Adaptability in occupational adjustment involves the ability to modify one's skills and behaviors effectively in response to evolving work demands, ensuring sustained performance. Change enthusiasm reflects a proactive attitude towards embracing new challenges and opportunities, fostering innovation and growth within the workplace. Balancing adaptability with change enthusiasm cultivates resilience and a positive mindset, enhancing career development and job satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
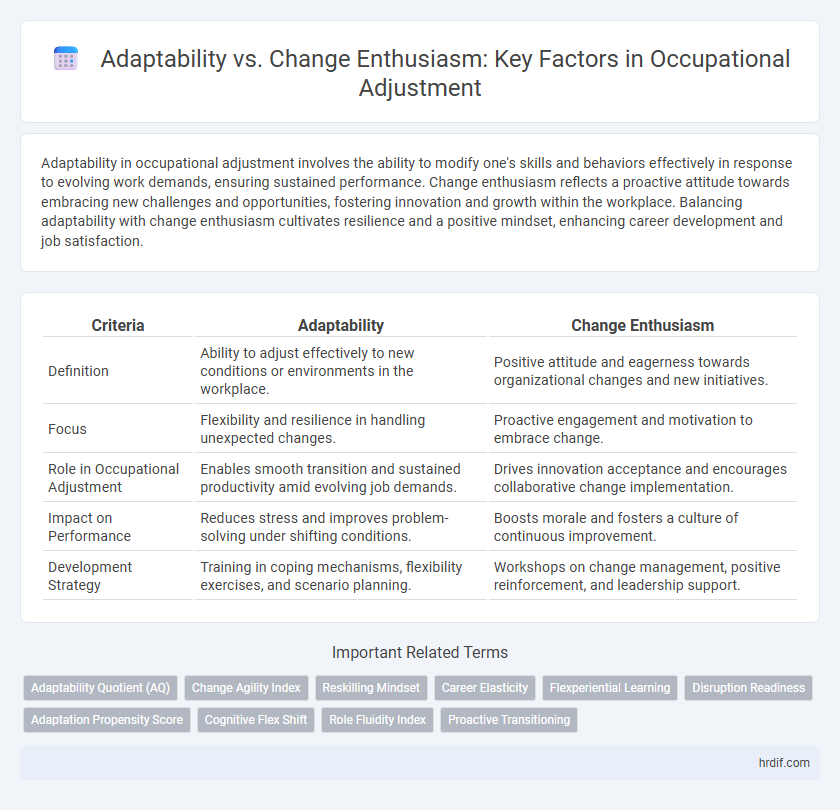
| Criteria | Adaptability | Change Enthusiasm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adjust effectively to new conditions or environments in the workplace. | Positive attitude and eagerness towards organizational changes and new initiatives. |
| Focus | Flexibility and resilience in handling unexpected changes. | Proactive engagement and motivation to embrace change. |
| Role in Occupational Adjustment | Enables smooth transition and sustained productivity amid evolving job demands. | Drives innovation acceptance and encourages collaborative change implementation. |
| Impact on Performance | Reduces stress and improves problem-solving under shifting conditions. | Boosts morale and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. |
| Development Strategy | Training in coping mechanisms, flexibility exercises, and scenario planning. | Workshops on change management, positive reinforcement, and leadership support. |
Understanding Adaptability in the Modern Workplace
Adaptability in the modern workplace involves the ability to modify behavior and strategies in response to evolving job demands, contrasting with change enthusiasm, which reflects a positive attitude toward new initiatives. Research indicates that employees with high adaptability demonstrate better problem-solving and resilience during organizational shifts. Understanding these distinctions enhances workforce development and supports effective occupational adjustment strategies.
Defining Change Enthusiasm: Beyond Basic Flexibility
Change enthusiasm transcends basic flexibility by embodying a proactive eagerness to embrace new occupational challenges and innovations. It involves not only adapting to change but actively seeking opportunities for professional growth and skill enhancement. This mindset drives individuals to anticipate industry trends and contribute creatively to organizational transformation.
Key Differences: Adaptability vs Change Enthusiasm
Adaptability refers to the ability to modify behaviors, skills, and approaches in response to new occupational demands, emphasizing flexibility and resilience in evolving work environments. Change enthusiasm involves a proactive eagerness and positive attitude towards embracing and initiating change, often manifesting as motivation to seek out new opportunities and innovations. While adaptability centers on managing and coping with change effectively, change enthusiasm drives proactive engagement and enthusiasm for transformational processes in the workplace.
Benefits of Adaptability in Career Advancement
Adaptability enhances career advancement by enabling professionals to effectively adjust to evolving job demands and industry trends, fostering continuous skill development and resilience. This flexibility allows employees to navigate workplace challenges, seize new opportunities, and maintain relevance in competitive environments. Embracing adaptability cultivates problem-solving abilities and emotional intelligence, critical for leadership roles and long-term career success.
The Role of Change Enthusiasm in Occupational Success
Change enthusiasm plays a critical role in occupational success by fostering a proactive mindset that embraces new challenges and continuous learning. Employees who exhibit high change enthusiasm demonstrate greater resilience and flexibility, leading to quicker adaptation to evolving work environments and technologies. This positive attitude toward change enhances problem-solving capabilities and drives sustained career growth in dynamic industries.
