Education provides a comprehensive foundation of knowledge and skills that employers often require for job qualification, establishing credibility through formal degrees and certifications. Microcredential badges offer targeted, specific skill validation that complements traditional education by demonstrating practical expertise in niche areas. Combining both enhances employability by showcasing a solid educational background alongside proof of current, relevant competencies.
Table of Comparison
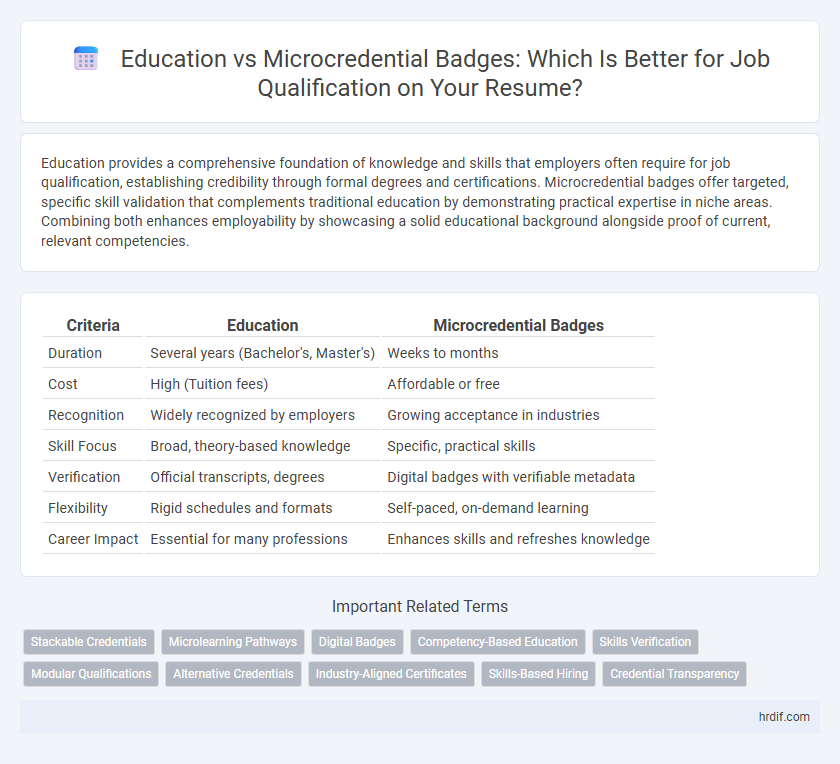
| Criteria | Education | Microcredential Badges |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Several years (Bachelor's, Master's) | Weeks to months |
| Cost | High (Tuition fees) | Affordable or free |
| Recognition | Widely recognized by employers | Growing acceptance in industries |
| Skill Focus | Broad, theory-based knowledge | Specific, practical skills |
| Verification | Official transcripts, degrees | Digital badges with verifiable metadata |
| Flexibility | Rigid schedules and formats | Self-paced, on-demand learning |
| Career Impact | Essential for many professions | Enhances skills and refreshes knowledge |
Understanding Traditional Education in the Job Market
Traditional education remains a cornerstone in the job market by providing comprehensive knowledge, critical thinking skills, and recognized degrees from accredited institutions. Employers often prioritize formal degrees as benchmarks for candidate qualification, ensuring a standardized evaluation of expertise and commitment. While microcredential badges offer targeted skills training, traditional education delivers foundational competencies essential for long-term career growth and adaptability.
What Are Microcredential Badges?
Microcredential badges are digital certifications that validate specific skills or knowledge acquired through short, focused learning experiences, offering a flexible alternative to traditional degrees. These badges are often issued by educational institutions, professional organizations, or online platforms, enhancing a candidate's resume by showcasing targeted competencies relevant to job qualifications. Employers increasingly recognize microcredential badges as evidence of practical expertise and commitment to continuous learning within specific industries or roles.
Comparing Education and Microcredentials: Key Differences
Traditional education offers comprehensive knowledge through degrees, emphasizing theoretical foundations and long-term academic development. Microcredential badges focus on specific skills or competencies, validated by industry-recognized assessments that highlight practical expertise and immediate job relevance. Employers increasingly value microcredentials for their flexibility, targeted learning outcomes, and ability to demonstrate up-to-date proficiencies compared to conventional education.
Employer Perspectives: Degrees vs Badges
Employers often view traditional degrees as a reliable benchmark of comprehensive knowledge and critical thinking skills, while microcredential badges showcase specific, targeted competencies relevant to evolving industry needs. Degree programs typically signify long-term commitment and theoretical depth, whereas badges highlight adaptability and continuous learning in specialized areas. Hiring managers increasingly value a combination of both, using degrees for foundational qualifications and badges to identify candidates with up-to-date technical skills and practical expertise.
Cost and Time Investment: Degrees vs Microcredentials
Traditional degrees often require several years and significant financial investment, with average undergraduate tuition in the U.S. exceeding $35,000 annually and total completion time ranging from 3 to 4 years. Microcredential badges offer a cost-effective alternative, typically costing between $200 to $2,000 and can be earned in weeks or months, providing faster skill validation. Employers increasingly recognize microcredentials for specific competencies, making them a practical choice for professionals seeking rapid upskilling without the extensive time and expense of full degrees.
