Adaptability refers to the ability to adjust quickly to new job environments and changing tasks, while career plasticity emphasizes a broader capacity to reshape one's career path and develop new skills over time. In the modern workforce, adaptability ensures immediate responsiveness to challenges, whereas career plasticity supports long-term growth and versatility across different roles or industries. Employers value both traits as they drive resilience and sustained professional development in dynamic markets.
Table of Comparison
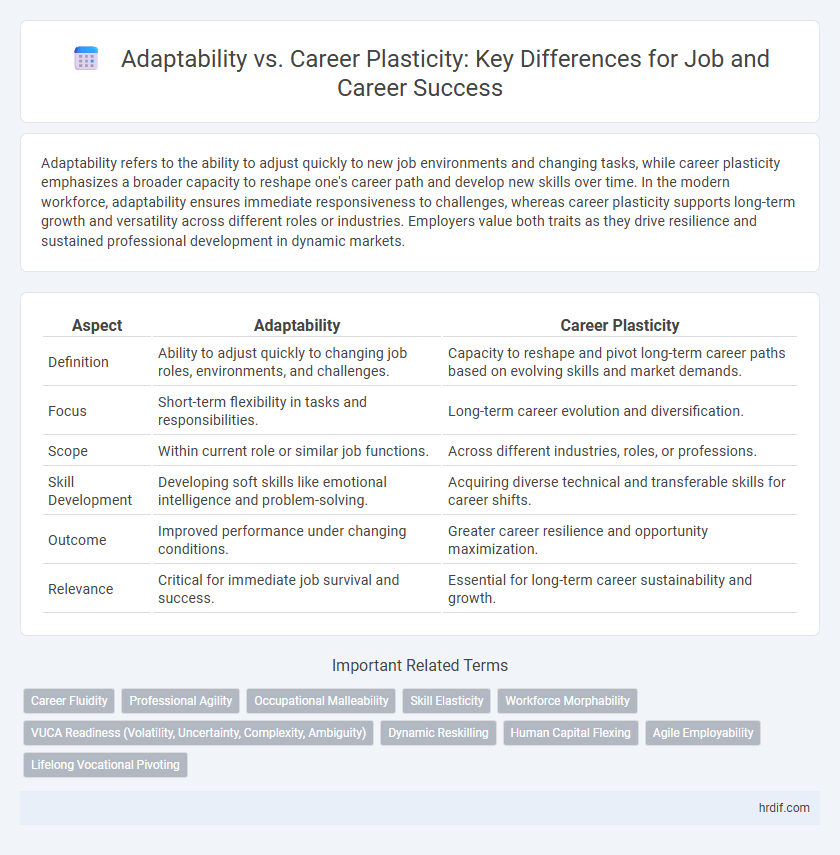
| Aspect | Adaptability | Career Plasticity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adjust quickly to changing job roles, environments, and challenges. | Capacity to reshape and pivot long-term career paths based on evolving skills and market demands. |
| Focus | Short-term flexibility in tasks and responsibilities. | Long-term career evolution and diversification. |
| Scope | Within current role or similar job functions. | Across different industries, roles, or professions. |
| Skill Development | Developing soft skills like emotional intelligence and problem-solving. | Acquiring diverse technical and transferable skills for career shifts. |
| Outcome | Improved performance under changing conditions. | Greater career resilience and opportunity maximization. |
| Relevance | Critical for immediate job survival and success. | Essential for long-term career sustainability and growth. |
Defining Adaptability and Career Plasticity
Adaptability refers to the ability to adjust effectively to new challenges, environments, or changes in the workplace, emphasizing flexibility and resilience in job roles. Career plasticity describes a broader capacity for significant career shifts, including acquiring new skills and exploring different industries or professions over time. Understanding these concepts helps individuals navigate dynamic job markets by balancing short-term adaptability with long-term career transformation potential.
Key Differences Between Adaptability and Career Plasticity
Adaptability refers to an individual's ability to adjust quickly to changing work environments and job demands, emphasizing flexibility in skills and mindset. Career plasticity involves a broader, long-term capacity to reshape career paths entirely, often requiring continuous learning and strategic shifts. Key differences lie in adaptability's short-term responsiveness contrasted with career plasticity's proactive, sustained career evolution.
The Role of Adaptability in Modern Careers
Adaptability plays a crucial role in modern careers by enabling professionals to navigate rapid technological changes and evolving industry demands effectively. Unlike career plasticity, which emphasizes structural flexibility in career pathways, adaptability focuses on an individual's capacity to learn new skills, adjust mindset, and respond proactively to workplace challenges. This dynamic skill set directly enhances employability and long-term career resilience in competitive job markets.
Career Plasticity: Shaping Professional Trajectories
Career plasticity enables professionals to reshape their trajectories by acquiring diverse skills and embracing evolving industry demands, fostering long-term employability. Unlike adaptability, which focuses on responding to immediate changes, career plasticity involves proactive transformation and strategic skill development aligned with future career opportunities. This dynamic approach empowers individuals to navigate complex job markets and capitalize on emerging trends for sustained professional growth.
Benefits of Embracing Adaptability at Work
Embracing adaptability at work enhances resilience, enabling professionals to navigate rapid industry changes and technological advancements efficiently. Unlike career plasticity, adaptability fosters continuous learning and skill development, ensuring long-term employability and relevance. Organizations benefit from adaptable employees through increased innovation, improved problem-solving, and a proactive response to evolving market demands.
