Reference testimony provides direct insights from individuals who have previously worked with the candidate, offering detailed evaluations of their skills, work ethic, and reliability. Peer testimony often reflects the candidate's ability to collaborate and integrate within a team, highlighting interpersonal skills and day-to-day performance. Combining both types of testimony can create a comprehensive understanding of a candidate's qualifications and workplace behavior for informed hiring decisions.
Table of Comparison
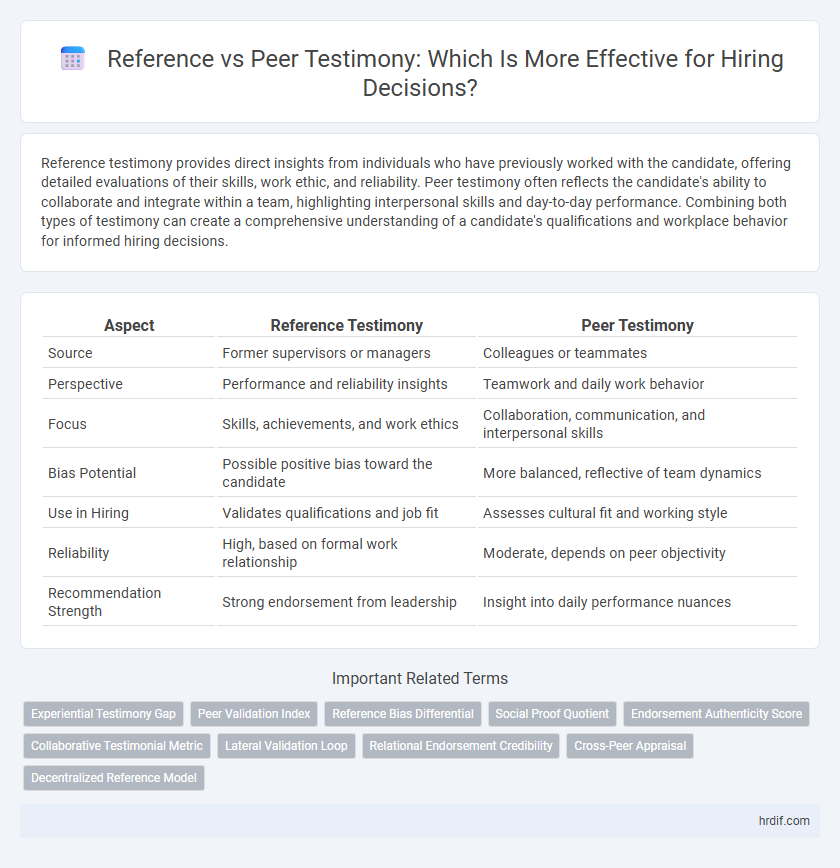
| Aspect | Reference Testimony | Peer Testimony |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Former supervisors or managers | Colleagues or teammates |
| Perspective | Performance and reliability insights | Teamwork and daily work behavior |
| Focus | Skills, achievements, and work ethics | Collaboration, communication, and interpersonal skills |
| Bias Potential | Possible positive bias toward the candidate | More balanced, reflective of team dynamics |
| Use in Hiring | Validates qualifications and job fit | Assesses cultural fit and working style |
| Reliability | High, based on formal work relationship | Moderate, depends on peer objectivity |
| Recommendation Strength | Strong endorsement from leadership | Insight into daily performance nuances |
Understanding Reference and Peer Testimony
Reference and peer testimony serve distinct roles in hiring decisions, with references typically providing formal assessments of a candidate's past work performance from supervisors or managers, while peer testimony offers insights into collaborative skills and team dynamics from colleagues. Understanding the difference is crucial as references often emphasize reliability and competence, whereas peer testimonies highlight interpersonal abilities and cultural fit within the organization. Employers benefit from integrating both types of feedback to form a comprehensive evaluation of a candidate's qualifications and suitability for the role.
Key Differences Between Reference and Peer Testimony
Reference and peer testimony serve distinct roles in the hiring process, with references typically providing formal assessments from previous supervisors or professional contacts, while peer testimonies offer insights from colleagues working alongside the candidate. References focus on verifying qualifications, work ethics, and overall job performance, whereas peer testimonies emphasize interpersonal skills, teamwork, and day-to-day interactions. Understanding these key differences enhances hiring accuracy by combining formal evaluation with peer-level perceptions.
Importance of References in the Hiring Process
References provide verified insights into a candidate's past performance, work ethic, and interpersonal skills that peer testimonies may lack due to limited objectivity. Hiring managers rely on references from former supervisors or professional contacts to corroborate resume claims and assess cultural fit within the organization. The credibility and depth of information found in references significantly influence the accuracy of hiring decisions and reduce hiring risks.
How Peer Testimony Adds Value in Recruitment
Peer testimony enhances recruitment by providing authentic insights into a candidate's work ethic, teamwork, and problem-solving skills that formal references may overlook. It offers real-time, situational feedback from colleagues who have directly collaborated with the candidate, increasing the reliability of the assessment. Incorporating peer perspectives enables employers to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the candidate's potential cultural fit and day-to-day performance within the team.
Reliability: Reference vs Peer Testimony
Reference checks provide structured insights from previous employers, offering reliable evaluations based on documented performance and professional behavior, which enhances hiring accuracy. Peer testimony can capture real-time collaboration and interpersonal skills but may introduce bias due to personal relationships or limited perspective. Combining both approaches improves overall reliability by balancing verified records with current team dynamics.
