Specialists deepen expertise in a single field, allowing for mastery and recognition within a specific niche. Portfolio careerists diversify their skills across multiple areas, creating flexibility and adaptability in dynamic job markets. Choosing between specialization and portfolio careers depends on personal goals and industry demands, balancing depth versus breadth of knowledge.
Table of Comparison
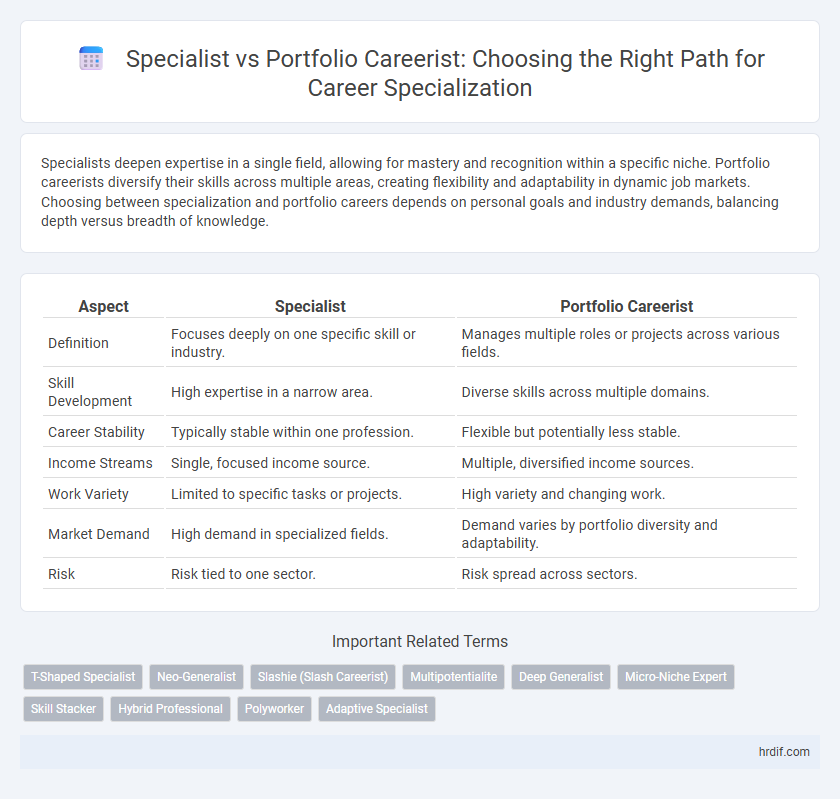
| Aspect | Specialist | Portfolio Careerist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses deeply on one specific skill or industry. | Manages multiple roles or projects across various fields. |
| Skill Development | High expertise in a narrow area. | Diverse skills across multiple domains. |
| Career Stability | Typically stable within one profession. | Flexible but potentially less stable. |
| Income Streams | Single, focused income source. | Multiple, diversified income sources. |
| Work Variety | Limited to specific tasks or projects. | High variety and changing work. |
| Market Demand | High demand in specialized fields. | Demand varies by portfolio diversity and adaptability. |
| Risk | Risk tied to one sector. | Risk spread across sectors. |
Defining Specialists and Portfolio Careerists
Specialists possess deep expertise and focus narrowly on a specific domain, developing advanced skills and knowledge that create high value in their field. Portfolio careerists pursue multiple roles or projects across various industries, leveraging diverse skills without concentrating on a single specialization. The distinction lies in specialists building mastery and authority in one area, while portfolio careerists emphasize adaptability and breadth over singular expertise.
Key Differences Between Specialists and Portfolio Careerists
Specialists develop deep expertise in a specific field, focusing on mastering one area to deliver high-value, niche skills sought by employers or clients. Portfolio careerists diversify their skills across multiple domains, creating a flexible career path that adapts to market changes and broadens professional opportunities. Key differences include the depth versus breadth of skills, risk management through specialization or diversification, and the career stability associated with focused expertise compared to the adaptability prioritized by portfolio careerists.
Advantages of Specializing in a Single Field
Specializing in a single field enhances deep expertise, making specialists highly valuable in niche markets and complex problem-solving scenarios. This focused career path often leads to higher earning potential and stronger professional reputation due to recognized mastery. Employers and clients consistently seek specialists for their proven ability to deliver expert-level solutions efficiently.
The Benefits of Building a Portfolio Career
Building a portfolio career offers unparalleled flexibility by allowing professionals to diversify their skill sets across multiple industries, reducing dependency on a single employer. Portfolio careerists can rapidly adapt to evolving job markets and leverage varied experiences to enhance creativity and innovation. This multi-disciplinary approach not only broadens income streams but also fosters resilience in dynamic economic conditions.
Ideal Profiles: Who Should Specialize vs. Diversify?
Specialists excel in roles requiring deep expertise, ideal for industries like medicine, law, or engineering where precise knowledge drives success. Portfolio careerists thrive in dynamic environments, leveraging diverse skills across multiple fields to adapt and innovate, suitable for freelance creators, consultants, and entrepreneurs. Individuals should specialize when industry demands technical mastery, while diversification suits those seeking flexibility and broad market opportunities.
Career Growth: Specialist vs. Portfolio Approaches
Specialists deepen expertise in a focused domain, accelerating career growth through advanced skills and industry recognition within a niche. Portfolio careerists build diverse skills across multiple roles, enhancing adaptability and long-term career resilience in dynamic job markets. Career advancement for specialists often hinges on mastery and reputation, while portfolio careerists leverage versatility and broad networks for opportunities.
