Adaptability in career development emphasizes the ability to adjust quickly to changing environments and new challenges, ensuring sustained growth in dynamic industries. Polymathy involves acquiring deep expertise across multiple disciplines, fostering innovation through diverse knowledge integration. Balancing adaptability with polymathy equips professionals to navigate complex career landscapes by combining flexibility with broad, cross-functional skills.
Table of Comparison
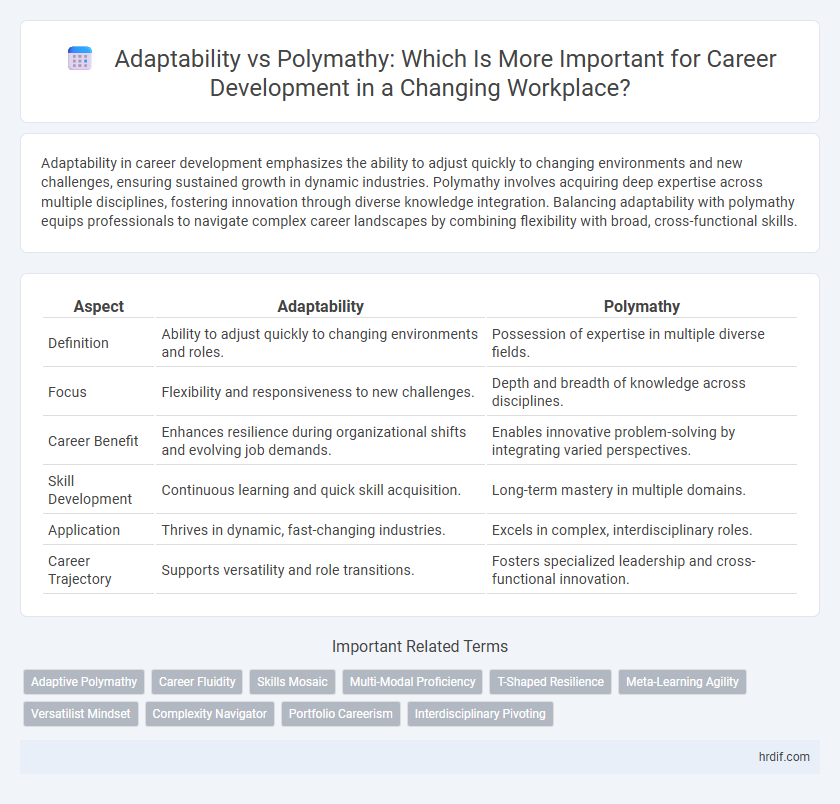
| Aspect | Adaptability | Polymathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adjust quickly to changing environments and roles. | Possession of expertise in multiple diverse fields. |
| Focus | Flexibility and responsiveness to new challenges. | Depth and breadth of knowledge across disciplines. |
| Career Benefit | Enhances resilience during organizational shifts and evolving job demands. | Enables innovative problem-solving by integrating varied perspectives. |
| Skill Development | Continuous learning and quick skill acquisition. | Long-term mastery in multiple domains. |
| Application | Thrives in dynamic, fast-changing industries. | Excels in complex, interdisciplinary roles. |
| Career Trajectory | Supports versatility and role transitions. | Fosters specialized leadership and cross-functional innovation. |
Defining Adaptability and Polymathy in Career Development
Adaptability in career development refers to the ability to adjust skills and approaches in response to changing job demands and industry trends, enhancing resilience and continuous growth. Polymathy involves cultivating expertise across multiple disciplines, enabling innovative problem-solving and cross-functional collaboration in diverse career paths. Both concepts prioritize flexibility but differ in scope: adaptability centers on evolving within or across roles, while polymathy emphasizes broad, interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition.
Core Differences Between Adaptability and Polymathy
Adaptability emphasizes the ability to quickly adjust skills and approaches in response to changing environments, promoting resilience and continuous learning within a specific domain. Polymathy involves possessing deep expertise across multiple diverse fields, enabling innovative problem-solving through interdisciplinary knowledge integration. While adaptability focuses on flexibility within a career path, polymathy drives breadth and synthesis of complex ideas across varied disciplines.
The Role of Adaptability in Navigating Career Shifts
Adaptability plays a crucial role in navigating career shifts by enabling professionals to quickly adjust to changing industry trends, technologies, and job requirements. It fosters resilience and continuous learning, allowing individuals to pivot effectively between roles and acquire new skills essential for evolving career landscapes. Unlike polymathy, which emphasizes broad knowledge across multiple fields, adaptability focuses on the ability to respond efficiently to change within specific career contexts, ensuring sustained professional growth.
Polymathy: The Power of Multiple Skills in the Workplace
Polymathy enhances career development by equipping professionals with a diverse skill set that fosters innovation, problem-solving, and cross-disciplinary collaboration. Unlike adaptability, which centers on adjusting to change, polymathy empowers individuals to proactively integrate knowledge from various fields to create novel solutions and seize emerging opportunities. This multidimensional expertise drives competitive advantage in the workplace, promoting continuous growth and resilience amid evolving industry demands.
Situational Advantage: When to Rely on Adaptability vs Polymathy
Adaptability excels in dynamic work environments requiring quick learning and flexible problem-solving, allowing professionals to pivot efficiently amid changing circumstances. Polymathy offers a situational advantage in complex, interdisciplinary projects where deep knowledge across multiple domains drives innovation and strategic insight. Choosing adaptability or polymathy depends on career contexts: adaptability fits roles demanding rapid adjustment, while polymathy suits careers benefiting from broad, integrative expertise.