When to Use Reference Over Peer Testimony
Reference is more reliable than peer testimony when verifying employment history and job performance due to its formal and documented nature. Employers should prioritize references during the initial hiring stages for objective validation of qualifications and work ethic. Peer testimony is better suited for assessing team dynamics and interpersonal skills but lacks the structured credibility of a formal reference.
Advantages of Peer Testimony in Modern Hiring
Peer testimony offers direct insights into a candidate's teamwork, communication, and problem-solving skills, providing a more comprehensive evaluation than traditional references. Modern hiring benefits from peer feedback by capturing real-time experiences and workplace behavior, resulting in better cultural fit and performance predictions. This approach enhances decision-making through nuanced perspectives that often go beyond the formal scope of reference letters.
Challenges With Reference and Peer Testimony
Challenges with reference and peer testimony in hiring processes include potential bias, lack of standardized evaluation criteria, and variability in the accuracy of the information provided. References may present overly positive assessments due to personal relationships, while peer testimonies can be influenced by workplace politics or limited interaction scope. These issues complicate the reliability of assessments and may lead to inconsistent hiring decisions.
Best Practices for Gathering Testimonials and References
Gathering effective testimonials and references involves targeting direct supervisors and colleagues familiar with the candidate's job performance to ensure credible insights. Prioritize specific examples of skills, accomplishments, and workplace behavior rather than generic praise for a more accurate assessment. Verifying details through multiple sources and structured questioning optimizes the reliability of references compared to broader peer testimonies.
Enhancing Hiring Decisions: Combining Reference and Peer Testimony
Combining reference and peer testimony significantly enhances hiring decisions by providing a comprehensive view of a candidate's skills, work ethic, and team dynamics. References offer verified insights from previous employers or supervisors, while peer testimony delivers firsthand observations from colleagues familiar with the candidate's daily performance and collaboration abilities. Integrating both sources reduces hiring risks and promotes selecting candidates with proven success in similar work environments.
Related Important Terms
Experiential Testimony Gap
References often provide limited insight due to the experiential testimony gap, where firsthand knowledge of a candidate's daily work performance is missing. Peer testimony, by contrast, offers direct observations that bridge this gap, enabling more accurate evaluations of skills and workplace behavior.
Peer Validation Index
The Peer Validation Index quantifies the reliability of peer testimony by measuring consistency and credibility across multiple references, enhancing the accuracy of hiring decisions compared to traditional reference checks. Utilizing Peer Validation Index data reduces biases and provides a comprehensive understanding of a candidate's skills and workplace behavior from actual team members.
Reference Bias Differential
Reference bias differential significantly affects hiring outcomes by skewing the perception of candidates due to varied evaluator perspectives and relationship contexts. Reference evaluations often show more leniency and positive skew compared to peer testimonies, leading to less reliable assessments of performance and potential.
Social Proof Quotient
References provide a structured evaluation of a candidate's past performance and reliability, offering verifiable insights, while peer testimony enhances the Social Proof Quotient by reflecting real-time social validation and teamwork dynamics within a professional community. Hiring decisions benefit from integrating both sources to balance objective credentials with social endorsement, thereby optimizing candidate assessment accuracy.
Endorsement Authenticity Score
Reference checks often provide a more reliable Endorsement Authenticity Score compared to peer testimony, as references typically come from verified professional relationships with direct knowledge of the candidate's work performance. Peer testimony may be influenced by personal biases, reducing the authenticity and accuracy of endorsement, whereas references are more likely to offer objective, experience-based validation.
Collaborative Testimonial Metric
Collaborative Testimonial Metric enhances hiring accuracy by integrating Reference and Peer testimonies to provide a comprehensive evaluation of candidate competencies and workplace behavior. This metric leverages cross-source validation, reducing biases inherent in single-source feedback and improving predictive validity for job performance.
Lateral Validation Loop
Reference checks provide qualitative insights into a candidate's past performance, but peer testimony offers a dynamic, real-time perspective that enhances hiring accuracy through lateral validation loops. These loops systematically cross-verify peer feedback within the team, reducing bias and improving the predictive reliability of candidate success in lateral hires.
Relational Endorsement Credibility
Reference letters provide relational endorsement credibility by highlighting direct experiences and trustworthiness from prior supervisors or colleagues, establishing a deeper validation of candidate skills. Peer testimony offers insights into teamwork and interpersonal dynamics but may lack the authoritative weight of hierarchical references in hiring decisions.
Cross-Peer Appraisal
Cross-peer appraisal offers a more comprehensive evaluation of a candidate's skills and work ethic compared to traditional reference checks, as it involves feedback from multiple colleagues across different levels. This method reduces bias and provides diverse perspectives, enhancing the reliability of hiring decisions by incorporating direct peer insights on collaboration, performance, and professional behavior.
Decentralized Reference Model
The Decentralized Reference Model enhances hiring accuracy by aggregating diverse, peer-sourced feedback rather than relying solely on traditional reference checks from a limited number of supervisors, enabling a more comprehensive evaluation of candidate skills and workplace behavior. Peer testimony contributes real-time, context-rich insights that reduce hiring biases and improve predictive validity compared to conventional reference methods.
Reference vs Peer testimony for hiring Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com