Challenges of Relying Solely on Adaptability
Relying solely on adaptability in occupational adjustment limits proactive engagement with emerging opportunities and may lead to reactive decision-making under pressure. While adaptability allows for flexibility, a lack of change enthusiasm can hinder innovation and reduce motivation to pursue continuous improvement. This imbalance often results in missed chances for career growth and diminished resilience in dynamic work environments.
Cultivating Change Enthusiasm Among Employees
Cultivating change enthusiasm among employees enhances occupational adjustment by fostering a proactive mindset towards evolving work environments. Emphasizing intrinsic motivation and structured support systems boosts adaptability, as enthusiastic employees are more likely to embrace innovation and continuous learning. Organizations that prioritize change enthusiasm experience higher engagement, resilience, and overall performance during transitions.
Balancing Adaptability and Change Enthusiasm for Career Growth
Balancing adaptability and change enthusiasm is crucial for effective occupational adjustment, as adaptability enables professionals to respond flexibly to evolving job demands while change enthusiasm drives proactive engagement with new opportunities. Cultivating adaptability involves improving problem-solving skills and emotional resilience, whereas change enthusiasm fosters motivation and innovation in dynamic work environments. Integrating both traits promotes sustained career growth by enhancing an individual's ability to navigate uncertainties and capitalize on emerging trends within their industry.
Practical Strategies for Fostering Occupational Adjustment
Developing adaptability involves cultivating a flexible mindset that embraces evolving job roles and work environments, which enhances occupational adjustment. Practical strategies include targeted skill development, seeking continuous feedback, and engaging in reflective practices to better understand personal responses to workplace changes. Encouraging proactive learning and resilience-building exercises supports employees in navigating transitions effectively and maintaining productivity during periods of organizational change.
Assessing Adaptability and Change Enthusiasm: Tools and Metrics
Assessing adaptability in occupational adjustment involves evaluating behavioral flexibility, problem-solving skills, and emotional resilience through validated instruments such as the Adaptability Scale and Work Adjustment Inventory. Change enthusiasm is measured using metrics like the Change Readiness Assessment and Employee Change Engagement Surveys, which capture motivation and positive attitudes toward transformation. Integrating these tools provides a comprehensive profile of an employee's capacity to navigate and embrace workplace changes effectively.
Related Important Terms
Adaptability Quotient (AQ)
The Adaptability Quotient (AQ) measures an individual's capacity to adjust effectively to new occupational demands, emphasizing cognitive flexibility and emotional resilience. Unlike mere change enthusiasm, AQ reflects the deeper ability to navigate uncertainty and maintain performance during workforce transitions.
Change Agility Index
The Change Agility Index measures an individual's capacity to swiftly and effectively adjust to evolving workplace demands, distinguishing adaptability as a dynamic skill beyond mere change enthusiasm. High scores on this index correlate with enhanced occupational adjustment, reflecting proactive learning and resilience rather than just a positive attitude toward change.
Reskilling Mindset
A reskilling mindset prioritizes continuous learning and skill acquisition, enabling individuals to adapt effectively to evolving occupational demands rather than simply embracing change enthusiasm superficially. This proactive approach fosters sustainable career growth by aligning competencies with market shifts and technological advancements.
Career Elasticity
Career elasticity reflects an individual's capacity to adjust effectively to evolving job roles and market demands without losing performance quality. While adaptability emphasizes skillful responses to change, change enthusiasm drives a proactive and positive attitude that accelerates successful occupational adjustment.
Flexperiential Learning
Adaptability in occupational adjustment emphasizes flexible experiential learning, allowing individuals to modify skills and approaches based on evolving job demands. Change enthusiasm drives proactive engagement with new challenges but relies heavily on adaptability to translate enthusiasm into effective, real-world skill application.
Disruption Readiness
Adaptability enables employees to effectively respond to evolving workplace demands by developing skills that ensure disruption readiness, while change enthusiasm reflects a positive attitude toward new initiatives but may lack the practical preparedness needed for sudden occupational shifts. Workforce strategies emphasizing adaptability cultivate resilience and proactive problem-solving, critical for maintaining productivity during technological or organizational disruptions.
Adaptation Propensity Score
Adaptation Propensity Score quantifies an individual's ability to successfully adjust to new occupational environments, providing a more precise measure of adaptability compared to general change enthusiasm. Higher scores correlate with faster integration and improved job performance during workplace transitions, emphasizing the critical role of adaptability in effective occupational adjustment.
Cognitive Flex Shift
Cognitive Flex Shift plays a critical role in occupational adjustment by enabling individuals to seamlessly transition between various mental frameworks and problem-solving approaches, fostering strong adaptability in dynamic work environments. This cognitive agility surpasses mere change enthusiasm by equipping professionals with the ability to modify thought processes strategically, enhancing performance amid evolving job demands.
Role Fluidity Index
The Role Fluidity Index quantifies an individual's capacity to seamlessly transition between roles, serving as a critical metric for adaptability in occupational adjustment. Higher index scores correlate with enhanced job performance and resilience, distinguishing adaptability from mere change enthusiasm by emphasizing functional flexibility over general positivity toward change.
Proactive Transitioning
Proactive transitioning enhances occupational adjustment by fostering adaptability, allowing individuals to anticipate and respond effectively to evolving work environments. Embracing adaptability over mere change enthusiasm leads to sustained career growth through strategic preparation and skill development.
Adaptability vs Change Enthusiasm for occupational adjustment. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com