Simulation training offers a controlled environment where technical professionals can practice complex tasks repeatedly, enhancing hands-on skills and error management without real-world risks. Augmented reality training overlays digital information onto physical equipment, enabling immersive learning experiences that improve spatial understanding and real-time problem-solving. Both methods boost technical proficiency, but augmented reality provides interactive, context-rich scenarios that can accelerate skill acquisition in dynamic work environments.
Table of Comparison
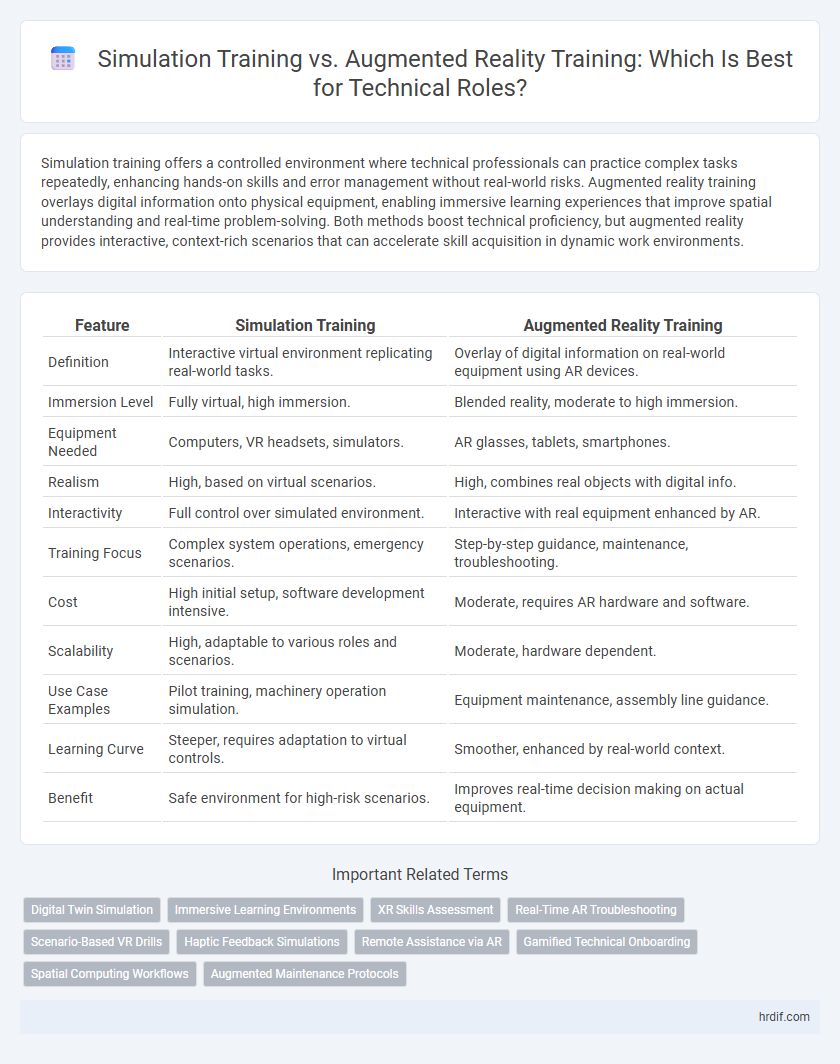
| Feature | Simulation Training | Augmented Reality Training |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interactive virtual environment replicating real-world tasks. | Overlay of digital information on real-world equipment using AR devices. |
| Immersion Level | Fully virtual, high immersion. | Blended reality, moderate to high immersion. |
| Equipment Needed | Computers, VR headsets, simulators. | AR glasses, tablets, smartphones. |
| Realism | High, based on virtual scenarios. | High, combines real objects with digital info. |
| Interactivity | Full control over simulated environment. | Interactive with real equipment enhanced by AR. |
| Training Focus | Complex system operations, emergency scenarios. | Step-by-step guidance, maintenance, troubleshooting. |
| Cost | High initial setup, software development intensive. | Moderate, requires AR hardware and software. |
| Scalability | High, adaptable to various roles and scenarios. | Moderate, hardware dependent. |
| Use Case Examples | Pilot training, machinery operation simulation. | Equipment maintenance, assembly line guidance. |
| Learning Curve | Steeper, requires adaptation to virtual controls. | Smoother, enhanced by real-world context. |
| Benefit | Safe environment for high-risk scenarios. | Improves real-time decision making on actual equipment. |
Introduction to Simulation and Augmented Reality in Technical Training
Simulation training replicates real-world technical scenarios through virtual environments, enabling hands-on practice without physical risks or equipment costs. Augmented reality training overlays digital information onto the physical workspace, enhancing technical learning by providing real-time guidance and interactive visuals. Both methods accelerate skill acquisition, with simulation emphasizing immersive replication and augmented reality focusing on contextual, on-site support.