Advantages of Career Plasticity in Career Progression
Career plasticity enhances career progression by enabling professionals to pivot across industries and roles, leveraging transferable skills to seize emerging opportunities. This flexibility reduces vulnerability to market fluctuations and technological disruptions, fostering long-term employability and growth. Employers increasingly value career plasticity for its demonstration of resilience, continuous learning, and ability to innovate within diverse work environments.
When to Rely on Adaptability vs Plasticity
Adaptability is essential for navigating immediate changes in job roles or workplace environments, enabling quick responses to unforeseen challenges. Career plasticity, however, emphasizes long-term career shifts and the ability to reinvent professional identity across industries or functions. Rely on adaptability for short-term problem-solving and on career plasticity when planning significant career transitions or skill set overhauls.
Building Adaptability Skills for Career Growth
Developing adaptability skills enhances career growth by enabling professionals to navigate changing job markets and evolving technology trends effectively. Unlike career plasticity, which emphasizes flexibility in career choices, adaptability focuses on adjusting behaviors and skillsets within a chosen role to meet new challenges. Cultivating resilience, continuous learning, and emotional intelligence plays a crucial role in building adaptability for sustained professional success.
Strategies to Foster Career Plasticity
Cultivating career plasticity requires proactive strategies such as continuous skill development, networking across diverse industries, and embracing interdisciplinary learning to remain agile in a rapidly evolving job market. Prioritizing adaptability through personalized career planning and leveraging emerging technologies enables professionals to pivot effectively and seize new opportunities. Building resilience by seeking feedback and modeling flexible problem-solving enhances long-term career sustainability amid shifting economic landscapes.
Choosing the Right Approach: Adaptability or Plasticity for Success
Choosing between adaptability and career plasticity depends on the job's demands and long-term goals. Adaptability focuses on adjusting skills and behaviors within a specific career path to stay relevant amid change, while career plasticity emphasizes versatility across multiple roles or industries for broader opportunities. Evaluating industry trends, personal strengths, and market stability helps determine whether honing adaptability or cultivating career plasticity will drive professional success.
Related Important Terms
Career Fluidity
Career fluidity highlights the dynamic nature of career paths, emphasizing continuous skill acquisition and the ability to pivot across industries in response to evolving job markets. Unlike traditional adaptability, which focuses on adjusting within a specific role, career fluidity embraces career plasticity by fostering a versatile professional identity that thrives amid constant change and uncertainty.
Professional Agility
Professional agility enhances career adaptability by enabling individuals to quickly adjust to evolving job requirements and market trends, fostering resilience in uncertain environments. Career plasticity complements this by supporting ongoing skill development and role flexibility, essential for long-term career sustainability and growth.
Occupational Malleability
Occupational malleability emphasizes the capacity to reshape professional skills and roles in response to evolving job market demands, distinguishing it from general adaptability by highlighting structural flexibility within careers. Career plasticity extends this concept by incorporating personal growth trajectories and mindset shifts that enable sustained relevance and progression across diverse occupational environments.
Skill Elasticity
Skill elasticity enhances adaptability by enabling professionals to flexibly apply and expand their competencies across diverse roles, outperforming rigid career plasticity models. This capacity for continuous skill transformation drives sustainable career growth and resilience in evolving job markets.
Workforce Morphability
Workforce morphability emphasizes the dynamic capacity of employees to adjust skills and roles in response to evolving job demands, surpassing traditional career plasticity by fostering continuous adaptability rather than mere role flexibility. Embracing workforce morphability enhances organizational resilience and individual career sustainability in rapidly changing markets.
VUCA Readiness (Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity, Ambiguity)
Adaptability enhances VUCA readiness by enabling professionals to quickly respond to volatility and uncertainty through flexible skill sets and mindset shifts. Career plasticity extends this by fostering continuous learning and role evolution, ensuring resilience in complex and ambiguous job markets.
Dynamic Reskilling
Dynamic reskilling emphasizes continuous skill development, enabling professionals to remain adaptable in rapidly changing job markets, whereas career plasticity reflects a broader capacity to pivot across different roles and industries. Prioritizing dynamic reskilling enhances employability by aligning up-to-date competencies with evolving employer demands, thereby driving sustained career growth.
Human Capital Flexing
Human capital flexing emphasizes the ability to rapidly acquire and apply new skills, making adaptability a key factor in career plasticity for thriving in dynamic job markets. This flexibility enables professionals to pivot roles efficiently, enhancing employability and long-term career growth.
Agile Employability
Adaptability in Agile Employability emphasizes the ability to quickly acquire new skills and navigate changing job roles, while career plasticity highlights long-term flexibility in career paths and roles. Employers value adaptability for immediate responsiveness, whereas career plasticity supports sustained employability through continuous personal and professional growth.
Lifelong Vocational Pivoting
Adaptability involves continuously updating skills and embracing change within a chosen career path, while career plasticity emphasizes the capacity to pivot across different industries or roles throughout one's working life. Lifelong vocational pivoting requires cultivating both adaptability to evolving job demands and career plasticity to navigate diverse professional landscapes effectively.
Adaptability vs Career Plasticity for job and career. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com