Flexibility and Accessibility of Microcredentials
Microcredential badges offer greater flexibility and accessibility compared to traditional education, allowing professionals to acquire targeted skills quickly and adapt to evolving job market demands. These credentials are often more affordable, can be earned online, and provide immediate proof of competency recognized by employers. Microcredentials enable continuous learning pathways without the time and cost commitments associated with conventional degrees.
Industry Recognition and Credibility
Industry recognition for traditional education is well-established, with degrees from accredited institutions often serving as standardized credentials. Microcredential badges, however, offer targeted skill validation and are increasingly recognized by employers for specific competencies, enhancing job qualification relevance. Credibility of microcredentials depends heavily on the issuing organization's reputation and alignment with industry standards, making them complementary rather than a full substitute for formal education.
Enhancing a Resume with Microcredential Badges
Microcredential badges demonstrate specialized skills and practical knowledge, providing targeted validation that can complement traditional education on a resume. Employers increasingly value these verified credentials as evidence of continuous learning and adaptability in specific fields or technologies. Integrating microcredential badges enhances a resume's appeal by showcasing up-to-date competencies aligned with industry demands.
Case Studies: Hiring Trends and Qualification Preferences
Case studies reveal a shifting hiring trend where employers increasingly value microcredential badges for their specificity and relevance to current job requirements, often favoring them over traditional degrees in tech and digital sectors. Data from leading HR platforms indicate a 37% rise in job postings requiring or preferring microcredentials within the past three years, emphasizing skills verification and rapid upskilling. Employers report that candidates with targeted microcredentials demonstrate practical expertise and adaptability, which enhances job performance and shortens onboarding periods compared to conventional educational backgrounds.
Future Outlook: Evolving Job Qualifications
Future job qualifications increasingly emphasize microcredential badges alongside traditional education, reflecting a shift toward skills-based hiring. Employers value these digital credentials for their ability to verify specific competencies rapidly and adapt to evolving industry demands. The integration of microcredentials with formal degrees is expected to redefine professional qualifications, offering a more dynamic and personalized pathway for career advancement.
Related Important Terms
Stackable Credentials
Stackable credentials, including microcredential badges, offer targeted skill verification that complements traditional education by enabling professionals to demonstrate industry-relevant competencies quickly. Unlike conventional degrees, these modular qualifications enhance job readiness and adaptability in dynamic labor markets by providing focused, scalable learning pathways.
Microlearning Pathways
Microcredential badges, validated through microlearning pathways, offer precise skills verification that aligns closely with evolving industry demands, enhancing job qualification beyond traditional education credentials. These targeted learning modules enable rapid upskilling and demonstrate competency in specific areas, providing employers with tangible evidence of candidates' practical expertise.
Digital Badges
Digital badges offer verifiable, skills-based microcredentials that complement traditional education by providing employers with clear evidence of specific competencies, often updated more rapidly than formal degrees. These credentials enhance job qualification by demonstrating practical expertise and continuous learning in targeted digital skills, bridging gaps in formal education for a competitive workforce.
Competency-Based Education
Competency-Based Education emphasizes mastery of skills and real-world application, making microcredential badges a valuable complement to traditional degrees by providing verifiable, industry-relevant competencies. Employers increasingly recognize microcredentials for demonstrating specific job qualifications and practical expertise that align closely with workforce demands.
Skills Verification
Microcredential badges provide targeted skills verification that complements traditional education by offering real-time evidence of specific competencies sought by employers. This skills validation enhances job qualification by demonstrating practical, up-to-date expertise beyond formal degrees.
Modular Qualifications
Modular qualifications through microcredential badges offer targeted skill validation that aligns closely with evolving industry demands, providing employers with precise evidence of job-relevant competencies beyond traditional degree programs. This approach enhances workforce adaptability by enabling candidates to showcase specialized expertise in specific areas, streamlining talent acquisition and professional development processes.
Alternative Credentials
Alternative credentials such as microcredential badges offer targeted skill validation and industry-relevant expertise that often complement or surpass traditional education credentials in demonstrating job readiness. Employers increasingly recognize these digital badges for their specificity, flexibility, and ability to showcase continuous learning and practical capabilities.
Industry-Aligned Certificates
Industry-aligned certificates, such as microcredential badges, offer targeted skills recognized by employers and bridge the gap between traditional education and practical job qualifications. These badges provide verifiable proof of competencies tailored to specific industries, enhancing employability by validating up-to-date expertise beyond conventional degree programs.
Skills-Based Hiring
Employers increasingly prioritize skills-based hiring, valuing microcredential badges for their ability to demonstrate specific, up-to-date competencies relevant to job performance, unlike traditional education which often emphasizes broad, theoretical knowledge. Microcredentials provide verifiable, targeted skill validation that aligns directly with industry needs, accelerating candidate qualification and improving workforce adaptability.
Credential Transparency
Credential transparency enhances job qualification clarity by distinctly differentiating traditional education degrees from microcredential badges, allowing employers to better assess specific skills and competencies. Microcredential badges offer targeted expertise and verifiable skill mastery, complementing broader educational frameworks and improving the precision of candidate evaluation.
Education vs Microcredential Badges for job qualification. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com