Adaptability in the workplace emphasizes an employee's ability to adjust behaviors and strategies to new environments and challenges, fostering long-term growth and resilience. Elasticity refers to the capacity to quickly bounce back or recover from setbacks, focusing on short-term rebound rather than sustained change. Prioritizing adaptability over elasticity ensures teams remain flexible and proactive amidst ongoing workplace transformations.
Table of Comparison
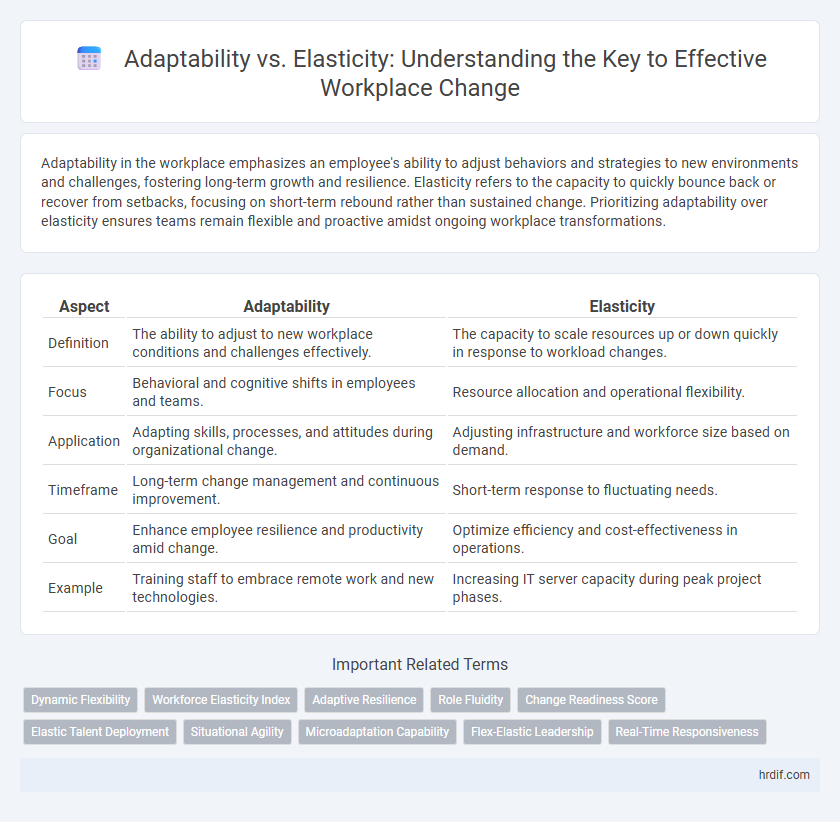
| Aspect | Adaptability | Elasticity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to adjust to new workplace conditions and challenges effectively. | The capacity to scale resources up or down quickly in response to workload changes. |
| Focus | Behavioral and cognitive shifts in employees and teams. | Resource allocation and operational flexibility. |
| Application | Adapting skills, processes, and attitudes during organizational change. | Adjusting infrastructure and workforce size based on demand. |
| Timeframe | Long-term change management and continuous improvement. | Short-term response to fluctuating needs. |
| Goal | Enhance employee resilience and productivity amid change. | Optimize efficiency and cost-effectiveness in operations. |
| Example | Training staff to embrace remote work and new technologies. | Increasing IT server capacity during peak project phases. |
Understanding Adaptability and Elasticity in the Workplace
Adaptability in the workplace refers to an employee's ability to adjust their approach and mindset in response to evolving tasks and environments, ensuring sustained performance and growth. Elasticity relates to the organization's structural capacity to absorb change and recover swiftly without compromising functionality or efficiency. Understanding these concepts enables businesses to foster resilient teams capable of thriving amid continuous market dynamics and technological advancements.
Key Differences Between Adaptability and Elasticity
Adaptability refers to the capacity of individuals and organizations to adjust their strategies and behaviors in response to changing workplace environments, emphasizing long-term transformation and learning. Elasticity involves the ability to quickly rebound or recover from disruptions without significant alteration to core functions, focusing on short-term flexibility and resilience. Key differences include adaptability's focus on proactive change and evolution, whereas elasticity centers on reactive recovery and maintaining stability under pressure.
The Role of Adaptability in Career Growth
Adaptability plays a critical role in career growth by enabling professionals to embrace change, acquire new skills, and navigate evolving workplace demands effectively. Unlike elasticity, which refers to the ability to return to a prior state after disruption, adaptability involves continuous learning and proactive adjustment to unpredictable environments. Cultivating adaptability enhances resilience, fosters innovation, and positions individuals for long-term success in dynamic industries.
How Elasticity Impacts Workplace Performance
Elasticity in the workplace directly influences performance by enabling systems and processes to dynamically adjust to fluctuating workloads without sacrificing efficiency. This flexibility ensures optimal resource allocation, minimizes downtime, and supports consistent productivity during periods of rapid change. Enhanced elasticity fosters resilience, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to shifting demands and maintain high performance standards.
Measuring Adaptability vs. Elasticity in Employees
Measuring adaptability in employees involves assessing their ability to learn new skills, adjust to evolving workplace demands, and demonstrate cognitive flexibility during change. Elasticity measurement focuses on how quickly employees recover from setbacks or stress without a decline in performance, highlighting resilience under pressure. Combining these metrics provides a comprehensive evaluation of workforce readiness, balancing proactive change management with recovery capacity.
