Reference pet validation relies on direct testimonials from trusted individuals familiar with the professional's work, offering personalized insights into skills and character. Peer review provides a systematic assessment by experts within the same field, ensuring standardized evaluation and credibility. Both methods complement each other, with references adding depth and peer reviews offering objective scrutiny for comprehensive professional validation.
Table of Comparison
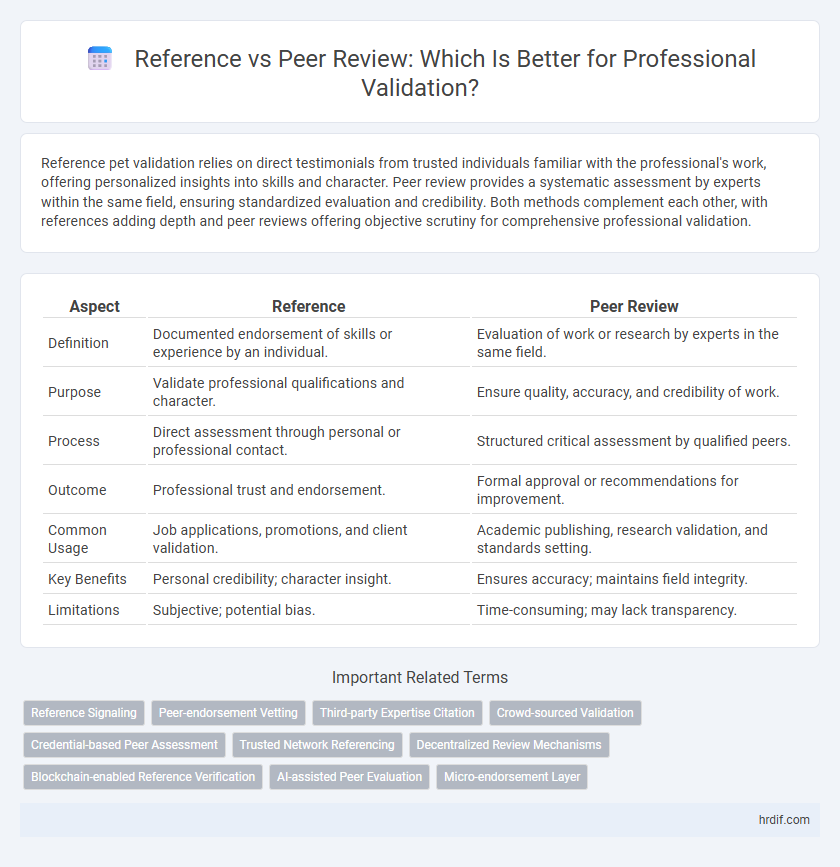
| Aspect | Reference | Peer Review |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Documented endorsement of skills or experience by an individual. | Evaluation of work or research by experts in the same field. |
| Purpose | Validate professional qualifications and character. | Ensure quality, accuracy, and credibility of work. |
| Process | Direct assessment through personal or professional contact. | Structured critical assessment by qualified peers. |
| Outcome | Professional trust and endorsement. | Formal approval or recommendations for improvement. |
| Common Usage | Job applications, promotions, and client validation. | Academic publishing, research validation, and standards setting. |
| Key Benefits | Personal credibility; character insight. | Ensures accuracy; maintains field integrity. |
| Limitations | Subjective; potential bias. | Time-consuming; may lack transparency. |
Understanding Reference Checks in Career Advancement
Reference checks play a critical role in career advancement by providing verified insights into a candidate's work ethic, skills, and professional behavior from previous employers or colleagues. Unlike peer review, which focuses on evaluating the quality and validity of academic or professional work, reference checks validate a candidate's real-world experience and reliability through direct testimonials. Employers rely on comprehensive reference assessments to mitigate hiring risks and ensure alignment with organizational culture and job requirements.
The Role of Peer Review in Professional Validation
Peer review serves as a critical mechanism for professional validation by systematically evaluating the quality, accuracy, and credibility of work through expert assessment. Unlike references, which provide personal or professional endorsements, peer review offers objective, standardized scrutiny that helps ensure adherence to industry standards and ethical guidelines. This process enhances the reliability and acceptance of professional contributions within the academic and professional communities.
Key Differences Between Reference and Peer Review Processes
References provide personalized evaluations from individuals familiar with a candidate's skills and work ethic, while peer reviews involve systematic assessments by independent experts within the same field to ensure validity and quality. References offer qualitative insights and subjective endorsement, whereas peer reviews emphasize objective scrutiny, reproducibility, and adherence to disciplinary standards. The reference process is typically less formal and more subjective; peer review requires structured protocols and is integral to maintaining scientific and professional credibility.
Impact of References on Job Applications
References significantly enhance job applications by providing credible validation of a candidate's skills and work ethic from previous employers or colleagues. Unlike peer review, which evaluates academic or scientific quality, references offer personalized insights into professional behavior and reliability, influencing hiring decisions. Employers often prioritize strong references as a key factor in confirming a candidate's suitability for the role.
