Traditional applications often rely heavily on resumes and cover letters, which may introduce bias based on candidates' backgrounds or personal information. Blind auditions remove identifying details, allowing recruiters to assess skills and qualifications objectively. This method enhances fairness and promotes diversity by focusing solely on candidates' abilities.
Table of Comparison
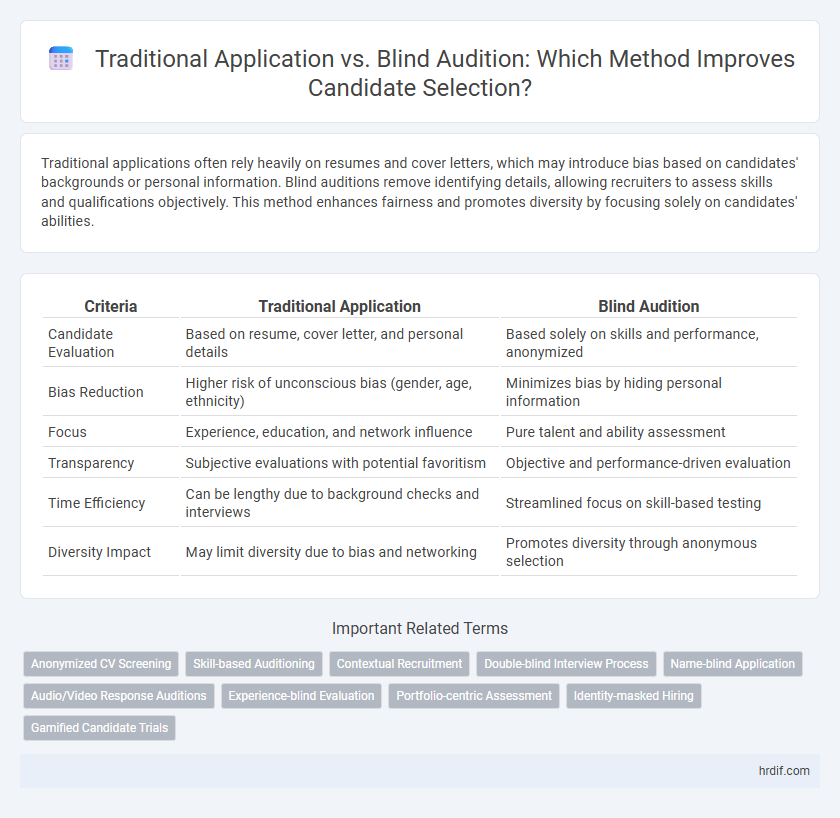
| Criteria | Traditional Application | Blind Audition |
|---|---|---|
| Candidate Evaluation | Based on resume, cover letter, and personal details | Based solely on skills and performance, anonymized |
| Bias Reduction | Higher risk of unconscious bias (gender, age, ethnicity) | Minimizes bias by hiding personal information |
| Focus | Experience, education, and network influence | Pure talent and ability assessment |
| Transparency | Subjective evaluations with potential favoritism | Objective and performance-driven evaluation |
| Time Efficiency | Can be lengthy due to background checks and interviews | Streamlined focus on skill-based testing |
| Diversity Impact | May limit diversity due to bias and networking | Promotes diversity through anonymous selection |
Understanding Traditional Application Methods
Traditional application methods involve candidates submitting detailed resumes and cover letters, enabling employers to assess qualifications, work experience, and skills directly. This approach allows for evaluation of educational background, references, and career progression, providing a comprehensive overview of each applicant. However, biases related to gender, ethnicity, and age may influence decision-making, potentially impacting diversity in hiring.
What is a Blind Audition in Recruitment?
A blind audition in recruitment is a method where candidates are evaluated solely on their skills and qualifications without revealing personal information such as name, gender, or ethnicity. This approach aims to eliminate unconscious bias and promote diversity by focusing purely on the candidate's abilities. Unlike traditional applications, blind auditions rely on anonymized assessments or work samples rather than resumes or interviews.
Key Differences Between Traditional Applications and Blind Auditions
Traditional applications rely on candidates' resumes, cover letters, and personal information, which can introduce unconscious bias into the selection process. Blind auditions remove identifying details such as name, gender, and background, focusing solely on the candidate's skills and performance. This method enhances fairness and diversity by promoting merit-based assessments over subjective judgments.
Advantages of Traditional Application Processes
Traditional application processes provide a comprehensive evaluation by allowing candidates to showcase their full range of qualifications, experiences, and communication skills through resumes, cover letters, and interviews. This method facilitates a holistic assessment of soft skills, cultural fit, and motivation, which are often critical to job performance but challenging to measure in blind auditions. Employers gain insights into candidates' career progression and specific achievements, enabling more informed decision-making.
Benefits of Blind Audition Approaches in Hiring
Blind audition approaches in hiring significantly reduce unconscious bias by anonymizing candidate information, leading to more diverse and inclusive talent pools. This method emphasizes skills and qualifications over demographic factors, improving the fairness and objectivity of the selection process. Employers experience enhanced candidate quality and innovation by focusing solely on merit without influence from resumes or personal details.