Key Differences Between Simulation and Augmented Reality Training
Simulation training offers immersive, controlled environments replicating real-world scenarios for skill practice without real consequences. Augmented reality training overlays digital information onto the physical workspace, enhancing situational awareness and interaction with real objects. Key differences include the level of immersion, with simulation fully virtual and AR blending virtual elements with reality, and the targeted cognitive engagement through AR's real-time feedback supporting problem-solving in live settings.
Benefits of Simulation Training for Technical Roles
Simulation training offers technical professionals a risk-free environment to practice complex tasks, enhancing skill retention and decision-making under pressure. It closely replicates real-world scenarios, enabling hands-on experience with equipment and systems without downtime or safety hazards. This method accelerates learning curves and reduces training costs by minimizing errors during actual operations.
Advantages of Augmented Reality Training in the Workplace
Augmented Reality (AR) training enhances technical skill development by providing immersive, real-time visual guidance, allowing trainees to interact with virtual objects alongside physical equipment. This method improves retention and reduces error rates by simulating complex scenarios without the risks associated with live environments. AR training also accelerates onboarding processes and facilitates remote collaboration, making it a cost-effective solution for workforce development in technical roles.
Cost Comparison: Simulation vs Augmented Reality Training
Simulation training typically demands higher initial investment in hardware and software development, but offers reusable environments that reduce long-term costs. Augmented reality training involves moderate upfront expenses with flexible, scalable applications, often lowering maintenance and update costs over time. Cost efficiency depends on training frequency and complexity, with AR favored for dynamic, evolving technical roles.
Real-World Applications in Technical Job Training
Simulation training enables technical professionals to engage in highly controlled, risk-free environments that closely mimic real-world scenarios, enhancing practical skills and decision-making abilities. Augmented reality training overlays digital information onto physical equipment, allowing trainees to interact with actual tools while receiving real-time guidance, which improves spatial awareness and hands-on proficiency. Both methods accelerate competence in technical roles by bridging theoretical knowledge with realistic, immersive experiences crucial for effective job performance.
Skills Enhancement: Which Approach Is More Effective?
Simulation training offers immersive, hands-on experiences that replicate real-world technical scenarios, enhancing problem-solving and decision-making skills through repeated practice. Augmented Reality (AR) training overlays digital information onto the physical environment, promoting situational awareness and interactive learning, which accelerates skill acquisition in complex tasks. While simulations provide comprehensive environment control for skill mastery, AR training excels in contextual learning and real-time feedback, making both approaches effective for different aspects of technical skill enhancement.
