Reference checks provide firsthand insights from previous employers, offering specific examples of a candidate's work ethic and performance. Peer review networks contribute broader perspectives by assessing collaboration skills and professional reputation within industry circles. Combining both methods enhances hiring decisions by balancing concrete evidence with community-based evaluations.
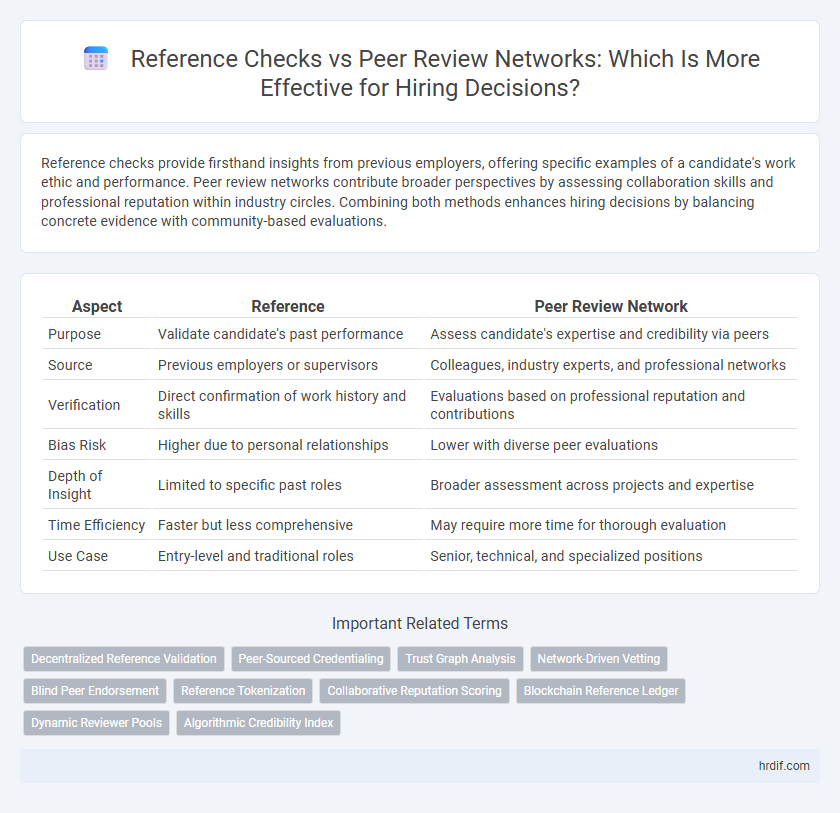
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reference | Peer Review Network |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Validate candidate's past performance | Assess candidate's expertise and credibility via peers |
| Source | Previous employers or supervisors | Colleagues, industry experts, and professional networks |
| Verification | Direct confirmation of work history and skills | Evaluations based on professional reputation and contributions |
| Bias Risk | Higher due to personal relationships | Lower with diverse peer evaluations |
| Depth of Insight | Limited to specific past roles | Broader assessment across projects and expertise |
| Time Efficiency | Faster but less comprehensive | May require more time for thorough evaluation |
| Use Case | Entry-level and traditional roles | Senior, technical, and specialized positions |
Introduction to Reference Checks and Peer Review Networks
Reference checks involve gathering firsthand evaluations from previous employers or colleagues to assess a candidate's skills, work ethic, and reliability, providing qualitative insights essential for hiring decisions. Peer review networks leverage feedback from industry professionals and experts who assess a candidate's technical abilities and professional reputation within their field, offering a deeper understanding of specialized competencies. Both methods complement each other by combining direct experience with expert validation, enhancing the accuracy and thoroughness of candidate evaluations.
Defining Reference Checks in Recruitment
Reference checks in recruitment involve contacting previous employers, colleagues, or academic sources to verify a candidate's work history, skills, and performance. Unlike peer review networks that provide collective professional evaluations, reference checks deliver personalized and direct insights into a candidate's reliability, behavior, and achievements. This process ensures hiring decisions are grounded in validated information rather than solely on peer opinions or self-reported qualifications.
What is a Peer Review Network in Hiring?
A Peer Review Network in hiring is a structured system where candidates are evaluated by professionals within the same industry or field to assess their skills, experience, and cultural fit. Unlike traditional references, which often come from previous employers or personal contacts, peer review networks provide real-time, unbiased, and specialized feedback from colleagues who understand the job requirements deeply. This method enhances hiring accuracy by leveraging collective expertise, reducing bias, and improving candidate quality.
Key Differences Between Reference Checks and Peer Review Networks
Reference checks primarily involve direct feedback from previous employers or supervisors, providing insights into a candidate's work history and professional behavior. Peer review networks gather evaluations from colleagues at similar hierarchical levels, emphasizing collaborative skills and team dynamics. These differences influence hiring decisions by contrasting hierarchical accountability with peer-based credibility and cultural fit.
Advantages of Using Reference Checks for Hiring Decisions
Reference checks provide direct insights into a candidate's past job performance, work ethic, and interpersonal skills from verified sources, offering practical and personalized information unattainable through peer review networks. They enable employers to validate qualifications and experiences, reducing the risk of hiring mismatches and enhancing decision accuracy. This method supports a more comprehensive evaluation by capturing specific behavioral examples and context from former supervisors or colleagues.
