A reference graph maps genuine professional relationships and past collaborations, providing authentic validation of skills and work ethic. An endorsement graph often includes broader, sometimes less rigorous acknowledgments that may lack depth or context. Understanding the difference enhances credibility assessment and helps professionals showcase verified achievements more effectively.
Table of Comparison
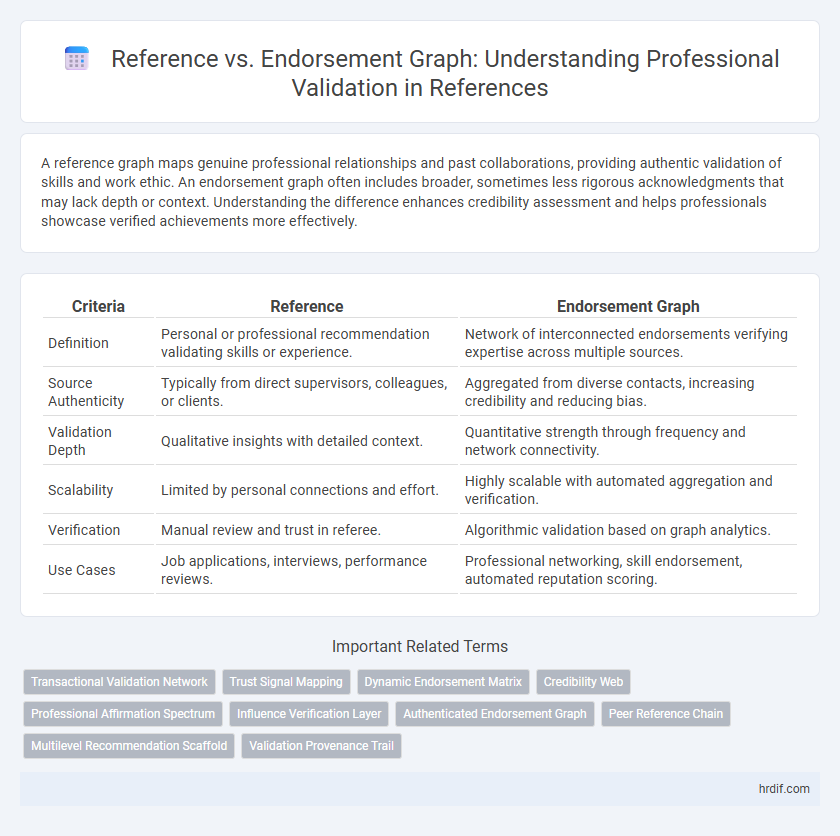
| Criteria | Reference | Endorsement Graph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personal or professional recommendation validating skills or experience. | Network of interconnected endorsements verifying expertise across multiple sources. |
| Source Authenticity | Typically from direct supervisors, colleagues, or clients. | Aggregated from diverse contacts, increasing credibility and reducing bias. |
| Validation Depth | Qualitative insights with detailed context. | Quantitative strength through frequency and network connectivity. |
| Scalability | Limited by personal connections and effort. | Highly scalable with automated aggregation and verification. |
| Verification | Manual review and trust in referee. | Algorithmic validation based on graph analytics. |
| Use Cases | Job applications, interviews, performance reviews. | Professional networking, skill endorsement, automated reputation scoring. |
Understanding Reference and Endorsement in Professional Validation
References provide detailed evaluations of an individual's skills and character, offering personalized insights from trusted sources, while endorsements represent quick affirmations of specific abilities from colleagues within a professional network. Understanding the difference between reference and endorsement graphs aids in accurately assessing professional validation by balancing qualitative depth with quantitative breadth. Leveraging both frameworks enhances credibility and ensures a comprehensive representation of expertise in professional evaluations.
Reference vs Endorsement: Key Differences
References provide detailed, personalized evaluations of a professional's skills and work ethic, often supported by direct experience and documented achievements. Endorsements, typically brief and general, serve as quick confirmations of particular skills but lack the depth and context that references offer. The reference graph maps comprehensive, qualitative insights connecting professionals, while the endorsement graph captures quantitative, surface-level validations from broader networks.
How References Influence Career Opportunities
References provide credible validation from previous employers or colleagues, directly impacting hiring decisions by substantiating skills and work ethic within a professional endorsement graph. These verified endorsements create a robust network of trust that enhances a candidate's visibility and attractiveness to recruiters. Career opportunities expand as references reinforce reputation, enabling professionals to access higher-level roles and niche positions.
The Power of Endorsements in Building Professional Credibility
Endorsement graphs amplify professional credibility by showcasing verified expert opinions and peer validations within a network, unlike traditional reference lists that merely cite names without direct context. The dynamic nature of endorsements enables real-time updates and widespread visibility, reinforcing trust and authority through collective validation. Leveraging endorsement networks enhances reputation management and career advancement by highlighting influential connections and authentic professional strengths.
Visualizing Professional Validation: The Reference vs Endorsement Graph
Visualizing professional validation through the Reference vs Endorsement Graph highlights distinct pathways of credibility, where references provide detailed, context-rich insights into an individual's skills and work ethic, while endorsements offer quick, surface-level affirmations from a wider network. The graph maps these interactions, showcasing the depth and breadth of professional validation by illustrating how references build trust through qualitative narratives and endorsements amplify reputation via quantitative signals. This dual structure enables employers and collaborators to assess candidates holistically, balancing narrative authenticity with social proof intensity.
