Online applications provide a structured and standardized process for submitting information, ensuring consistency and ease of evaluation by organizations. Social profile applications leverage existing data from platforms like LinkedIn or Facebook, allowing for quicker application submissions while showcasing a candidate's social presence and network. Choosing between the two depends on the need for detailed customization versus convenience and social credibility in the application process.
Table of Comparison
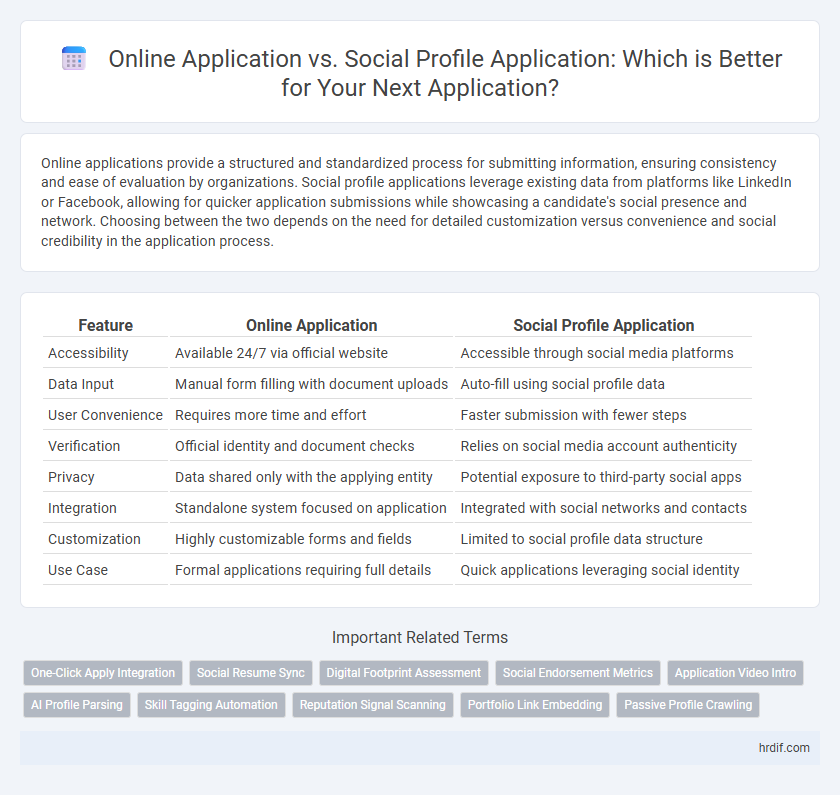
| Feature | Online Application | Social Profile Application |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Available 24/7 via official website | Accessible through social media platforms |
| Data Input | Manual form filling with document uploads | Auto-fill using social profile data |
| User Convenience | Requires more time and effort | Faster submission with fewer steps |
| Verification | Official identity and document checks | Relies on social media account authenticity |
| Privacy | Data shared only with the applying entity | Potential exposure to third-party social apps |
| Integration | Standalone system focused on application | Integrated with social networks and contacts |
| Customization | Highly customizable forms and fields | Limited to social profile data structure |
| Use Case | Formal applications requiring full details | Quick applications leveraging social identity |
Understanding Online Application Processes
Online applications require users to submit structured forms with specific data fields, ensuring accurate and consistent information for processing. In contrast, social profile applications pull data directly from existing social media accounts, streamlining user input but risking incomplete or outdated details. Understanding these differences helps optimize applicant experience and data reliability in digital recruitment platforms.
The Rise of Social Profile Applications
Social profile applications leverage user-generated content and social interactions to enhance personalized experiences, driving higher engagement compared to traditional online applications. These platforms utilize data from social networks to streamline onboarding, improve user verification, and offer tailored recommendations. The rise of social profile applications reflects a shift towards more integrated, user-centric application processes supported by real-time social data analytics.
Speed and Convenience: A Comparative Analysis
Online applications typically offer faster processing times due to automated data entry and streamlined submission interfaces. Social profile applications enhance convenience by allowing users to import existing information from platforms like LinkedIn or Facebook, reducing manual input. Both methods improve user experience, but online applications prioritize speed while social profile applications emphasize ease of use.
Data Privacy Concerns in Both Approaches
Online applications often require users to submit extensive personal information directly, raising concerns about data storage security and potential unauthorized access. Social profile applications, while streamlining login processes through platforms like Facebook or Google, may inadvertently share sensitive user data across multiple services, increasing exposure risks. Both approaches demand stringent privacy protocols and transparent data handling policies to protect user information effectively.
Customization vs Standardization of Job Applications
Online applications offer high customization, allowing candidates to tailor responses, upload specific documents, and provide detailed work histories aligned with job requirements. Social profile applications prioritize standardization by using existing social media data to quickly populate fields, emphasizing speed over personalized detail. Employers seeking efficiency prefer standardized applications, while roles demanding specialized skills benefit from customizable online applications.