Benefits of Peer Review Networks in Talent Acquisition
Peer review networks enhance talent acquisition by providing comprehensive, unbiased evaluations from multiple industry experts, reducing the risk of hiring mismatches. These networks leverage collective insights to validate candidates' skills, experience, and cultural fit more accurately than traditional references. Using peer review networks accelerates decision-making and ensures higher-quality hires through collaborative assessment and real-time feedback.
Limitations of Traditional Reference Checks
Traditional reference checks often rely on subjective opinions from former employers, resulting in biased or incomplete assessments of a candidate's capabilities. These checks lack standardized evaluation criteria, making comparisons across candidates inconsistent and potentially misleading. The limited scope of information provided in reference checks hinders employers from fully understanding a candidate's skills, work ethic, and cultural fit.
Challenges of Implementing Peer Review Networks
Implementing peer review networks for hiring decisions faces challenges including potential bias from personal relationships among reviewers, inconsistencies in evaluation criteria, and the time-intensive nature of gathering comprehensive assessments from multiple peers. Unlike traditional references, peer review networks require robust structures to ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability in the feedback process. These complexities often hinder seamless integration into organizational hiring workflows, impacting the reliability and efficiency of candidate evaluations.
Reference Checks vs Peer Review Networks: Which Is More Effective?
Reference checks provide direct insights from previous employers or colleagues, offering specific examples of a candidate's past performance and work ethic. Peer review networks gather evaluations from multiple industry professionals, delivering a broader perspective on skills and reputation within the field. Studies indicate reference checks yield more tailored assessments for hiring decisions, while peer review networks offer valuable validation but may lack the detailed context needed for accurate candidate evaluation.
Best Practices for Integrating Reference and Peer Review Processes
Integrating reference checks with peer review networks enhances hiring decisions by providing comprehensive insights into candidate competencies and cultural fit. Best practices include standardized reference questionnaires aligned with peer review criteria, ensuring consistent evaluation metrics and reducing biases. Leveraging structured feedback from both references and peers facilitates more informed and balanced judgments in talent acquisition.
Related Important Terms
Decentralized Reference Validation
Decentralized Reference Validation enhances hiring decisions by leveraging blockchain technology to create immutable, transparent records of candidate feedback, reducing biases inherent in traditional peer review networks. This approach ensures verifiable, tamper-proof recommendations that improve trustworthiness and streamline candidate assessment processes.
Peer-Sourced Credentialing
Peer-sourced credentialing enhances hiring decisions by leveraging verified expertise and direct professional interactions within a peer review network, offering a more dynamic and reliable assessment than traditional references. This method prioritizes real-time validation of skills and accomplishments through transparent peer evaluations, reducing bias and improving candidate quality in talent acquisition.
Trust Graph Analysis
Trust Graph Analysis in hiring decisions leverages Reference data and Peer Review Networks to evaluate candidate reliability by mapping and quantifying professional relationships and endorsements. While Reference checks provide direct feedback from known contacts, Peer Review Networks expand trust metrics through multi-source validation, enhancing predictive accuracy in assessing applicant qualifications.
Network-Driven Vetting
Network-driven vetting leverages peer review networks to provide dynamic, real-time assessments of candidates based on verified professional interactions and reputational data, enhancing the accuracy and timeliness of hiring decisions. Unlike traditional references, peer review networks integrate multidimensional feedback and social proof, reducing bias and improving the predictive validity of candidate performance in organizational contexts.
Blind Peer Endorsement
Blind Peer Endorsement leverages anonymous evaluations from trusted peers within specialized networks, enhancing objectivity and reducing bias in hiring decisions compared to traditional reference checks, which often rely on subjective and self-selected contacts. This method improves the accuracy and fairness of candidate assessments by prioritizing verified peer insights over potentially partial or incomplete references.
Reference Tokenization
Reference tokenization enhances hiring decisions by converting qualitative feedback into quantifiable data, enabling seamless integration with peer review networks for comprehensive candidate evaluation. This process improves accuracy and efficiency by standardizing reference inputs, facilitating better comparison and data-driven hiring outcomes.
Collaborative Reputation Scoring
Collaborative Reputation Scoring leverages both Reference and Peer Review Networks to enhance hiring decisions by aggregating multi-source feedback, improving accuracy and reducing bias in candidate evaluation. Integrating decentralized peer reviews with verified references creates a dynamic reputation profile that reflects real-world performance and teamwork capabilities more effectively than traditional reference checks alone.
Blockchain Reference Ledger
Blockchain Reference Ledger offers a tamper-proof and transparent alternative to traditional peer review networks by securely validating candidate credentials and performance histories. This decentralized system reduces bias and fraud, streamlining hiring decisions through verifiable, immutable records of professional references.
Dynamic Reviewer Pools
Dynamic reviewer pools enhance the peer review network by enabling real-time selection of evaluators with specific expertise, improving the accuracy of hiring decisions compared to static references. Leveraging adaptive algorithms to identify relevant reviewers fosters a more comprehensive and unbiased assessment, crucial for effective talent acquisition.
Algorithmic Credibility Index
The Algorithmic Credibility Index enhances hiring decisions by quantifying the reliability of references and peer review networks, providing an objective metric for candidate evaluation. This index integrates data from references and peer assessments to reduce bias and improve the accuracy of credibility scores in recruitment processes.
Reference vs Peer Review Network for hiring decisions Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com