A skills-based profile highlights a candidate's relevant competencies and practical experiences, offering a clearer picture of their suitability for specific roles compared to traditional resumes that focus on job titles and dates. This approach enables recruiters to identify transferable skills and assess potential beyond formal job history. Emphasizing skills over chronological work experience improves the evaluation process by aligning candidate capabilities with job requirements more effectively.
Table of Comparison
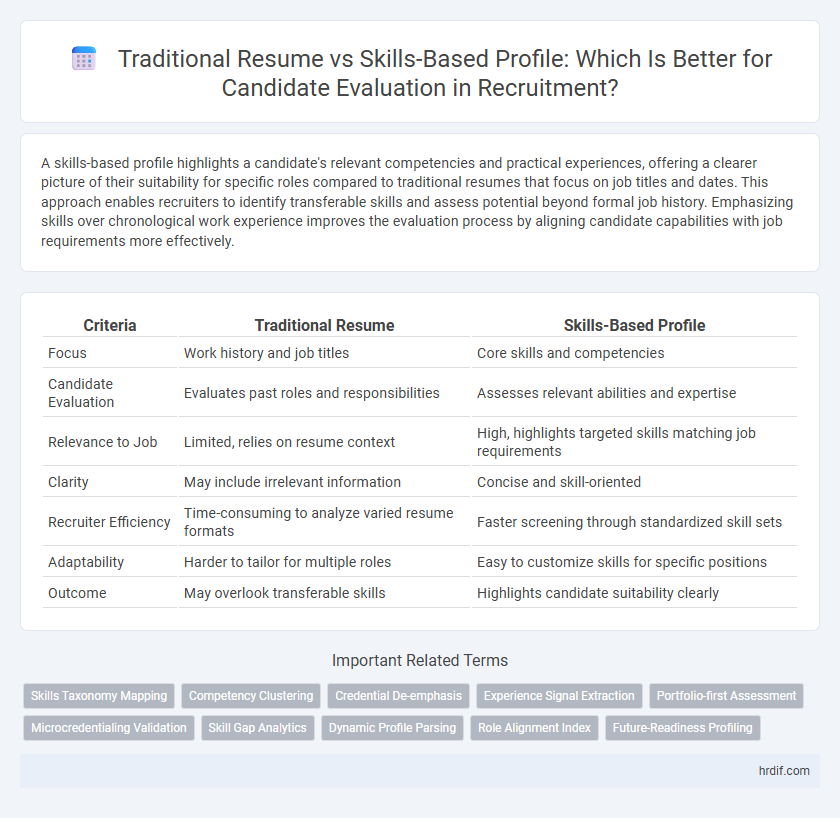
| Criteria | Traditional Resume | Skills-Based Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Work history and job titles | Core skills and competencies |
| Candidate Evaluation | Evaluates past roles and responsibilities | Assesses relevant abilities and expertise |
| Relevance to Job | Limited, relies on resume context | High, highlights targeted skills matching job requirements |
| Clarity | May include irrelevant information | Concise and skill-oriented |
| Recruiter Efficiency | Time-consuming to analyze varied resume formats | Faster screening through standardized skill sets |
| Adaptability | Harder to tailor for multiple roles | Easy to customize skills for specific positions |
| Outcome | May overlook transferable skills | Highlights candidate suitability clearly |
Understanding Traditional Resumes
Traditional resumes emphasize chronological work history, highlighting job titles, employers, and dates of employment to showcase a candidate's career progression. This format prioritizes educational background and certifications alongside specific roles, often reflecting stability and experience within an industry. Employers relying on traditional resumes may risk overlooking transferable skills and practical competencies critical for diverse or evolving job functions.
Defining Skills-Based Profiles
Skills-based profiles prioritize core competencies and abilities relevant to job performance, offering a clear picture of a candidate's practical expertise beyond chronological work history. Unlike traditional resumes, which focus on job titles and dates, skills-based profiles categorize and highlight technical skills, soft skills, certifications, and project outcomes. This approach enables recruiters to match candidates more accurately with role requirements, improving selection efficiency and reducing bias.
Key Differences Between Resumes and Skills-Based Profiles
Traditional resumes emphasize chronological work history and formal education, often highlighting job titles and companies, whereas skills-based profiles focus on specific competencies and practical abilities directly related to the job. Resumes provide a linear career progression, while skills-based profiles prioritize transferable skills, making them ideal for candidates with diverse or non-linear career paths. Employers seeking targeted expertise tend to favor skills-based profiles due to their clear demonstration of relevant capabilities and problem-solving potential.
The Role of Traditional Resumes in Recruitment
Traditional resumes provide a structured overview of a candidate's work history, education, and certifications, serving as a baseline for recruiters to assess qualifications and career progression. Their standardized format simplifies initial screening processes and facilitates comparison between applicants by highlighting job titles, employers, and tenure. Despite growing interest in skills-based profiles, traditional resumes remain a critical tool for evaluating professional experience and verifying chronological career development.
Advantages of Skills-Based Profiles for Employers
Skills-based profiles enable employers to identify candidates with specific competencies and measurable abilities, improving the accuracy of job fit predictions. Unlike traditional resumes, these profiles highlight relevant skills directly aligned with job requirements, reducing time spent filtering irrelevant information. This approach enhances diversity by valuing practical expertise over chronological career progression, broadening the talent pool and fostering innovation.
