Expert specialization allows professionals to develop deep knowledge and advanced skills in a specific area, leading to higher quality output and recognition as a subject matter authority. Slash workers juggle multiple roles or skills but often lack the focused mastery that defines true expertise, which can limit career growth and effectiveness in specialized tasks. Prioritizing expert specialization enhances proficiency, increases job satisfaction, and creates more valuable opportunities within niche markets.
Table of Comparison
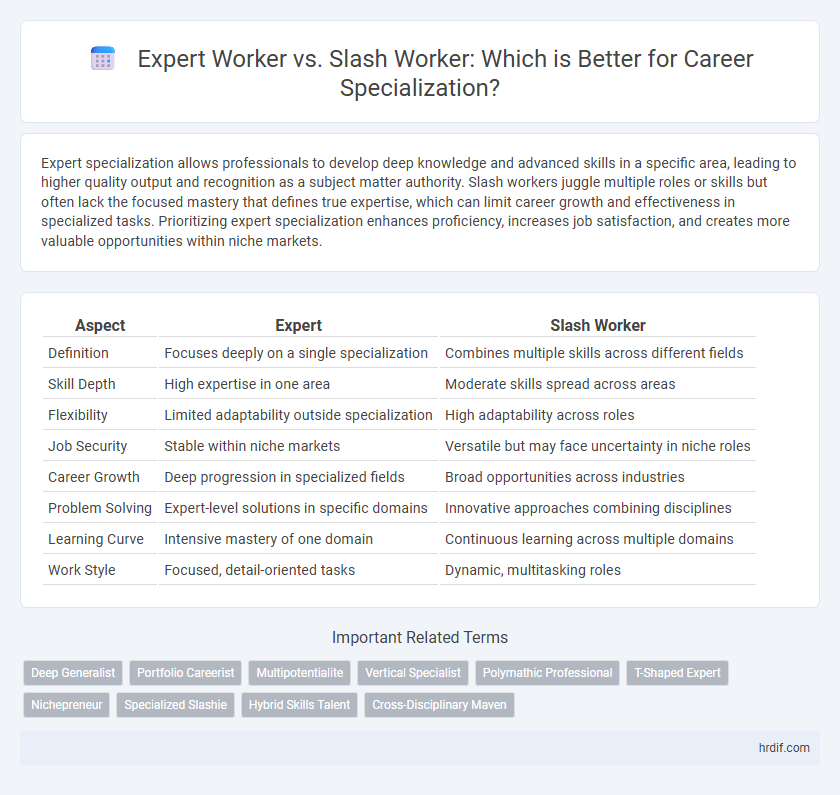
| Aspect | Expert | Slash Worker |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses deeply on a single specialization | Combines multiple skills across different fields |
| Skill Depth | High expertise in one area | Moderate skills spread across areas |
| Flexibility | Limited adaptability outside specialization | High adaptability across roles |
| Job Security | Stable within niche markets | Versatile but may face uncertainty in niche roles |
| Career Growth | Deep progression in specialized fields | Broad opportunities across industries |
| Problem Solving | Expert-level solutions in specific domains | Innovative approaches combining disciplines |
| Learning Curve | Intensive mastery of one domain | Continuous learning across multiple domains |
| Work Style | Focused, detail-oriented tasks | Dynamic, multitasking roles |
Understanding Specialization: Experts vs Slash Workers
Understanding specialization requires recognizing the core differences between experts and slash workers. Experts dedicate themselves to mastering a single domain, achieving deep knowledge and high proficiency, while slash workers diversify their skills across multiple fields, enhancing flexibility and adaptability. This distinction impacts career development, with experts excelling in niche roles and slash workers thriving in dynamic, interdisciplinary environments.
Defining the Expert: Deep Niche Mastery
An expert possesses deep niche mastery, demonstrating extensive knowledge and skills within a narrowly defined field that distinguishes them from generalists. Their specialized expertise enables precision problem-solving and innovation tailored to complex domain-specific challenges. This level of proficiency commands high trust and value in industries demanding authoritative insights and advanced technical capabilities.
The Rise of the Slash Worker: Juggling Multiple Roles
The rise of the slash worker reflects a shift toward embracing multiple professional identities, such as designer/writer or developer/consultant, instead of pursuing deep expertise in a single specialization. This diversification enables adaptability and broad skill sets, catering to the gig economy's demand for versatile talent across various industries. Organizations increasingly value slash workers for their ability to integrate cross-functional knowledge, driving innovation and dynamic problem-solving.
Advantages of Expert Specialization in the Workforce
Expert specialization in the workforce drives deep knowledge and mastery in a specific field, leading to higher quality outputs and innovative solutions. This focused expertise enhances problem-solving efficiency and positions professionals as industry leaders, increasing their market value and career growth opportunities. Organizations benefit from expert specialists through improved productivity and the ability to tackle complex tasks that require advanced skills.
Benefits of the Slash Worker Model for Career Flexibility
The Slash Worker model offers increased career flexibility by allowing professionals to combine multiple skill sets and revenue streams under one personal brand. This approach mitigates the risks associated with market fluctuations in a single industry and enhances adaptability in a rapidly evolving job market. Slash Workers benefit from diverse experiences that foster continuous learning and expanded professional networks, promoting long-term career resilience.