Analyzing Validation Patterns: What the Graph Reveals
The Reference vs Endorsement Graph reveals distinct validation patterns by mapping professional relationships and influence flows, highlighting how endorsements often indicate surface-level approval while references provide deeper, experience-based validation. Analysis of these graphs uncovers clusters of trusted professionals and the weight of their validation within industries, aiding in the identification of key opinion leaders and authentic expertise. This distinction enhances talent acquisition and network-building strategies by prioritizing genuine professional validation over superficial endorsements.
When to Seek References vs Endorsements
Seeking references is crucial when detailed, personalized validation from supervisors or colleagues is needed to verify specific skills and work experience. Endorsements serve as quick affirmations from a broader network, ideal for showcasing general competencies and enhancing professional reputation on platforms like LinkedIn. Prioritize references during job applications or promotions, while endorsements support ongoing credibility and networking efforts.
Leveraging Both References and Endorsements for Career Growth
Integrating both reference letters and endorsement graphs enhances professional validation by providing a comprehensive view of skills and credibility, with references offering detailed, personalized assessments while endorsements supply quick, scalable credibility signals from peers. Leveraging a combined approach allows professionals to showcase verified expertise and broad support, improving visibility in recruitment algorithms and strengthening networks. This dual strategy accelerates career growth by aligning qualitative and quantitative validations, optimizing influence within professional ecosystems.
Limitations of References Compared to Endorsements
References often provide subjective evaluations based on personal interactions, limiting their scalability and objectivity in professional validation. Endorsement graphs aggregate multiple independent validations, offering a more quantifiable and network-driven assessment of skills and expertise. Consequently, references may lack the comprehensive coverage and statistical reliability that endorsement graphs deliver in verifying professional credentials.
Best Practices for Strengthening Your Professional Validation Graph
A robust professional validation graph prioritizes authentic references over endorsements, emphasizing detailed feedback and specific achievements to enhance credibility. Incorporating diverse, verifiable references from reputable industry sources strengthens the graph's reliability and showcases a comprehensive skill set. Regularly updating the validation graph with recent projects and peer validations ensures ongoing relevance and trustworthiness in professional networks.
Related Important Terms
Transactional Validation Network
Transactional Validation Networks enable granular professional validation by mapping explicit exchanges and endorsements between individuals, contrasting with broader Reference and Endorsement Graphs that often aggregate generalized reputational data. This approach enhances trustworthiness and authenticity in professional validation through verifiable, transaction-based connections.
Trust Signal Mapping
Reference graphs provide a robust trust signal mapping by illustrating verified professional relationships through documented interactions, whereas endorsement graphs often rely on subjective affirmations lacking contextual depth. Mapping trust via reference graphs enables more accurate validation of expertise by leveraging concrete evidence of collaboration and performance.
Dynamic Endorsement Matrix
The Dynamic Endorsement Matrix enhances professional validation by mapping real-time, multi-dimensional relationships between references and endorsements, enabling a comprehensive assessment of skills and credibility. This approach surpasses traditional endorsement graphs by incorporating contextual data and temporal factors, ensuring a more accurate representation of an individual's professional capabilities.
Credibility Web
Reference graphs map verified professional connections to establish credibility through documented interactions, while endorsement graphs rely on subjective peer affirmations that may lack rigorous validation. The Credibility Web enhances trustworthiness by integrating reference data into a decentralized network, ensuring accountability and resistance to manipulation.
Professional Affirmation Spectrum
Reference and endorsement graphs represent distinct layers within the Professional Affirmation Spectrum, with reference graphs emphasizing documented professional validation through verified experiences and achievements. Endorsement graphs capture broader peer recognition and skill acknowledgment, often reflecting subjective affirmation rather than formal validation.
Influence Verification Layer
The Influence Verification Layer in the Reference vs Endorsement Graph critically distinguishes authentic professional validation by analyzing relational strength and contextual relevance rather than mere endorsements. This layer ensures that references carry verified influence and credibility, enhancing the reliability of validation networks in professional settings.
Authenticated Endorsement Graph
Authenticated Endorsement Graphs provide a robust framework for professional validation by leveraging cryptographically verified connections between endorsers and endorsees, ensuring integrity and authenticity. Unlike traditional Reference systems, these graphs enable dynamic, scalable, and tamper-resistant representation of professional competencies and reputation across decentralized networks.
Peer Reference Chain
Peer Reference Chain leverages interconnected endorsements from professional colleagues, enhancing credibility beyond traditional Reference methods by creating a dynamic Endorsement Graph. This graph structure enables scalable validation of skills and reputations within industry networks, promoting more accurate professional assessments.
Multilevel Recommendation Scaffold
The Multilevel Recommendation Scaffold structures professional validation through a layered approach, distinguishing Reference graphs--verifiable attestations of skills and experiences--from Endorsement graphs, which capture network-based affirmations of capabilities. This hierarchy enhances credibility assessment by integrating direct references with broader endorsements, optimizing trustworthiness in professional ecosystems.
Validation Provenance Trail
Validation provenance trail in professional contexts ensures traceability and authenticity of qualifications by mapping the origination and verification path of references, unlike endorsement graphs which primarily aggregate support signals. This detailed trail enables organizations to assess credibility systematically through documented interactions and verifiable validation sources, enhancing trust in professional validation processes.
Reference vs Endorsement Graph for professional validation Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com