enabling more precise identification of applicant strengths and gaps. By leveraging Skill Graphs, organizations can enhance talent matching and development through a granular understanding of competencies relevant to specific roles.
Micro-credential Badging
Traditional CVs typically list qualifications and job history without detailed evidence of specific competencies, while skill graphs enhanced by micro-credential badging provide verifiable, granular data on skill acquisition and proficiency. Micro-credential badges function as digital certificates linked to skill graphs, enabling applications to showcase precise, validated expertise for better matching with job requirements.
Skills Graph
Skill Graphs provide dynamic, interconnected representations of an applicant's abilities, enabling more precise matching with job requirements compared to static traditional CVs. Integrating skill relationships and proficiency levels, Skill Graphs enhance talent acquisition by highlighting relevant competencies and uncovering hidden potential.
Digital Portfolio
A digital portfolio integrated with a skill graph offers a dynamic representation of competencies linked to specific projects and achievements, surpassing the static nature of a traditional CV by providing real-time updates and personalized skill mappings. This approach enhances applicant visibility by leveraging data-driven insights that align skills with job requirements, improving precision in candidate evaluation.
Automated Skill Inference
Automated skill inference enhances the skill graph by dynamically extracting and updating candidates' abilities from diverse data sources, unlike traditional CVs that rely on manually listed qualifications. This technology improves accuracy in matching applications with job requirements by continuously refining skill profiles through machine learning algorithms.
CV Parsing AI
Traditional CV parsing relies on keyword extraction and basic pattern recognition, often missing nuanced skills and contextual relationships. Skill Graph technology enhances CV parsing AI by mapping skills to job requirements through semantic connections, enabling more accurate candidate matching and talent acquisition.
Proficiency Ledger
The Proficiency Ledger in Skill Graph applications offers a dynamic, granular record of an individual's competencies unlike the static nature of Traditional CVs, enabling real-time tracking and validation of skills evolution. This innovative approach enhances talent matching accuracy and provides organizations with actionable insights for precise workforce development.
Career Skills Ontology
Traditional CVs present static lists of qualifications and experiences, often lacking contextual relationships between skills and roles, whereas Skill Graphs leverage Career Skills Ontology to map and connect competencies dynamically, enhancing application accuracy and personalized career pathing. The integration of ontologies enables automated skill inference and semantic alignment, improving applicant screening and job matching efficiency in talent acquisition systems.
Skills-Based Recruitment
Skills-based recruitment leverages Skill Graphs to map candidates' competencies and experiences dynamically, offering a more granular and real-time assessment compared to static traditional CVs that rely heavily on job titles and tenure. By focusing on specific skills and their interconnections, Skill Graphs enhance talent matching accuracy and identify transferable abilities that traditional resumes often overlook.
Traditional CV vs Skill Graph for Application Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com