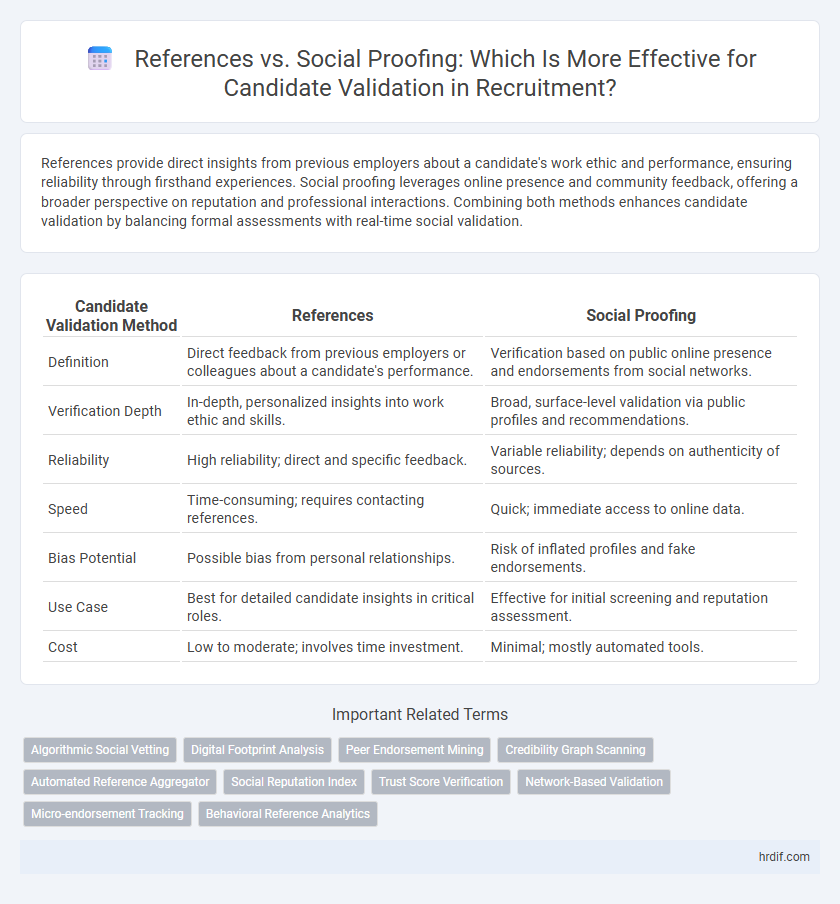
References provide direct insights from previous employers about a candidate's work ethic and performance, ensuring reliability through firsthand experiences. Social proofing leverages online presence and community feedback, offering a broader perspective on reputation and professional interactions. Combining both methods enhances candidate validation by balancing formal assessments with real-time social validation.
Table of Comparison
| Candidate Validation Method | References | Social Proofing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct feedback from previous employers or colleagues about a candidate's performance. | Verification based on public online presence and endorsements from social networks. |
| Verification Depth | In-depth, personalized insights into work ethic and skills. | Broad, surface-level validation via public profiles and recommendations. |
| Reliability | High reliability; direct and specific feedback. | Variable reliability; depends on authenticity of sources. |
| Speed | Time-consuming; requires contacting references. | Quick; immediate access to online data. |
| Bias Potential | Possible bias from personal relationships. | Risk of inflated profiles and fake endorsements. |
| Use Case | Best for detailed candidate insights in critical roles. | Effective for initial screening and reputation assessment. |
| Cost | Low to moderate; involves time investment. | Minimal; mostly automated tools. |
Understanding References in Candidate Validation
References provide detailed, personalized insights from previous employers or colleagues that help verify a candidate's skills, work ethic, and cultural fit. Unlike social proofing, which relies on broader online reputation signals like endorsements and reviews, references offer direct, context-specific feedback critical for in-depth candidate validation. Accurate reference checks reduce hiring risks by confirming qualifications and uncovering potential red flags through firsthand professional experiences.
The Rise of Social Proofing in Recruitment
Social proofing has surged as a pivotal tool in recruitment, leveraging online endorsements, social media presence, and peer reviews to validate candidate credibility beyond traditional references. Platforms like LinkedIn and industry-specific forums provide real-time, dynamic insights into a candidate's professional network, skills, and reputation. This evolution enhances hiring accuracy by supplementing conventional references with broader, context-rich social validation.
Key Differences: References vs Social Proofing
References involve direct feedback from previous employers or colleagues, providing verified insights into a candidate's past performance and work ethic. Social proofing leverages public endorsements, such as LinkedIn recommendations or social media interactions, to gauge reputation and professional network influence. While references offer formal validation, social proofing supplies broader context on interpersonal skills and industry standing.
Pros and Cons of Traditional References
Traditional references provide verified insights from former employers or colleagues, offering direct evidence of a candidate's work ethic and skills, which aids in reducing hiring risks. However, these references can be biased, limited in scope, and may not reflect recent performance or fit within the new company culture. The process is often time-consuming and relies heavily on the reference's willingness to share honest feedback, potentially leading to incomplete candidate validation.
Benefits of Social Proofing for Recruiters
Social proofing enhances candidate validation by providing recruiters with real-time insights from diverse sources such as social media activity, professional endorsements, and peer reviews, offering a broader perspective beyond traditional references. This method reduces bias and improves decision accuracy by capturing dynamic behavioral and reputational data that references alone may not reveal. Leveraging social proofing enables recruiters to identify cultural fit and soft skills more effectively, streamlining hiring processes and increasing overall recruitment success.
