Reference signals provide a stable and consistent baseline for candidate selection, ensuring accurate synchronization and channel estimation. Network signals, however, can vary due to environmental factors and interference, making them less reliable for precise measurement. Using reference signals enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the selection process in communication systems.
Table of Comparison
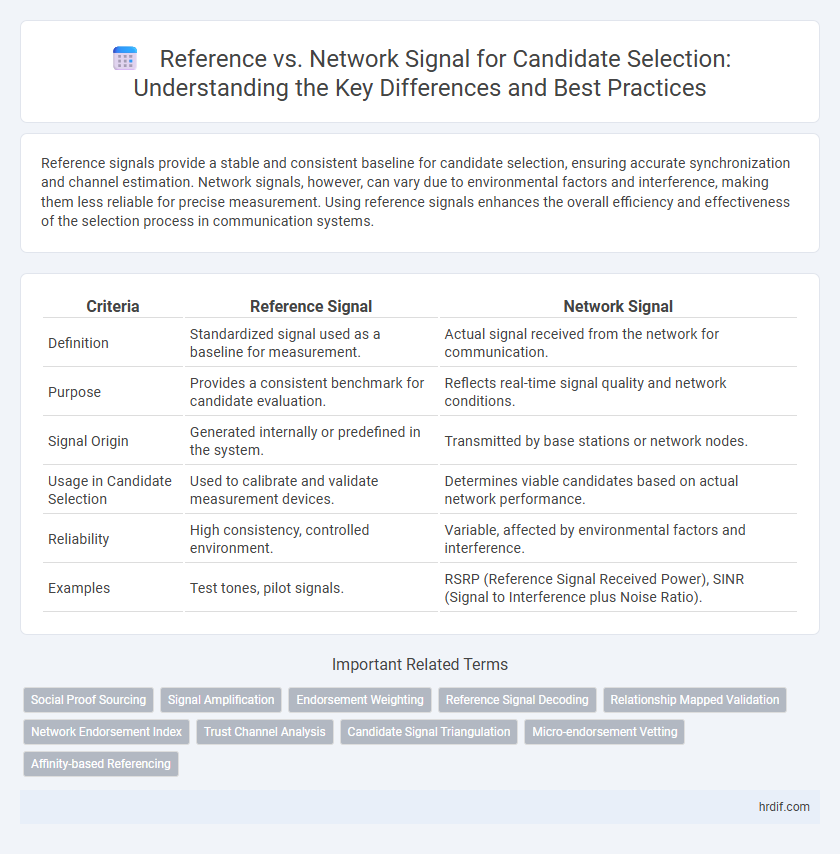
| Criteria | Reference Signal | Network Signal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standardized signal used as a baseline for measurement. | Actual signal received from the network for communication. |
| Purpose | Provides a consistent benchmark for candidate evaluation. | Reflects real-time signal quality and network conditions. |
| Signal Origin | Generated internally or predefined in the system. | Transmitted by base stations or network nodes. |
| Usage in Candidate Selection | Used to calibrate and validate measurement devices. | Determines viable candidates based on actual network performance. |
| Reliability | High consistency, controlled environment. | Variable, affected by environmental factors and interference. |
| Examples | Test tones, pilot signals. | RSRP (Reference Signal Received Power), SINR (Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio). |
Understanding Reference and Network Signals
Reference signals provide precise channel estimation and synchronization for candidate selection, ensuring accurate link quality assessment. Network signals encompass broader metrics, such as signal strength, interference, and load conditions, offering comprehensive context for optimal candidate prioritization. Understanding the balance between Reference and Network signals enhances the reliability of selection algorithms in wireless communication systems.
The Role of References in Candidate Selection
References provide verified insights into a candidate's past performance, skills, and work ethic, offering objective data that enhances the reliability of the selection process. Unlike network signals, which often rely on subjective impressions or social connections, references deliver concrete evaluations from previous employers or colleagues. Leveraging references helps organizations reduce hiring risks by validating candidate qualifications and ensuring alignment with job requirements.
Assessing Network Signals During Recruitment
Assessing network signals during recruitment involves analyzing candidates' professional connections, endorsements, and online activity to gauge their industry reputation and potential cultural fit. References provide direct, personalized insights into a candidate's work ethic, skills, and performance from previous employers or colleagues, offering qualitative depth. While network signals offer broader, data-driven perspectives on influence and engagement, combining both approaches yields a more comprehensive evaluation of candidate suitability.
Reference Checks: Strengths and Limitations
Reference checks provide objective insights into a candidate's past performance and professional behavior, offering verified information that network signals may lack. However, they can be limited by bias, outdated perspectives, and the willingness of references to disclose critical feedback. While network signals offer broader social proof and real-time reputation data, reference checks remain crucial for validating specific competencies and experiences.
How Networking Impacts Hiring Decisions
Networking significantly enhances candidate selection by expanding the talent pool beyond traditional references, allowing employers to access passive candidates through professional connections. Strong networks provide real-time insights into a candidate's skills, work ethic, and cultural fit, often more reliable than formal references alone. Leveraging professional networks such as LinkedIn or industry groups increases the accuracy and efficiency of hiring decisions by harnessing firsthand peer evaluations.
