Adaptability in the workforce emphasizes the ability to quickly learn new skills and adjust to changing job requirements, ensuring employees remain effective in diverse environments. Transdisciplinarity goes beyond by integrating knowledge across multiple disciplines to solve complex problems, fostering innovative approaches in dynamic workplaces. Developing both adaptability and transdisciplinary skills is essential for workforce readiness, as it prepares employees to navigate evolving challenges while collaborating across varied domains.
Table of Comparison
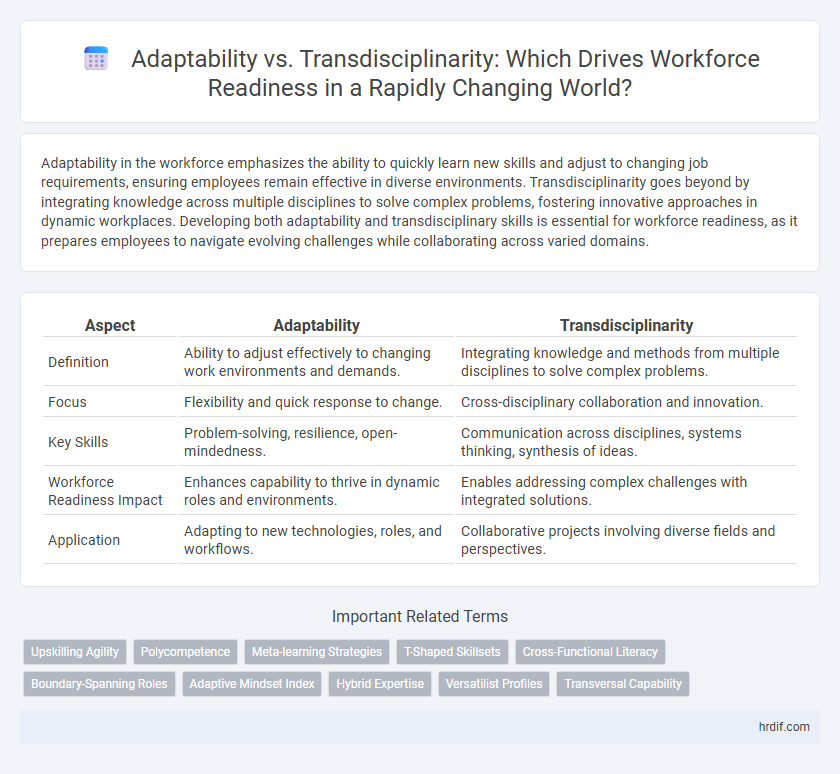
| Aspect | Adaptability | Transdisciplinarity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adjust effectively to changing work environments and demands. | Integrating knowledge and methods from multiple disciplines to solve complex problems. |
| Focus | Flexibility and quick response to change. | Cross-disciplinary collaboration and innovation. |
| Key Skills | Problem-solving, resilience, open-mindedness. | Communication across disciplines, systems thinking, synthesis of ideas. |
| Workforce Readiness Impact | Enhances capability to thrive in dynamic roles and environments. | Enables addressing complex challenges with integrated solutions. |
| Application | Adapting to new technologies, roles, and workflows. | Collaborative projects involving diverse fields and perspectives. |
Understanding Adaptability in the Modern Workforce
Understanding adaptability in the modern workforce requires recognizing its role in navigating rapid technological and market changes. Adaptable employees excel at continuous learning, problem-solving, and adjusting strategies swiftly, which enhances organizational resilience. Unlike transdisciplinarity that integrates multiple disciplines for innovation, adaptability emphasizes flexibility and responsiveness essential for workforce readiness in dynamic environments.
Defining Transdisciplinarity: Beyond Multidisciplinary Skills
Transdisciplinarity in workforce readiness transcends multidisciplinary skills by integrating knowledge, methods, and perspectives from various disciplines to solve complex real-world problems holistically. This approach fosters adaptability by encouraging employees to think beyond traditional boundaries, facilitating innovative solutions that respond dynamically to evolving challenges. Emphasizing transdisciplinary learning equips the workforce with the agility to navigate interconnected systems and shifting environments effectively.
The Growing Demand for Adaptable Employees
The growing demand for adaptable employees in workforce readiness highlights the necessity for individuals who can quickly adjust to changing environments, tasks, and technologies. Adaptability fosters resilience and continuous learning, allowing workers to thrive across diverse roles without the rigid boundaries of transdisciplinarity. Employers increasingly value this flexibility as businesses navigate rapid innovation and market shifts, making adaptability a critical asset for career sustainability.
Transdisciplinarity as a Catalyst for Innovation
Transdisciplinarity drives workforce readiness by integrating diverse fields to foster innovative problem-solving and agile thinking essential in dynamic markets. Its collaborative approach transcends traditional boundaries, cultivating a versatile skill set that enhances adaptability in rapidly evolving industries. Embracing transdisciplinary methods accelerates innovation cycles and empowers teams to respond effectively to complex challenges.
Comparing Adaptability and Transdisciplinarity: Key Differences
Adaptability involves the ability to quickly change and adjust skills in response to evolving job demands, while transdisciplinarity emphasizes integrating knowledge and methods across multiple disciplines to solve complex problems. Workforce readiness benefits from adaptability through enhanced flexibility and resilience, whereas transdisciplinarity drives innovation by fostering collaboration across diverse expertise. Understanding these differences helps organizations develop training programs that build both agile mindsets and interdisciplinary competence.