Common Pitfalls with Candidate References
Candidate references often suffer from bias, limited perspective, and outdated information, reducing their reliability for thorough validation. Social proofing leverages real-time, diverse digital footprints that provide a broader, more current view of a candidate's skills and behavior. Overreliance on traditional references can lead to overlooking red flags and incomplete candidate assessments in recruitment.
Leveraging Social Media for Candidate Validation
Social media platforms provide real-time insights into a candidate's professional behavior, endorsements, and network interactions, offering a dynamic alternative to traditional references. Leveraging LinkedIn profiles, endorsements, and activity can reveal soft skills and cultural fit that references may overlook. Integrating social proof through social media analysis increases hiring accuracy by validating candidate qualifications and reputation in a broader context.
Best Practices for Verifying Social Proof
Validating candidate qualifications through social proof requires meticulous verification of online endorsements, professional network feedback, and digital portfolios to ensure authenticity and relevance. Best practices include cross-referencing social media profiles with official employment history, analyzing peer recommendations for consistency, and using reliable digital tools to detect fabricated or exaggerated claims. Maintaining a structured approach to social proof verification enhances recruitment accuracy and reduces hiring risks.
Combining References and Social Proof Effectively
Combining references and social proof effectively enhances candidate validation by providing a comprehensive view of a candidate's professional background and reputation. References offer detailed, specific insights from direct supervisors or colleagues, while social proof, such as endorsements, recommendations, and online reviews, validates track records and interpersonal skills across broader networks. Integrating both methods increases hiring accuracy by leveraging qualitative feedback and measurable social validation simultaneously.
Future Trends in Candidate Validation Methods
Future trends in candidate validation emphasize the growing role of social proofing alongside traditional references, leveraging real-time digital footprints and peer endorsements to assess candidate reliability and cultural fit. Advanced AI tools analyze social media interactions and professional networks, providing nuanced insights beyond static reference letters. This shift enhances predictive accuracy in hiring decisions by combining qualitative endorsements with quantitative data from multiple online sources.
Related Important Terms
Algorithmic Social Vetting
Algorithmic social vetting leverages data-driven analysis of candidates' online presence and social networks, offering scalable insights beyond traditional reference checks. This method enhances recruitment accuracy by validating skills and cultural fit through quantifiable social proofing signals derived from digital footprints.
Digital Footprint Analysis
Digital footprint analysis offers a comprehensive method for candidate validation by evaluating online behavior, social media activity, and professional interactions, providing real-time insights beyond traditional reference checks. This approach uncovers authentic patterns and reputational signals that references may overlook or fail to disclose, enhancing recruitment accuracy and risk mitigation.
Peer Endorsement Mining
Peer endorsement mining leverages social proofing by analyzing authentic feedback from candidates' professional networks to validate skills and work ethic more effectively than traditional references. This data-driven approach uncovers nuanced insights and strengthens hiring decisions through real-time, peer-generated endorsements.
Credibility Graph Scanning
References provide direct insights from previous employers or colleagues, offering verified feedback on a candidate's skills and work ethic, while social proofing leverages broader online presence data to assess reputation and professionalism in the industry. Credibility graph scanning enhances validation by mapping and analyzing interconnected professional relationships, delivering a comprehensive view of trustworthiness and expertise beyond traditional references.
Automated Reference Aggregator
Automated Reference Aggregators streamline candidate validation by efficiently collecting and analyzing verified feedback from previous employers and colleagues, providing more reliable and scalable insights than traditional references. This technology enhances recruitment accuracy by integrating social proofing elements such as endorsements and performance metrics directly into the hiring process.
Social Reputation Index
Social Reputation Index offers a dynamic metric to evaluate candidate credibility by aggregating online presence and peer endorsements, providing a comprehensive supplement to traditional reference checks. This digital footprint analysis enhances recruitment accuracy by revealing consistent professional behavior and reputational trends across multiple platforms.
Trust Score Verification
References provide direct insights from previous employers, ensuring authentic candidate validation, while social proofing aggregates broader social signals like endorsements and online activity to enhance trust score verification. Combining both methods increases accuracy in assessing candidate credibility and reduces hiring risks by leveraging qualitative feedback and quantitative social data.
Network-Based Validation
Network-based validation in recruitment leverages references and social proofing to verify a candidate's skills and reputation through trusted connections within professional networks. References offer direct testimonials from previous employers, while social proofing aggregates endorsements and interactions across platforms like LinkedIn, providing comprehensive insights into a candidate's reliability and industry standing.
Micro-endorsement Tracking
References provide formal validation of a candidate's skills and work history through direct feedback from previous employers, while social proofing leverages micro-endorsement tracking across digital platforms to capture real-time, peer-driven insights into a candidate's professional reputation. Micro-endorsement tracking enables recruiters to quantify subtle signals like endorsements, recommendations, and interactions on networks such as LinkedIn, enhancing candidate validation with authentic, data-driven social validation beyond traditional references.
Behavioral Reference Analytics
Behavioral Reference Analytics leverages data-driven insights from past colleague feedback and performance reviews to validate candidate competencies more accurately than traditional references. Social proofing gathers broader social and professional signals, but behavioral analytics provides targeted, contextual evaluations essential for predicting future job performance.
References vs Social Proofing for candidate validation Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com