Peer Review as a Benchmark for Professional Credibility
Peer review serves as a critical benchmark for professional credibility by providing a systematic evaluation of work through expert scrutiny, ensuring accuracy and reliability in the field. Unlike references, which offer subjective endorsements, peer review delivers objective validation based on established standards and criteria. This rigorous process enhances trustworthiness and fosters continuous improvement in professional practices.
Advantages and Limitations of Reference Checks
Reference checks provide direct, personalized insights into a candidate's previous job performance and interpersonal skills, offering practical advantages over peer review's often broader evaluative approach. They can reveal specific examples and behaviors not captured in formal assessments but may be limited by potential bias, incomplete information, or reluctance from referees to share negative feedback. Unlike peer review, reference checks depend heavily on the quality and honesty of the referee, which can sometimes result in inconsistent validation for professional qualification.
Peer Review: Ensuring Quality and Integrity in the Workplace
Peer review serves as a critical mechanism for ensuring quality and integrity in professional environments by facilitating expert evaluation of work before acceptance. Unlike references, which offer subjective opinions based on past experiences, peer review relies on systematic, objective assessment aligned with industry standards and ethical guidelines. This process minimizes errors, enhances credibility, and promotes continuous improvement within organizations.
When to Rely on References vs Peer Review
References are essential for professional validation when assessing an individual's past performance, skills, and reliability based on firsthand experience. Peer review is more appropriate for evaluating the quality, accuracy, and credibility of academic work, research findings, or technical content before publication. Rely on references for personal and job-related verification, and trust peer review for scholarly and scientific validation.
Challenges in Using Reference and Peer Review for Validation
Challenges in using reference for professional validation include potential bias, lack of standardization, and variability in the credibility of sources. Peer review faces difficulties such as delays in feedback, inconsistent reviewer expertise, and the risk of subjective judgment affecting assessment quality. Both methods require careful management to ensure accurate and reliable validation outcomes.
Best Practices for Leveraging Reference and Peer Review
References provide direct insights from individuals familiar with a professional's work ethic and skills, offering personalized validation that complements the structured scrutiny of peer reviews. Combining detailed, specific references with comprehensive peer-reviewed evaluations strengthens credibility and supports holistic professional validation. Best practices involve selecting credible references aligned with peer review criteria and integrating feedback to enhance overall assessment reliability.
Related Important Terms
Reference Signaling
Reference signaling provides direct professional validation by highlighting specific expertise and experience through credible endorsements from industry peers or supervisors. Unlike peer review, which evaluates general quality and methodology, reference signaling emphasizes personalized trustworthiness and demonstrated performance within a professional network.
Peer-endorsement Vetting
Peer review functions as a rigorous vetting mechanism in professional validation, ensuring that work undergoes critical evaluation by experts within the same field. Unlike traditional references, peer-endorsement emphasizes impartial scrutiny and standardized assessment to uphold quality and credibility in scholarly and professional outputs.
Third-party Expertise Citation
Reference letters provide personalized endorsements from known contacts, while peer review offers a rigorous evaluation by independent experts within the same field, ensuring objective third-party expertise citation. Peer review's standardized process validates research integrity and credibility more effectively than individual references.
Crowd-sourced Validation
Crowd-sourced validation leverages collective input from diverse professionals, offering dynamic and broad-based endorsement beyond traditional reference checks. Peer review relies on expert evaluation but may lack the scale and real-time feedback inherent in crowd-sourced methods, enhancing reliability through diversified validation.
Credential-based Peer Assessment
Credential-based peer assessment offers a more rigorous and standardized approach to professional validation compared to traditional references by relying on experts with recognized qualifications to evaluate competence and performance. This method enhances credibility through structured evaluation criteria, ensuring that endorsements reflect verified skills and achievements within the professional community.
Trusted Network Referencing
Trusted Network Referencing ensures professional validation by leveraging authenticated feedback from verified industry contacts, providing a more reliable and context-rich assessment than traditional peer review. This method reduces bias and enhances credibility through transparent, reciprocal endorsements within established professional networks.
Decentralized Review Mechanisms
Decentralized review mechanisms offer enhanced transparency and resistance to bias compared to traditional peer review, leveraging blockchain technology to validate professional credentials through cryptographically secure references. These systems enable direct verification of expertise from multiple independent sources, increasing reliability and reducing gatekeeping in professional validation processes.
Blockchain-enabled Reference Verification
Blockchain-enabled reference verification offers enhanced professional validation by providing immutable, transparent records that prevent fraud and ensure authenticity. Unlike traditional peer review, this decentralized approach enables real-time validation of credentials and work history, streamlining trust and credibility in professional settings.
AI-assisted Peer Evaluation
AI-assisted peer evaluation enhances professional validation by combining traditional reference reliability with automated bias detection and consistency checks, ensuring more objective and comprehensive assessments. This integration improves the accuracy and credibility of peer reviews, surpassing the limitations of conventional reference-based validation methods.
Micro-endorsement Layer
The Micro-endorsement Layer enhances professional validation by providing granular, peer-driven evaluations that extend beyond traditional reference formats, ensuring authentic and specific endorsements. Unlike broad peer reviews, this layer captures precise skill validations and micro-feedback, increasing credibility and trust in professional qualifications.
Reference vs Peer Review for professional validation Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com