Comparing Reference and Network Validation
Reference validation offers a stable benchmark for candidate selection by using predefined ground-truth data to ensure accuracy, whereas network validation relies on live signal quality metrics, reflecting real-time environmental conditions. Reference-based methods typically achieve higher precision in verifying candidate relevance but may lack adaptability to network dynamics, while network validation provides contextual responsiveness by evaluating signal strength, latency, and error rates. Combining both approaches enhances candidate selection robustness, balancing reliable accuracy from reference data with responsiveness to network fluctuations.
Potential Biases in Reference vs. Network Signals
Reference signals often exhibit potential biases due to their limited scope and reliance on historical data, which can skew candidate selection by favoring established profiles. Network signals, derived from broader relational and social interactions, may introduce biases linked to social homophily and network structure, potentially marginalizing diverse or less-connected candidates. Balancing both reference and network signals is crucial to mitigate inherent biases and enhance fairness in candidate evaluation.
Enhancing Selection Accuracy with Combined Signals
Integrating reference signals with network signals significantly enhances candidate selection accuracy by leveraging complementary data characteristics for more precise decision-making. Reference signals provide stable and consistent benchmarks, while network signals offer real-time, dynamic information about the environment. The combined analysis of these signals allows for improved filtering and ranking of candidates, leading to higher reliability and reduced selection errors in various applications such as telecommunications and machine learning.
Best Practices for Leveraging References and Networks
Leveraging references in candidate selection enhances the accuracy of assessing a candidate's performance and cultural fit by providing verified insights from previous employers. Integrating network signals allows access to passive candidates and broader talent pools, increasing diversity and uncovering hidden potential. Combining reference checks with network data optimizes decision-making, reduces hiring risks, and elevates candidate quality through a holistic evaluation approach.
Future Trends in Candidate Evaluation Methods
Emerging candidate evaluation methods increasingly leverage network signals derived from social graphs, professional connections, and digital footprints to enhance the precision of talent identification beyond traditional reference checks. Future trends indicate a shift towards integrating real-time network analytics and machine learning algorithms that assess candidate influence, engagement, and reputation within industry-specific networks. This approach promises more dynamic, data-driven selection processes that complement or even surpass conventional reference-based assessments in predictive validity and hiring efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Social Proof Sourcing
Social Proof Sourcing leverages references as verified endorsements reflecting authentic candidate performance, offering higher reliability compared to indirect network signals prone to bias or incomplete data. References provide concrete evidence of skills and work ethic, enhancing the precision of candidate selection beyond generalized network signal indicators.
Signal Amplification
Reference signals provide a stable baseline for candidate selection by offering consistent and measurable signal strength, whereas network signals vary dynamically, influencing amplification needs for accurate detection. Effective signal amplification relies on leveraging reference signals to optimize receiver sensitivity and minimize interference in fluctuating network conditions.
Endorsement Weighting
Endorsement weighting in candidate selection prioritizes reference signals over raw network signals by assigning greater credibility to verified endorsements, enhancing the accuracy of candidate evaluation. Reference signals, being explicitly authenticated, provide a more reliable basis for ranking candidates, while network signals may introduce noise due to indirect or inferred connections.
Reference Signal Decoding
Reference signals play a crucial role in candidate selection by providing accurate channel state information through reliable signal decoding, which enhances the detection of optimal transmission paths. Efficient reference signal decoding outperforms network signal metrics alone by reducing errors and improving the precision of candidate evaluation in wireless communication systems.
Relationship Mapped Validation
Reference signals provide a stable baseline for candidate selection by enabling Relationship Mapped Validation to accurately assess signal quality and interference patterns, ensuring optimal network performance. Network signals fluctuate due to environmental factors, but integrating Reference signals ensures the validation process reliably discriminates between candidate sources and maintains robust connectivity.
Network Endorsement Index
Network Endorsement Index (NEI) quantitatively measures the strength of candidate endorsements within professional networks, providing a more dynamic and predictive metric compared to traditional reference checks. Unlike static references, NEI captures real-time peer validations and signal intensities across digital platforms, enhancing the accuracy of candidate selection processes.
Trust Channel Analysis
Trust Channel Analysis prioritizes reference signals over standard network signals for candidate selection due to their higher reliability and accuracy in validating user authenticity. Leveraging multi-source reference data enhances the detection of fraudulent behavior by correlating trust indicators across diverse, verified channels.
Candidate Signal Triangulation
Candidate signal triangulation improves selection accuracy by utilizing multiple network signals, such as Wi-Fi, GPS, and cellular data, rather than relying solely on a single reference signal. This multi-source approach enhances spatial resolution and reduces errors in positioning, providing robust and precise candidate location estimation.
Micro-endorsement Vetting
Reference signals provide verified endorsements directly linked to candidate performance, enhancing the accuracy of micro-endorsement vetting by reducing reliance on broader network signals prone to bias and dilution. Utilizing reference-based vetting in candidate selection ensures higher integrity and precision, optimizing recruitment outcomes through focused, credible validation.
Affinity-based Referencing
Affinity-based referencing improves candidate selection by utilizing both reference and network signals, prioritizing candidates with stronger relational ties and shared attributes. This approach leverages semantic affinity metrics to enhance accuracy, outperforming traditional network signal methods reliant solely on connection strength.
Reference vs Network signal for candidate selection. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com