Advantages of Adaptability During Organizational Change
Adaptability in the workplace fosters a proactive response to organizational change by enabling employees to adjust skills and mindsets quickly, which enhances overall resilience. Unlike elasticity, which focuses on returning to a previous state after disruption, adaptability drives continuous improvement and innovation, supporting long-term growth. This dynamic approach reduces downtime, minimizes resistance, and boosts team morale, ultimately leading to a more agile and competitive organization.
Elasticity: The Secret to Surviving Sudden Shifts
Elasticity in the workplace refers to an organization's ability to rapidly absorb and respond to sudden shifts without losing productivity or morale. Unlike adaptability, which involves gradual adjustments over time, elasticity enables immediate flexibility in resource allocation, workflows, and employee roles. Companies exhibiting high elasticity maintain operational stability and competitive advantage during abrupt market changes or crises.
Developing Adaptable Skills for Future Careers
Developing adaptable skills enhances workforce resilience by fostering creativity, problem-solving, and continuous learning necessary for navigating dynamic career landscapes. Unlike elasticity, which implies returning to a previous state after change, adaptability involves proactively evolving skills and mindsets to meet new challenges and opportunities. Emphasizing adaptability equips professionals to thrive amid technological advancements and shifting industry demands, ensuring sustained career growth.
When to Prioritize Adaptability Over Elasticity
Prioritize adaptability over elasticity in workplace change when the environment is highly unpredictable and requires continuous learning and innovation. Adaptability emphasizes evolving skills, mindset, and behaviors to meet emerging challenges, whereas elasticity focuses on temporary responsiveness and recovery. Organizations facing complex, long-term transformations benefit more from adaptability to sustain growth and resilience.
Building a Resilient Workforce: Combining Adaptability and Elasticity
Building a resilient workforce requires integrating adaptability, the ability to learn and adjust to new challenges, with elasticity, which emphasizes rapid recovery from setbacks. Emphasizing adaptability fosters continuous skill development and proactive problem-solving, while elasticity ensures employees can quickly rebound and maintain performance under pressure. Combining these traits enhances organizational agility and supports sustainable success in dynamic workplace environments.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Flexibility
Dynamic flexibility in the workplace emphasizes real-time responsiveness and proactive adjustment to evolving challenges, distinguishing adaptability from elasticity, which primarily involves returning to a previous state after disruption. Adaptability fosters continuous growth and innovation by enabling employees and organizations to pivot strategies, workflows, and mindsets seamlessly in response to complex, unpredictable changes.
Workforce Elasticity Index
The Workforce Elasticity Index quantifies an organization's ability to scale labor resources quickly in response to fluctuating business demands, distinguishing it from adaptability, which emphasizes individual and cultural flexibility in the workplace. Higher elasticity scores correlate with improved operational efficiency and faster response times to market changes, making elasticity a critical metric for managing dynamic workforce requirements.
Adaptive Resilience
Adaptive resilience in the workplace emphasizes the ability to not only recover from change but also to evolve and thrive amidst uncertainty, distinguishing it from elasticity which primarily focuses on bouncing back to a previous state. Organizations that cultivate adaptive resilience develop dynamic capabilities that enable continuous learning, innovation, and transformation in response to complex and shifting environments.
Role Fluidity
Role fluidity in workplace change highlights adaptability by enabling employees to seamlessly transition between tasks and responsibilities, fostering resilience and innovation. Unlike elasticity, which emphasizes bouncing back to a previous state, adaptability through role fluidity supports continuous evolution and dynamic collaboration in rapidly shifting environments.
Change Readiness Score
Adaptability in the workplace strongly correlates with higher Change Readiness Scores, as it reflects an individual's or team's capacity to embrace new challenges and modify behaviors proactively. Unlike elasticity, which denotes a return to a previous state after disruption, adaptability emphasizes continuous growth and innovation, driving sustained organizational resilience during change.
Elastic Talent Deployment
Elastic talent deployment enhances workplace adaptability by rapidly reallocating skilled professionals across projects, meeting evolving business demands without long-term commitments. This flexible staffing strategy optimizes resource utilization and accelerates response to market fluctuations, surpassing traditional adaptability's slower adjustment pace.
Situational Agility
Situational agility emphasizes real-time responsiveness to unique workplace challenges, enabling employees to adjust behaviors and strategies effectively without rigid constraints. Unlike elasticity, which implies a return to original states, adaptability fosters continuous learning and dynamic evolution in response to changing work environments.
Microadaptation Capability
Microadaptation capability allows employees to rapidly and incrementally adjust to workplace changes, enhancing overall adaptability by fostering continuous, small-scale behavioral shifts. Unlike elasticity, which emphasizes rebound from disruption, microadaptation targets proactive, real-time modifications to work processes, driving sustained productivity and resilience in dynamic environments.
Flex-Elastic Leadership
Flex-elastic leadership prioritizes adaptability by enabling leaders to dynamically adjust strategies and workflows in response to unpredictable workplace changes, contrasting with elasticity which emphasizes restoring prior states after disruptions. This approach fosters continuous innovation, resilience, and employee engagement by embracing change as an opportunity for growth rather than merely recovering equilibrium.
Real-Time Responsiveness
Adaptability in the workplace prioritizes real-time responsiveness, enabling teams to promptly adjust strategies and workflows to evolving conditions without delay. Unlike elasticity, which refers to the capacity to return to a previous state after change, adaptability emphasizes continuous evolution and seamless integration of new information to maintain optimal performance.
Adaptability vs Elasticity for workplace change. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com