The Role of Adaptability in Career Advancement
Adaptability significantly enhances career advancement by enabling professionals to respond effectively to evolving job demands and diverse work environments. Unlike transdisciplinarity, which integrates knowledge across multiple disciplines, adaptability focuses on the ability to adjust skills and approaches dynamically in the face of change. Employers prioritize adaptable individuals who can learn rapidly, solve unforeseen problems, and thrive in uncertain conditions, making adaptability a critical factor in workforce readiness and long-term career growth.
Fostering Transdisciplinary Competencies in Employees
Fostering transdisciplinary competencies in employees enhances workforce adaptability by integrating diverse knowledge domains, enabling innovative problem-solving across complex, real-world challenges. Developing skills such as critical thinking, collaboration, and systems thinking prepares employees to navigate rapidly changing environments and evolving industry demands. Organizations investing in transdisciplinary training improve their agility, ensuring a competitive edge through workforce readiness and continuous learning.
Adaptability vs Transdisciplinarity: Which Drives Workforce Resilience?
Adaptability enables employees to rapidly adjust to changing workplace demands and emerging technologies, fostering resilience through continuous learning and flexibility. In contrast, transdisciplinarity integrates knowledge across multiple disciplines to solve complex problems, promoting holistic understanding but potentially requiring longer development periods. Workforce resilience is often more immediately driven by adaptability, as the ability to pivot and respond in real-time directly enhances survival and success in dynamic labor markets.
Integrating Adaptability and Transdisciplinarity in Professional Development
Integrating adaptability and transdisciplinarity in professional development enhances workforce readiness by fostering flexible problem-solving and cross-sector collaboration skills. Professionals trained in both adaptability and transdisciplinarity can navigate complex, evolving work environments and drive innovation through holistic understanding. Structured learning programs that combine adaptive mindset cultivation with transdisciplinary knowledge synthesis prepare employees to meet dynamic industry challenges effectively.
Preparing for the Future: Balancing Adaptability and Transdisciplinarity in Workforce Readiness
Balancing adaptability and transdisciplinarity enhances workforce readiness by equipping employees with flexible skills and integrated knowledge to navigate evolving industries. Adaptability enables swift response to change, while transdisciplinarity fosters collaboration across domains, driving innovative problem-solving. Organizations that prioritize both create resilient teams capable of meeting future challenges with agility and broad expertise.
Related Important Terms
Upskilling Agility
Upskilling agility through adaptability enhances workforce readiness by enabling employees to quickly acquire new skills in response to evolving job demands. Unlike transdisciplinarity, which integrates knowledge across disciplines, adaptability emphasizes flexible learning processes that prioritize rapid skill acquisition and real-time problem solving.
Polycompetence
Polycompetence in workforce readiness integrates adaptability and transdisciplinarity by cultivating diverse skills across multiple disciplines, enabling employees to seamlessly navigate dynamic work environments. This approach emphasizes flexible problem-solving and continuous learning, essential for thriving in complex, rapidly evolving industries.
Meta-learning Strategies
Meta-learning strategies enhance adaptability by enabling workers to efficiently acquire, unlearn, and relearn skills across diverse disciplines, fostering cognitive flexibility necessary for transdisciplinary integration. This dynamic approach cultivates workforce readiness by preparing individuals to navigate complex problem-solving scenarios that demand continuous skill evolution beyond singular expertise.
T-Shaped Skillsets
Adaptability in workforce readiness emphasizes flexible problem-solving and continuous learning, while transdisciplinarity integrates diverse disciplinary perspectives for holistic innovation; the T-shaped skillset combines deep expertise with broad collaborative abilities, enabling employees to navigate complex challenges effectively. Prioritizing adaptability alongside transdisciplinary approaches fosters agile professionals capable of thriving in dynamic environments and driving cross-functional success.
Cross-Functional Literacy
Cross-functional literacy enhances workforce adaptability by equipping employees with diverse skills across multiple disciplines, enabling seamless collaboration and problem-solving in complex environments. Unlike transdisciplinarity, which integrates knowledge from various fields into new frameworks, adaptability relies on the ability to rapidly shift roles and apply cross-disciplinary insights to evolving workplace challenges.
Boundary-Spanning Roles
Boundary-spanning roles enhance workforce readiness by integrating adaptability with transdisciplinarity, enabling employees to navigate and bridge multiple domains effectively. This ability to cross traditional boundaries fosters innovative problem-solving and agility essential in dynamic work environments.
Adaptive Mindset Index
The Adaptive Mindset Index reveals workforce readiness relies more on adaptability, emphasizing cognitive flexibility and learning agility over the broader knowledge integration seen in transdisciplinarity. Prioritizing an adaptive mindset fosters resilience and rapid problem-solving, essential for navigating dynamic job environments and evolving industry demands.
Hybrid Expertise
Hybrid expertise enhances workforce readiness by integrating adaptability with transdisciplinarity, enabling professionals to navigate complex challenges across multiple domains. This dynamic blend fosters agility and innovation, equipping employees to rapidly acquire new skills and apply diverse knowledge in evolving job markets.
Versatilist Profiles
Versatilist profiles exemplify adaptability by integrating diverse skills across multiple disciplines, enhancing workforce readiness through flexible problem-solving and continuous learning. This contrasts with transdisciplinarity, which emphasizes collaborative knowledge integration, whereas versatilism prioritizes individual capacity to navigate varied roles and rapidly adjust to evolving work environments.
Transversal Capability
Transdisciplinarity fosters transversal capabilities by integrating knowledge and skills across diverse disciplines, enhancing workforce adaptability in complex, dynamic environments. Developing transversal skills such as critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving through transdisciplinary approaches better prepares individuals to navigate multifaceted challenges and continuous change in the modern workforce.
Adaptability vs Transdisciplinarity for workforce readiness Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com