Building an Adaptability Mindset for Career Success
Building an adaptability mindset for career success involves embracing continuous learning and flexibility to navigate changing job markets and industry demands. Unlike polymathy, which focuses on acquiring diverse, deep expertise across multiple fields, adaptability emphasizes the ability to quickly adjust skills and approaches in response to new challenges. Cultivating adaptability enhances resilience and responsiveness, key traits that drive long-term career growth and opportunity in dynamic environments.
Nurturing Polymathic Skills for Professional Growth
Nurturing polymathic skills enhances adaptability by enabling professionals to integrate diverse knowledge areas and rapidly adjust to evolving career landscapes. Developing expertise across multiple domains fosters innovative problem-solving and broadens opportunities for leadership in interdisciplinary projects. Emphasizing polymathy accelerates professional growth by cultivating cognitive flexibility and resilience in dynamic work environments.
Employer Perspectives: Adaptable Employees vs Polymathic Talent
Employers prioritize adaptable employees who demonstrate flexibility and quick learning in dynamic work environments, ensuring seamless integration across evolving roles. Polymathic talent offers broad interdisciplinary knowledge, but adaptability enables focused skill application aligned with organizational goals, increasing immediate value. Companies increasingly seek candidates with resilience and the capacity to pivot skills rapidly, favoring adaptability as a critical asset for sustained career growth.
Case Studies: Real-World Outcomes of Adaptability and Polymathy
Case studies reveal that adaptability in career development leads to successful navigation of rapidly changing industries by fostering resilience and continuous learning, while polymathy enables individuals to apply diverse knowledge across multiple fields, driving innovation and problem-solving. Real-world outcomes show adaptable professionals quickly pivot roles during market shifts, whereas polymaths often integrate cross-disciplinary insights to create unique career paths. Companies valuing adaptability report higher employee retention, and those embracing polymathy experience increased creative outputs and competitive advantage.
Future-Proofing Your Career: Integrating Adaptability and Polymathy
Integrating adaptability with polymathy enhances future-proofing your career by cultivating diverse skills and a flexible mindset that responds swiftly to evolving job markets. Embracing adaptability allows professionals to pivot and learn continuously, while polymathy provides broad knowledge across disciplines, fostering innovation and resilience. Together, these qualities equip individuals to navigate uncertainties and seize emerging opportunities in dynamic career landscapes.
Related Important Terms
Adaptive Polymathy
Adaptive polymathy enhances career development by combining deep expertise across multiple fields with the agility to apply diverse skills in changing environments. This fusion of adaptability and polymathic knowledge empowers professionals to navigate complex challenges, stay relevant, and innovate consistently in dynamic industries.
Career Fluidity
Career fluidity thrives on adaptability, empowering professionals to pivot across industries and roles by continuously acquiring relevant skills and embracing change. Unlike polymathy, which emphasizes deep expertise in multiple domains, adaptability prioritizes agile learning and responsiveness to evolving career landscapes for sustained professional growth.
Skills Mosaic
Adaptability enhances career development by enabling professionals to quickly adjust to evolving industries, whereas polymathy involves cultivating a diverse Skills Mosaic of expertise across multiple domains, fostering innovative problem-solving and broadening opportunities. Emphasizing a Skills Mosaic blends adaptability with interdisciplinary knowledge, empowering individuals to navigate complex challenges and pivot effectively in dynamic job markets.
Multi-Modal Proficiency
Adaptability in career development emphasizes the ability to quickly adjust skills and approaches across varying contexts, while polymathy involves deep expertise across multiple domains. Multi-modal proficiency integrates both, enabling professionals to seamlessly switch between specialized knowledge and versatile problem-solving strategies for enhanced career resilience and growth.
T-Shaped Resilience
T-shaped resilience, combining deep expertise with broad adaptability, enhances career development by balancing specialization and versatile skill sets, enabling professionals to thrive amid evolving job demands. Unlike polymathy, which emphasizes mastering multiple disciplines, adaptability centers on flexible problem-solving and continuous learning within and beyond one's core competency.
Meta-Learning Agility
Adaptability in career development emphasizes the ability to quickly learn and apply new skills in changing environments, driven by meta-learning agility, whereas polymathy involves possessing deep expertise across multiple disciplines. Focusing on meta-learning agility enables professionals to continuously acquire, unlearn, and relearn skills, fostering resilience and sustained relevance in rapidly evolving industries.
Versatilist Mindset
A versatilist mindset, combining adaptability with polymathy, enhances career development by enabling professionals to quickly acquire diverse skills and pivot across various industries. Emphasizing continuous learning and cognitive flexibility, this approach fosters resilience and innovation, positioning individuals to thrive in rapidly changing job markets.
Complexity Navigator
Adaptability in career development emphasizes the ability to respond swiftly and effectively to changing environments, whereas polymathy involves deep expertise across diverse fields, enabling broader problem-solving. Complexity navigators leverage adaptability to manage uncertainty and dynamic challenges, making it a crucial skill in evolving professional landscapes.
Portfolio Careerism
Adaptability enables professionals to pivot quickly across roles, fostering resilience in the dynamic job market, while polymathy cultivates broad expertise that enriches a portfolio career with diverse skills and knowledge. Embracing a portfolio careerism approach leverages adaptability to integrate varied competencies, enhancing career longevity and growth through continuous learning and versatile experiences.
Interdisciplinary Pivoting
Adaptability in career development emphasizes the ability to swiftly adjust skills and knowledge to new industries or roles, enhancing resilience in changing job markets. Polymathy, through interdisciplinary pivoting, fosters deep learning across multiple domains, enabling innovative problem-solving and unique value creation beyond traditional specialization.
Adaptability vs Polymathy for career development Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com