Adaptability in a job or career refers to the ability to adjust to new conditions, learn new skills, and navigate changing environments effectively. Adaptive intelligence goes beyond simple flexibility by involving problem-solving skills and the capacity to apply knowledge creatively in unfamiliar situations. While adaptability ensures survival and smooth transitions, adaptive intelligence drives innovation and long-term success in a rapidly evolving workplace.
Table of Comparison
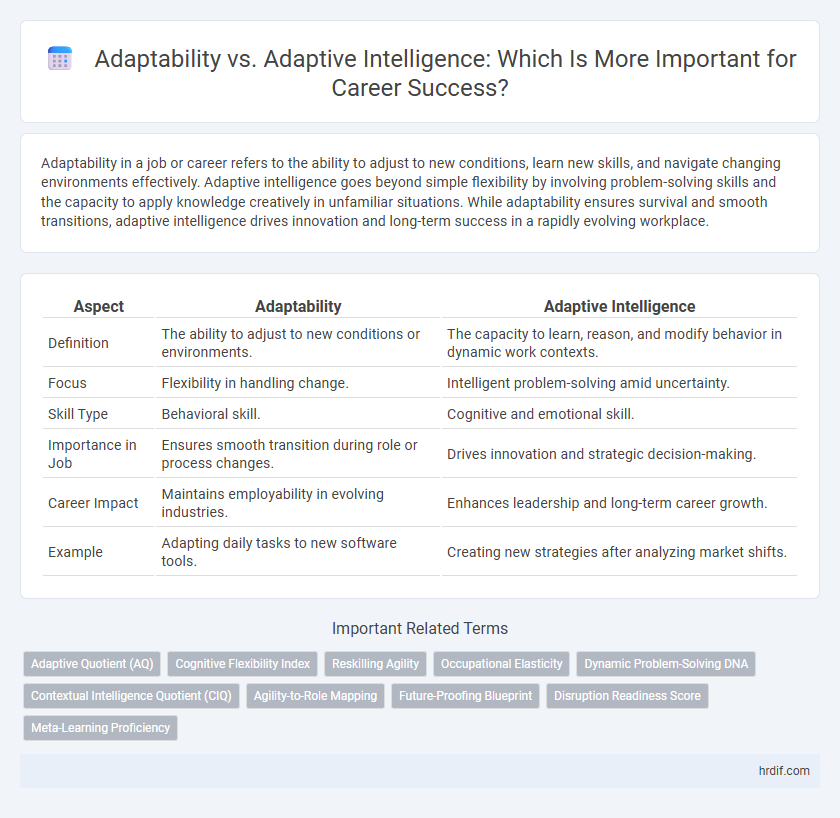
| Aspect | Adaptability | Adaptive Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to adjust to new conditions or environments. | The capacity to learn, reason, and modify behavior in dynamic work contexts. |
| Focus | Flexibility in handling change. | Intelligent problem-solving amid uncertainty. |
| Skill Type | Behavioral skill. | Cognitive and emotional skill. |
| Importance in Job | Ensures smooth transition during role or process changes. | Drives innovation and strategic decision-making. |
| Career Impact | Maintains employability in evolving industries. | Enhances leadership and long-term career growth. |
| Example | Adapting daily tasks to new software tools. | Creating new strategies after analyzing market shifts. |
Understanding Adaptability in the Workplace
Adaptability in the workplace refers to the ability to adjust effectively to changing job demands, environments, and technologies, ensuring sustained performance and growth. Adaptive intelligence encompasses the cognitive skills and emotional resilience that enable individuals to learn from experience and navigate complex situations with flexibility. Employers increasingly value both traits as they drive innovation, problem-solving, and long-term career success in dynamic professional landscapes.
Defining Adaptive Intelligence for Career Success
Adaptive intelligence is the cognitive ability to adjust strategies and behaviors in response to changing work environments, enabling professionals to navigate complex challenges effectively. This skill encompasses problem-solving, emotional regulation, and learning agility, which are critical for sustaining career growth and achieving long-term success. Unlike general adaptability, adaptive intelligence integrates continuous self-assessment and proactive skill development to align with evolving industry demands.
Key Differences Between Adaptability and Adaptive Intelligence
Adaptability refers to the ability to adjust behavior and strategies in response to changing circumstances, while adaptive intelligence encompasses a broader cognitive capacity to solve novel problems and learn from experience. Key differences include adaptability's emphasis on flexibility and resilience in practical situations, contrasted with adaptive intelligence's focus on analytical thinking, creativity, and learning agility. In career development, adaptability enables quick responses to new roles or environments, whereas adaptive intelligence drives strategic innovation and continuous personal growth.
The Role of Adaptability in Career Growth
Adaptability plays a crucial role in career growth by enabling professionals to navigate changing job requirements and evolving industry trends effectively. Unlike adaptive intelligence, which focuses on problem-solving and learning from experiences, adaptability emphasizes the willingness to embrace change and develop new skills continuously. Employers prioritize adaptability as a key attribute that drives innovation, resilience, and long-term success in dynamic work environments.
How Adaptive Intelligence Influences Job Performance
Adaptive intelligence enhances job performance by enabling employees to effectively navigate changing work environments and solve complex problems. It integrates cognitive flexibility, emotional regulation, and situational awareness to improve decision-making and collaboration under pressure. Organizations that prioritize adaptive intelligence report higher productivity, innovation, and employee resilience during market disruptions.