User Experience: Engagement and Retention in Training Programs
Simulation training offers immersive scenarios that closely mimic real-world technical challenges, enhancing user engagement through hands-on problem-solving and immediate feedback. Augmented reality training overlays digital information onto physical equipment, improving retention by enabling interactive learning in authentic environments without risking operational downtime. Both methods boost engagement and knowledge retention, but AR provides continuous contextual learning, making it especially effective for complex technical roles requiring spatial awareness and real-time decision-making.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Simulation training for technical roles often faces implementation challenges such as high initial costs, complex setup requirements, and limited scenario scalability. Augmented reality training addresses these issues by offering interactive, real-time overlays that reduce hardware dependency and allow flexible content updates, but it requires robust software integration and user adaptability. Solutions involve leveraging cloud-based platforms for scalable deployment, investing in user-centric design to ease adoption, and continuous system optimization to enhance training efficacy and technical accessibility.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Technical Role Training
Simulation training for technical roles leverages immersive virtual environments to replicate real-world scenarios, enhancing hands-on skills without physical risks. Augmented reality (AR) training overlays digital information onto the physical workspace, enabling real-time guidance and interactive learning that improves task accuracy and efficiency. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach combining simulation's comprehensive scenario replication with AR's contextual support, driving more adaptive, scalable, and personalized training solutions in technical fields.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin Simulation
Digital Twin Simulation offers an advanced platform for technical roles by creating precise, real-time digital replicas of physical systems, enhancing the effectiveness of simulation training through realistic scenario replication and data-driven feedback. Augmented Reality Training complements this by overlaying digital information onto the physical environment, but Digital Twin Simulation provides deeper system insights and predictive analytics crucial for complex technical skill development.
Immersive Learning Environments
Simulation training offers highly controlled, realistic scenarios for technical roles, enabling repetitive practice and skill refinement without real-world risks. Augmented reality training enhances immersive learning environments by overlaying digital information onto physical equipment, improving situational awareness and hands-on experience in live settings.
XR Skills Assessment
Simulation training offers immersive, controlled environments ideal for replicating complex technical scenarios, enhancing decision-making and procedural skills. Augmented reality training integrates real-world contexts with digital overlays, providing dynamic XR skills assessment that evaluates performance accuracy and situational awareness in real time.
Real-Time AR Troubleshooting
Simulation training provides controlled, risk-free environments for technical skill development, while augmented reality (AR) training enhances real-time troubleshooting by overlaying interactive digital information directly onto physical equipment. Real-time AR troubleshooting accelerates problem-solving efficiency, reduces downtime, and improves hands-on learning retention for complex technical roles.
Scenario-Based VR Drills
Scenario-based VR drills in simulation training offer immersive, hands-on experiences that replicate real-world technical tasks with high fidelity, enhancing skill acquisition and decision-making under pressure. Augmented reality training overlays digital information onto physical environments, providing contextual guidance but often lacks the fully immersive engagement critical for mastering complex procedural scenarios.
Haptic Feedback Simulations
Haptic feedback simulations enhance both simulation training and augmented reality training for technical roles by providing realistic tactile sensations that improve skill acquisition and muscle memory retention. These advanced haptic systems allow trainees to interact with virtual components as if they were real, resulting in more effective hands-on practice and increased technical proficiency.
Remote Assistance via AR
Simulation training offers immersive, controlled environments for technical skill development, while augmented reality training enhances remote assistance by overlaying real-time guidance and diagnostics directly onto equipment, increasing efficiency and reducing downtime. Remote AR assistance enables experts to provide immediate, context-aware support to field technicians, minimizing errors and accelerating problem resolution in complex technical roles.
Gamified Technical Onboarding
Gamified technical onboarding leverages simulation training to replicate real-world scenarios, enhancing skill acquisition through immersive, task-specific challenges that improve retention and practical application. Augmented reality training integrates interactive, contextual digital overlays with physical environments, accelerating hands-on learning and spatial understanding critical for complex technical roles.
Spatial Computing Workflows
Simulation training offers immersive, controlled environments ideal for practicing complex spatial computing workflows in technical roles, enhancing precision and task familiarity. Augmented reality training overlays digital information onto real-world settings, enabling interactive, context-rich learning experiences that improve spatial awareness and real-time problem-solving skills.
Augmented Maintenance Protocols
Augmented Reality (AR) training enhances technical roles by overlaying interactive maintenance protocols directly onto equipment, improving accuracy and reducing training time compared to traditional simulation methods. This immersive approach accelerates skill acquisition and minimizes errors during complex maintenance tasks by providing real-time guidance within the actual work environment.
Simulation Training vs Augmented Reality Training for technical roles. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com