Impact on Applicant Screening and Selection
Online applications provide structured data collection, enabling automated screening tools to efficiently analyze qualifications and experience, which streamlines applicant selection. Social profile applications offer richer, real-time insights into candidates' personalities, social behaviors, and cultural fit, enhancing qualitative evaluation during recruitment. Combining both methods improves accuracy in matching applicants to job requirements while reducing bias in the screening process.
Enhancing Employer Branding through Application Methods
Online applications streamline candidate assessment by providing standardized data and easy tracking, boosting employer branding through professionalism and efficiency. Social profile applications highlight cultural fit and personality, allowing employers to showcase a modern, inclusive brand image. Combining both methods enhances transparency and engagement, reinforcing a positive employer reputation in competitive talent markets.
Challenges and Limitations: Online vs Social Applications
Online applications often face challenges such as lengthy form completion, data entry errors, and lack of user engagement, leading to higher abandonment rates. Social profile applications can streamline registration by auto-filling user information but raise concerns about privacy, data security, and platform dependency. Both methods encounter limitations in ensuring data accuracy and user trust, impacting overall application success.
Candidate Experience and Engagement
Online applications streamline the candidate experience by providing structured forms that ensure consistent data capture and faster processing times. Social profile applications enhance engagement by allowing candidates to apply with a single click, leveraging existing data from platforms like LinkedIn or Facebook to reduce friction and personalize the experience. Integrating social profiles can lead to higher application completion rates and a more dynamic interaction between employers and candidates.
Future Trends in Job Application Technology
Online applications dominate job application technology by enabling applicants to submit resumes and cover letters through company portals, offering structured data for efficient candidate screening. Social profile applications leverage platforms like LinkedIn to showcase skills, endorsements, and real-time professional updates, providing dynamic and authentic insights beyond traditional resumes. Future trends emphasize AI integration and blockchain verification to enhance application accuracy, security, and personalization across both online and social profile-based systems.
Related Important Terms
One-Click Apply Integration
One-Click Apply integration streamlines the application process by allowing candidates to submit resumes directly through online applications, enhancing speed and data accuracy compared to social profile applications that rely on third-party platform data extraction. Online application systems equipped with One-Click Apply reduce drop-off rates by minimizing form filling, improving applicant experience and increasing completion rates.
Social Resume Sync
Social Resume Sync integrates social profile data directly into online applications, streamlining the submission process and enhancing data accuracy. This synchronization reduces manual entry errors and accelerates candidate evaluation by providing up-to-date professional information from platforms like LinkedIn.
Digital Footprint Assessment
Online applications provide detailed insights into candidates' skills and experiences directly submitted for review, offering a controlled environment for digital footprint assessment. Social profile applications complement this by revealing authentic behavioral patterns and interpersonal interactions across professional and social networks, enhancing the depth of candidate evaluation.
Social Endorsement Metrics
Social endorsement metrics in social profile applications provide real-time validation through likes, shares, and comments, enhancing credibility and trust compared to traditional online applications. These metrics offer richer insights into applicant engagement and influence by reflecting actual social interactions and network support.
Application Video Intro
Application video intros significantly enhance online application effectiveness by providing a dynamic, authentic representation of candidates beyond traditional resumes. Social profile applications, while convenient, often lack the personalized engagement and nuanced communication offered by tailored video introductions.
AI Profile Parsing
AI profile parsing enhances online application efficiency by automatically extracting and organizing structured data from resumes and cover letters, reducing manual input errors and processing time. Social profile applications leverage AI to seamlessly integrate and update candidate information from platforms like LinkedIn, offering real-time accuracy and comprehensive insights for recruiters.
Skill Tagging Automation
Online application platforms utilize advanced skill tagging automation to accurately identify and categorize candidate competencies, enhancing the efficiency of resume parsing and applicant screening. In contrast, social profile applications leverage real-time data extraction from user-generated content and endorsements, providing dynamic and continuously updated skill profiles that improve matching accuracy for recruiters.
Reputation Signal Scanning
Online applications utilize Reputation Signal Scanning to analyze user behavior, digital footprints, and feedback across various platforms for comprehensive credibility assessment. Social Profile Applications focus on scanning reputation signals embedded within social media profiles, such as endorsements, connections, and engagement metrics, to evaluate applicant authenticity and influence.
Portfolio Link Embedding
Online applications often allow direct portfolio link embedding, enhancing the presentation of a candidate's work and making it easily accessible to recruiters. Social profile applications integrate seamlessly with platforms like LinkedIn, enabling real-time updates and dynamic portfolio displays that reflect current skills and projects.
Passive Profile Crawling
Online applications often require users to manually input detailed information, which ensures data accuracy but can lead to longer submission times. Social profile applications leverage passive profile crawling to automatically extract user data from social media platforms, streamlining the process but raising concerns about data privacy and consent.
Online Application vs Social Profile Application for application. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com