Limitations of Traditional Resume Evaluation
Traditional resume evaluation often overlooks a candidate's practical skills and adaptability, focusing primarily on job titles and dates rather than demonstrated competencies. This method can miss critical soft skills and project-specific achievements that are essential for modern roles. Additionally, it may perpetuate biases by emphasizing formal education and previous employers over actual performance and potential.
How Skills-Based Profiles Enhance Talent Discovery
Skills-based profiles enhance talent discovery by highlighting candidates' core competencies and practical expertise rather than just job titles or chronological experience. This approach allows recruiters to identify relevant skills that match specific job requirements, improving the precision of candidate evaluation. By prioritizing skills, companies can uncover hidden talent and better predict successful job performance in varied roles.
Implementing Skills-Based Assessment in Hiring
Implementing skills-based assessment in hiring enhances candidate evaluation by prioritizing relevant competencies over traditional resume formats, which often emphasize job titles and tenure. Skills-based profiles provide targeted insights into a candidate's actual abilities, enabling recruiters to make data-driven decisions aligned with role requirements. This approach reduces bias, improves talent matching, and accelerates the hiring process by focusing on measurable skills rather than generalized experience.
Candidate Experience: Resumes vs Skills-Based Profiles
Skills-based profiles enhance candidate experience by highlighting relevant competencies, making evaluation more transparent and efficient. Traditional resumes often emphasize chronological work history, which may obscure key abilities and hinder quick assessment. Emphasizing skills streamlines recruitment and aligns candidate qualifications with job requirements more effectively.
Future Trends in Candidate Evaluation Methods
Skills-based profiles emphasize practical competencies and measurable achievements, aligning more closely with job performance metrics than traditional resumes. Future recruitment trends favor AI-driven tools that analyze these dynamic skill sets for better candidate-role matching. Embracing skills-based evaluation facilitates identifying adaptable talent capable of thriving in evolving workplace demands.
Related Important Terms
Skills Taxonomy Mapping
Skills taxonomy mapping enhances the evaluation process by systematically categorizing candidate competencies, enabling recruiters to match skills from traditional resumes and skills-based profiles with job requirements more precisely. This approach improves talent identification accuracy by aligning candidate expertise with organizational needs through standardized skill frameworks.
Competency Clustering
Competency clustering in candidate evaluation enhances skills-based profiles by grouping related abilities, offering a clearer representation of a candidate's expertise compared to traditional resumes that often list isolated experiences. This method improves recruitment accuracy by aligning clusters of competencies with job requirements, facilitating more effective talent matching and reducing bias.
Credential De-emphasis
Traditional resumes emphasize academic credentials and job titles, whereas skills-based profiles prioritize relevant competencies and practical experience, aligning better with modern recruitment needs. De-emphasizing credentials allows employers to identify candidates with applicable skills beyond formal qualifications, enhancing diversity and inclusivity in talent evaluation.
Experience Signal Extraction
Traditional resumes often rely on chronological experience listings that can obscure key competencies, whereas skills-based profiles emphasize Experience Signal Extraction by highlighting specific abilities and measurable achievements, enabling more precise candidate evaluation. Leveraging natural language processing and AI-driven tools enhances the extraction of relevant experience signals from diverse formats, improving recruiter efficiency and decision-making accuracy.
Portfolio-first Assessment
Skills-based profiles focusing on portfolio-first assessment highlight candidates' practical expertise through demonstrated projects and accomplishments, providing recruiters with tangible evidence of capabilities beyond traditional resume formats. This approach enhances talent evaluation by emphasizing relevant skills and real-world experience, allowing for more accurate and efficient candidate selection.
Microcredentialing Validation
Skills-based profiles enhanced by microcredentialing validation offer recruiters precise evidence of a candidate's specialized competencies and verified achievements, improving accuracy in matching job requirements. Traditional resumes often lack detailed proof of skills, whereas skills-based profiles leverage credible microcredentials to demonstrate up-to-date expertise and continuous learning.
Skill Gap Analytics
Skills-based profiles offer precise skill gap analytics by highlighting competencies needed for specific roles, enabling recruiters to identify areas for candidate development more effectively than traditional resumes that emphasize job history. This targeted approach enhances talent matching accuracy and supports strategic workforce planning by focusing on proficiency rather than titles.
Dynamic Profile Parsing
Dynamic profile parsing enhances candidate evaluation by extracting and organizing both traditional resume data and skills-based profile information, enabling recruiters to identify relevant competencies and experiences more efficiently. This technology supports a comprehensive analysis that highlights not only chronological work history but also specific skills, certifications, and project-based achievements, improving talent matching in recruitment processes.
Role Alignment Index
The Role Alignment Index measures how well a candidate's skills and experiences match the specific requirements of a job role, often favoring skills-based profiles over traditional resumes for a more precise fit. Skills-based profiles highlight relevant competencies and practical expertise, enhancing the accuracy of candidate evaluation and improving hiring outcomes.
Future-Readiness Profiling
Skills-based profiles emphasize competencies and adaptability crucial for future-readiness in recruitment, enabling employers to evaluate candidates on practical expertise and potential for growth rather than solely on chronological job history. Traditional resumes often overlook evolving skills and fail to capture a candidate's ability to thrive in dynamic work environments, making skills-based profiles more effective for assessing future-focused talent.
Traditional Resume vs Skills-based Profile for candidate evaluation. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com