Common Biases in Candidate Selection
Traditional applications often expose candidates to conscious and unconscious biases such as name-based discrimination, gender bias, and educational pedigree preferences. Blind auditions mitigate these biases by anonymizing identifiable information, allowing evaluators to focus solely on skills and qualifications. Studies show that blind audition processes increase diversity and fairness by reducing disparate impacts on underrepresented groups.
Assessing Skills: Resume Review vs. Anonymous Performance
Traditional application processes rely heavily on resume review, where candidate qualifications and experiences are assessed based on submitted documents that may include biases related to education, background, or personal information. Blind auditions remove identifiable information, focusing solely on evaluating the candidate's actual performance or skills, which leads to a more objective assessment of abilities. Studies have shown that blind auditions increase diversity and allow selectors to identify talent based purely on merit, reducing subconscious biases associated with traditional resume evaluations.
Enhancing Diversity Through Blind Auditions
Blind auditions significantly enhance diversity in candidate selection by removing identifiable personal information such as names, gender, and ethnicity from the evaluation process. This method reduces unconscious bias and encourages fair assessment based solely on skills and qualifications. Companies employing blind auditions report increased representation of underrepresented groups, fostering inclusivity and broadening their talent pool.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Selection Method
Traditional applications often suffer from biases related to name, gender, or educational background, limiting the diversity of candidate pools and potentially overlooking talent. Blind auditions reduce these biases by anonymizing candidates, but they may omit critical context such as work experience and collaborative skills, making holistic evaluation difficult. Both methods struggle with assessing intangible qualities like cultural fit and creativity, posing challenges for comprehensive candidate selection.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Choosing the right candidate selection approach depends on organizational goals and values; traditional applications provide comprehensive background information, while blind auditions emphasize unbiased evaluation of skills. Evaluating the trade-offs between thorough candidate history and mitigation of unconscious bias helps tailor the recruitment process effectively. Companies aiming for diversity and inclusivity may benefit from blind auditions, whereas roles requiring extensive qualifications might favor traditional applications.
Related Important Terms
Anonymized CV Screening
Anonymized CV screening enhances candidate selection by removing personal identifiers, reducing unconscious bias compared to traditional application methods. This approach fosters a more equitable hiring process, ensuring candidates are evaluated solely on their skills and qualifications.
Skill-based Auditioning
Skill-based auditioning prioritizes candidates' actual abilities and performance metrics over traditional applications that rely heavily on resumes and credentials. This approach enhances objectivity and diversity by minimizing biases linked to background or pedigree, ensuring selections are made based on demonstrated competence.
Contextual Recruitment
Traditional application processes rely on resumes and cover letters, which often introduce biases related to gender, ethnicity, or educational background, whereas blind auditions anonymize candidate information to enhance fairness and focus on skills and performance. Contextual recruitment leverages blind auditions to improve diversity and inclusivity by emphasizing relevant competencies and real-time assessment over potentially biased credentials.
Double-blind Interview Process
The double-blind interview process eliminates both candidate and interviewer biases by concealing identities and personal information, enhancing fairness and objectivity compared to traditional application methods. This approach, often used in blind auditions, increases diversity and merit-based selection by focusing solely on skills and qualifications rather than demographic data.
Name-blind Application
Name-blind application enhances fairness in candidate selection by removing personally identifiable information, reducing unconscious bias compared to traditional applications that include names and demographic details. Blind auditions further support equitable hiring by evaluating candidates solely on skills and qualifications, promoting diversity and inclusion in the recruitment process.
Audio/Video Response Auditions
Audio and video response auditions provide a more dynamic evaluation of candidates' skills and personalities compared to traditional applications, which rely heavily on resumes and written questionnaires. This method reduces bias and enhances the authenticity of candidate assessments by capturing real-time performance and communication abilities.
Experience-blind Evaluation
Experience-blind evaluation in candidate selection eliminates bias by masking prior work history during the assessment process, ensuring candidates are judged solely on their skills and potential. This method contrasts with traditional applications where experience can overshadow true ability, promoting a fairer, merit-based hiring approach.
Portfolio-centric Assessment
Portfolio-centric assessment in traditional application processes allows candidates to showcase tangible work samples and detailed project outcomes, providing hiring managers with concrete evidence of skills and accomplishments. Blind auditions emphasize anonymous evaluation of specific tasks or skills without candidate identifiers, reducing bias but potentially overlooking the depth and context that a comprehensive portfolio offers.
Identity-masked Hiring
Identity-masked hiring in blind auditions eliminates bias by anonymizing candidate information such as name, gender, and ethnicity, ensuring skill-based evaluation strictly through performance or task results. Traditional application processes often rely on identifiable details, which can inadvertently reinforce unconscious biases and hinder diversity in candidate selection.
Gamified Candidate Trials
Gamified candidate trials enhance traditional application methods by providing interactive, skill-based assessments that offer deeper insights into a candidate's abilities and cultural fit, surpassing the limitations of resume reviews. Unlike blind auditions that focus solely on anonymized performance, gamified trials integrate real-time problem-solving scenarios and behavioral metrics, optimizing the selection process for roles requiring creativity and adaptability.
Traditional Application vs Blind Audition for candidate selection. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com