Market Demand for Specialists and Portfolio Careerists
Specialists often enjoy higher market demand in industries requiring deep expertise and advanced technical skills, such as healthcare, engineering, and finance, where precision and mastery are critical. Portfolio Careerists attract market demand in dynamic sectors like creative industries, consulting, and technology startups, where versatility, adaptability, and multidisciplinary skills drive innovation and project-based work. Employers prioritize specialists for roles with defined, high-complexity tasks, while portfolio careerists meet the need for flexible problem-solving across diverse projects.
Navigating Job Security in Both Career Paths
Specialists build deep expertise in a specific field, enhancing job security through recognized mastery and demand for niche skills, while portfolio careerists mitigate risk by diversifying roles across industries, creating resilience against market fluctuations. Specialists benefit from strong reputations and higher earning potential in stable sectors, whereas portfolio careerists rely on adaptability and broad networks to secure continuous work. Navigating job security in these paths requires balancing focused depth with versatile experience tailored to evolving labor market demands.
Earning Potential: Specialized Roles vs. Portfolio Careers
Specialists often command higher earning potential in niche markets due to their deep expertise and demand for advanced skills, particularly in fields like medicine, law, and technology. Portfolio careerists diversify income streams by leveraging multiple competencies across varied roles, which can create financial stability but may limit peak salary growth in any single specialization. Employers frequently value specialists for roles requiring expert knowledge, while portfolio careerists excel in dynamic environments needing adaptability and broad skill sets.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right specialization path depends on individual goals, industry demands, and skill adaptability. Specialists excel by developing deep expertise in a specific field, ensuring high value in niche markets, while portfolio careerists build diverse skills across multiple disciplines, enhancing flexibility and resilience in dynamic job markets. Evaluating factors such as long-term career stability, passion for focused knowledge, and openness to varied experiences helps determine the optimal approach for professional growth.
Related Important Terms
T-Shaped Specialist
A T-shaped specialist combines deep expertise in a specific domain with broad skills across multiple disciplines, enabling effective collaboration and adaptability within diverse teams. Unlike traditional specialists who focus narrowly or portfolio careerists who diversify widely, T-shaped professionals balance specialization with versatility to enhance innovation and career resilience.
Neo-Generalist
Specialists develop deep expertise in a singular domain, optimizing skills for niche roles, whereas portfolio careerists thrive by combining diverse experiences across multiple fields. Neo-Generalists integrate specialized knowledge with broad adaptability, creating versatile skill sets that bridge specialization and generalization, driving innovation and multi-disciplinary collaboration.
Slashie (Slash Careerist)
Specialists develop deep expertise in a single field, enhancing their value through concentrated skills and knowledge, while Slash Careerists (Portfolio Careerists) embrace multiple roles, integrating diverse skills across various professions to create a dynamic, flexible career path. Slashies leverage specialization in several domains simultaneously, cultivating adaptability and innovation by combining distinct expertise into a unified professional identity.
Multipotentialite
Specialists develop deep expertise in a singular domain, maximizing proficiency and market value within that field, whereas portfolio careerists embrace a multipotentialite approach by diversifying skills across multiple disciplines to adapt to evolving industry demands. Multipotentialites harness interdisciplinary knowledge and flexibility, often excelling in dynamic roles that require broad competencies and continuous learning.
Deep Generalist
Specialists develop deep expertise in a single domain, enhancing technical mastery and industry-specific knowledge, while portfolio careerists cultivate a Deep Generalist approach by acquiring diverse skills across multiple fields, enabling adaptability and interdisciplinary problem-solving. This Deep Generalist specialization combines breadth and depth, fostering innovation and strategic thinking in complex, evolving professional landscapes.
Micro-Niche Expert
A Micro-Niche Expert specializes deeply in a highly specific area, offering unparalleled knowledge and skills that set them apart in their field. In contrast, a Portfolio Careerist diversifies across multiple roles or industries, prioritizing breadth over specialization, which may limit their depth in a single micro-niche.
Skill Stacker
Specialists deepen expertise in a single domain, becoming highly skilled in niche areas, while portfolio careerists focus on Skill Stacking by integrating diverse competencies across multiple fields to enhance adaptability and innovation. Skill Stackers leverage complementary skills, driving career flexibility and unique value creation beyond traditional specialization.
Hybrid Professional
A Hybrid Professional balances deep specialization with diverse skill sets, integrating expertise from multiple fields to enhance adaptability and innovation. Unlike pure Specialists who focus narrowly and Portfolio Careerists who pursue varied roles independently, Hybrid Professionals strategically combine specialization and breadth to maximize career resilience and market value.
Polyworker
Specialists develop deep expertise in a singular domain, while portfolio careerists, such as polyworkers, cultivate diversified skills across multiple fields to adapt and innovate. Polyworkers leverage specialization within varied areas, enabling flexible career paths that combine depth with breadth for increased professional resilience.
Adaptive Specialist
Adaptive specialists combine deep expertise with versatility, allowing them to pivot across industries while maintaining a strong core skill set. Their balanced approach merges specialization with portfolio career strategies, maximizing market relevance and career resilience.
Specialist vs Portfolio Careerist for specialization Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com