Building Adaptability Skills: Practical Tips
Building adaptability skills involves regular practice of flexibility, such as embracing change, learning new technologies, and seeking diverse experiences to enhance problem-solving abilities. Adaptive intelligence goes beyond adaptability by integrating emotional regulation, situational awareness, and quick decision-making in dynamic environments. Professionals who develop both adaptability and adaptive intelligence improve career resilience, increase innovation capacity, and maintain competitive advantage in rapidly evolving job markets.
Developing Adaptive Intelligence: Strategies for Professionals
Developing adaptive intelligence enables professionals to navigate complex job environments by enhancing cognitive flexibility and emotional resilience. Strategies include continuous learning, embracing change, and leveraging feedback to improve decision-making and problem-solving skills. Cultivating adaptive intelligence fosters career growth and success in dynamic industries.
Real-World Examples: Adaptability vs Adaptive Intelligence
Adaptability in the workplace refers to the ability to adjust quickly to changing circumstances, such as shifting project priorities or new technologies. Adaptive intelligence, however, encompasses not only flexibility but also problem-solving skills and the capacity to learn from experiences, as demonstrated by leaders who navigate complex market disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic with innovative strategies. Real-world examples include employees who swiftly embrace remote work setups versus those who proactively design new workflows, illustrating the deeper impact of adaptive intelligence on long-term career growth.
Measuring Success: Which Matters More for Career Advancement?
Measuring success in career advancement often hinges more on adaptive intelligence, which encompasses problem-solving skills, learning agility, and emotional regulation, than on general adaptability alone. Employers favor candidates who demonstrate adaptive intelligence because it enables effective decision-making and innovation in complex, changing work environments. Data shows that professionals with high adaptive intelligence achieve faster promotions and stronger leadership roles, making it a critical factor for long-term career growth.
Future-Proofing Your Career: Integrating Adaptability and Adaptive Intelligence
Future-proofing your career requires mastering both adaptability and adaptive intelligence, where adaptability allows quick response to change, and adaptive intelligence enables learning from experiences to solve novel problems. Integrating these skills helps professionals anticipate industry shifts and innovate solutions, ensuring long-term career resilience. Emphasizing continuous skill development and cognitive flexibility positions individuals to thrive amidst evolving job market demands.
Related Important Terms
Adaptive Quotient (AQ)
Adaptive Quotient (AQ) measures an individual's ability to learn, adjust, and thrive amid changing job demands better than general adaptability, directly influencing career success and resilience in dynamic work environments. High AQ enables professionals to anticipate challenges, acquire new skills rapidly, and innovate, making it a critical metric for sustained employability and leadership growth.
Cognitive Flexibility Index
The Cognitive Flexibility Index (CFI) measures an individual's ability to switch thinking and adapt to changing job demands, highlighting a key difference between adaptability and adaptive intelligence in career success. High CFI scores correlate with enhanced problem-solving and resilience, essential for navigating dynamic workplaces and advancing professional goals.
Reskilling Agility
Reskilling agility enhances adaptability by enabling professionals to quickly acquire new skills and pivot in evolving job markets, while adaptive intelligence involves applying problem-solving abilities and emotional insight to navigate complex workplace challenges. Prioritizing reskilling agility fosters continuous learning and career resilience, ensuring sustained relevance in dynamic industries.
Occupational Elasticity
Occupational elasticity measures an individual's capacity to adjust skills and behaviors in response to evolving job demands, highlighting the practical application of adaptability in career growth. Adaptive intelligence extends beyond basic flexibility by integrating problem-solving and learning agility, essential for navigating complex and dynamic professional environments.
Dynamic Problem-Solving DNA
Adaptability in a job context emphasizes flexibility and the ability to adjust to changing circumstances, while adaptive intelligence involves employing dynamic problem-solving DNA to analyze complex situations and generate innovative solutions. Professionals with adaptive intelligence demonstrate superior capabilities in navigating unpredictable environments by continuously learning and applying strategic thinking to evolving challenges.
Contextual Intelligence Quotient (CIQ)
Contextual Intelligence Quotient (CIQ) measures the ability to adapt cognitive strategies based on changing job environments, differentiating it from general adaptability which often lacks situational sensitivity. Higher CIQ enables professionals to navigate complex career landscapes by integrating cultural, organizational, and situational cues for optimized decision-making and performance.
Agility-to-Role Mapping
Agility-to-Role Mapping enhances career success by aligning individual adaptability with specific job demands, enabling employees to respond swiftly to evolving challenges and responsibilities. Adaptive Intelligence integrates cognitive flexibility with emotional awareness, but without precise agility-to-role alignment, adaptability alone may not fully optimize performance in dynamic work environments.
Future-Proofing Blueprint
Adaptability involves the ability to adjust to new conditions and challenges in the workplace, while adaptive intelligence refers to the cognitive capacity to learn from experience and apply knowledge to complex problems, essential for navigating evolving career landscapes. Future-proofing your career blueprint requires cultivating both adaptability and adaptive intelligence to remain resilient and innovative amid rapid technological advancements and shifting job market demands.
Disruption Readiness Score
Disruption Readiness Score quantifies an individual's adaptability by measuring their capacity to respond effectively to rapid industry changes and unpredictable job market shifts, crucial for career resilience. Adaptive intelligence complements this by integrating problem-solving skills and emotional agility, enabling professionals to navigate disruptions with strategic insight and continuous learning.
Meta-Learning Proficiency
Adaptability in a job context emphasizes practical flexibility to changing tasks and environments, whereas adaptive intelligence involves meta-learning proficiency that allows individuals to analyze and modify their learning strategies for continuous skill improvement. Developing meta-learning proficiency enhances career success by enabling faster acquisition of new competencies and better problem-solving in dynamic work conditions.
Adaptability vs Adaptive Intelligence for job and career. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com