Drawbacks of Hyper-Specialization
Hyper-specialization often limits adaptability as expert workers focus narrowly on specific skills, reducing their ability to handle diverse tasks or pivot in changing environments. Slash workers, by contrast, mitigate this risk by combining multiple skill sets, enhancing flexibility but potentially compromising deep expertise. The drawback of hyper-specialization lies in the vulnerability to industry shifts, where narrowly specialized experts may face obsolescence or decreased demand.
Challenges Facing Slash Workers in Job Markets
Slash workers, juggling multiple professional roles, face challenges such as fragmented career progression, inconsistent income streams, and limited access to traditional benefits like health insurance or retirement plans. The demand for diverse skill sets often leads to difficulties in establishing a clear professional identity, making it harder for employers to assess their expertise compared to specialized experts. Market volatility and the need for constant upskilling contribute to job insecurity, while networking opportunities remain scattered across different industries.
Which is More Future-Proof: Expert or Slash Worker?
Experts possess deep, specialized knowledge in one domain, often commanding high value in industries requiring advanced skills and complex problem-solving. Slash workers, combining multiple complementary skills (e.g., designer/writer/marketer), offer versatility and adaptability amid rapidly changing job markets driven by technological innovation. The future-proof advantage leans toward slash workers as automation and AI disrupt specialized roles, increasing demand for multifaceted professionals who can pivot across tasks and industries.
Building a Career Path: Choosing Your Specialization Strategy
Experts build deep knowledge in a single domain, enhancing credibility and demand for highly specialized roles. Slash workers diversify skills across multiple fields, increasing flexibility and opening broader career opportunities in interdisciplinary markets. Selecting a specialization strategy depends on market trends, personal strengths, and long-term career goals to optimize growth and job security.
Adapting to Change: Balancing Expertise and Versatility
Expert professionals possess deep knowledge in a singular domain, enabling precise problem-solving and innovation within their specialization. Slash workers combine multiple skills across different fields, enhancing adaptability and versatility in dynamic environments where roles frequently shift. Balancing deep expertise with cross-disciplinary abilities allows organizations and individuals to effectively respond to change while maintaining high performance.
Related Important Terms
Deep Generalist
Deep generalists combine expert-level skills across multiple domains, enabling them to solve complex problems that require interdisciplinary knowledge. Unlike experts who focus narrowly and slash workers who juggle unrelated roles, deep generalists achieve specialization by integrating broad expertise with profound depth in key areas.
Portfolio Careerist
A portfolio careerist blends expert depth with slash worker versatility, cultivating multiple specialized skills across diverse fields to adapt to evolving market demands. This hybrid approach maximizes professional resilience and innovation by balancing focused expertise with varied competencies.
Multipotentialite
Multipotentialites thrive by blending expert knowledge with diverse skills, allowing them to innovate and adapt across fields rather than confining themselves to narrow specialization like expert workers. Slash workers embody this flexibility, combining multiple career identities to leverage cross-disciplinary expertise while maintaining depth in select areas.
Vertical Specialist
Vertical specialists possess deep expertise within a specific industry or domain, enabling them to deliver highly targeted solutions and insights. Unlike slash workers who balance multiple roles across different fields, vertical specialists prioritize in-depth knowledge and skills within a single vertical, enhancing their value through specialization and industry-specific problem-solving.
Polymathic Professional
Expert professionals deepen their skills in a single domain, while slash workers develop competence across multiple fields, embodying the polymathic professional who leverages diverse expertise to innovate and adapt in dynamic industries. This polymathic approach enables slash workers to integrate cross-disciplinary knowledge, fostering creative problem-solving and enhancing career resilience in rapidly evolving job markets.
T-Shaped Expert
T-shaped experts combine deep knowledge in a specific domain with broad skills across multiple disciplines, enabling flexibility and collaboration in complex projects. Unlike slash workers who juggle unrelated roles, T-shaped professionals leverage their specialization while adapting to diverse challenges, enhancing innovation and effectiveness within teams.
Nichepreneur
Nichepreneurs benefit from adopting a slash worker approach by diversifying skills across multiple specialties, allowing flexibility and innovation within niche markets. Expert specialization offers depth and authority, but combining expertise fosters unique value propositions and resilience in competitive environments.
Specialized Slashie
A Specialized Slashie combines deep expertise in a primary field with proficient skills in complementary areas, enhancing adaptability and market value beyond a singular specialization. This blend fosters innovation and problem-solving by integrating diverse knowledge while maintaining focused proficiency.
Hybrid Skills Talent
Experts possess deep knowledge in a single domain, delivering high-value, specialized solutions, while slash workers leverage hybrid skills across multiple fields, enhancing adaptability and innovation. Hybrid skills talent merges expert proficiency with diverse competencies, driving cross-functional collaboration and fostering competitive advantage in dynamic industries.
Cross-Disciplinary Maven
Cross-disciplinary mavens blend deep specialization with versatile skills, outperforming pure experts by integrating diverse knowledge areas to solve complex problems creatively and efficiently. Unlike slash workers who juggle multiple unrelated roles, these professionals leverage interconnected expertise to drive innovation and strategic advantage.
Expert vs Slash Worker for specialization Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com