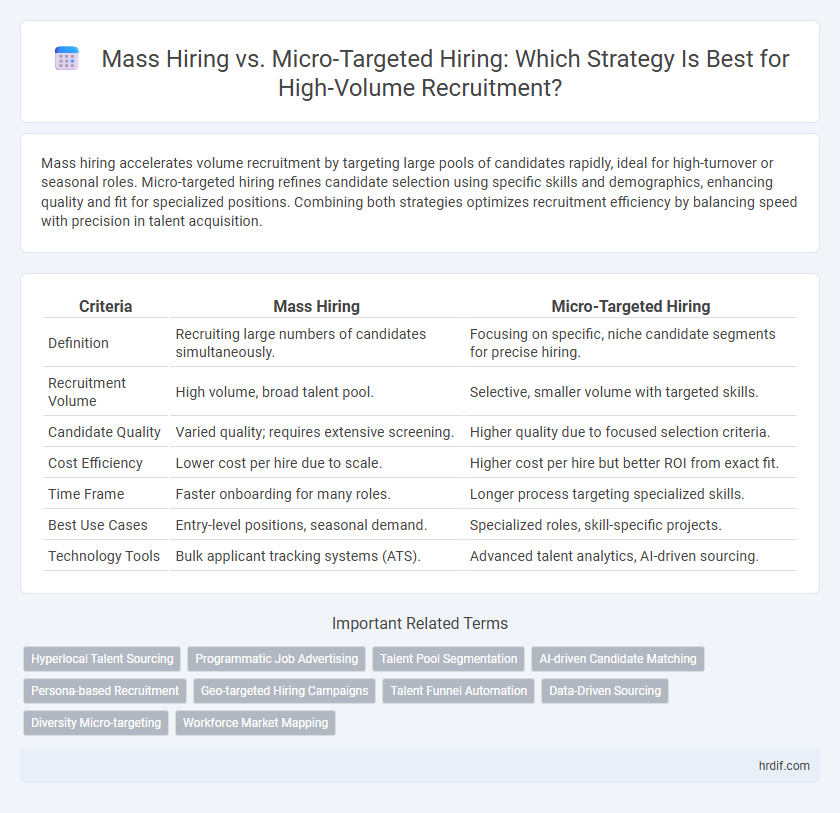
Mass hiring accelerates volume recruitment by targeting large pools of candidates rapidly, ideal for high-turnover or seasonal roles. Micro-targeted hiring refines candidate selection using specific skills and demographics, enhancing quality and fit for specialized positions. Combining both strategies optimizes recruitment efficiency by balancing speed with precision in talent acquisition.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Mass Hiring | Micro-Targeted Hiring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recruiting large numbers of candidates simultaneously. | Focusing on specific, niche candidate segments for precise hiring. |
| Recruitment Volume | High volume, broad talent pool. | Selective, smaller volume with targeted skills. |
| Candidate Quality | Varied quality; requires extensive screening. | Higher quality due to focused selection criteria. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost per hire due to scale. | Higher cost per hire but better ROI from exact fit. |
| Time Frame | Faster onboarding for many roles. | Longer process targeting specialized skills. |
| Best Use Cases | Entry-level positions, seasonal demand. | Specialized roles, skill-specific projects. |
| Technology Tools | Bulk applicant tracking systems (ATS). | Advanced talent analytics, AI-driven sourcing. |
Understanding Mass Hiring and Micro-targeted Hiring
Mass hiring involves recruiting large numbers of candidates simultaneously to quickly fill numerous positions, often using broad criteria and automated screening tools to manage volume efficiently. Micro-targeted hiring focuses on selecting smaller groups of candidates with specific skills, cultural fit, and roles in mind, leveraging detailed data analysis and personalized outreach to improve quality and retention. Understanding the strategic differences between mass hiring and micro-targeted hiring is crucial for balancing speed, cost, and candidate relevance in volume recruitment.
Key Differences Between Mass Hiring and Micro-targeted Hiring
Mass hiring emphasizes rapidly filling large volumes of positions using broad strategies and generalized criteria, often leveraging automated tools for efficiency. Micro-targeted hiring focuses on selecting candidates with specific skills and attributes tailored to niche roles, employing precise sourcing and personalized outreach. The key differences lie in scale, candidate quality, and recruitment customization, with mass hiring prioritizing speed and volume, while micro-targeted hiring optimizes talent fit and long-term retention.
Pros and Cons of Mass Hiring in Volume Recruitment
Mass hiring enables organizations to quickly fill large numbers of positions, reducing time-to-hire and addressing urgent workforce demands efficiently. However, it often results in lower candidate quality and less personalized fit, increasing turnover rates and training costs. This approach may also strain recruitment teams and lead to challenges in maintaining consistent employer branding during volume recruitment campaigns.
Pros and Cons of Micro-targeted Hiring for High-volume Needs
Micro-targeted hiring enhances recruitment efficiency by focusing on specific skill sets and candidate profiles, resulting in higher quality hires and improved retention rates. This approach can be resource-intensive and time-consuming compared to mass hiring, potentially limiting the speed needed to fill large volume positions. However, micro-targeted hiring reduces mismatch risks and training costs, making it valuable for organizations prioritizing long-term workforce stability.
Efficiency and Speed: Which Strategy Wins?
Mass hiring excels in speed by rapidly onboarding large numbers of candidates through standardized processes, ideal for urgent volume recruitment needs. Micro-targeted hiring enhances efficiency by focusing on specific skill sets and cultural fit, reducing turnover and improving long-term productivity. For organizations prioritizing immediate headcount growth, mass hiring wins, while efficiency-driven companies benefit more from micro-targeted hiring strategies.
Quality of Hire: Mass Approach vs. Personalized Targeting
Mass hiring enables rapid onboarding of large candidate pools but often compromises the quality of hire due to generic screening processes and limited candidate engagement. Micro-targeted hiring leverages personalized recruitment strategies, data-driven candidate profiling, and targeted outreach to enhance alignment with specific role requirements, resulting in higher employee retention and job performance. Quality of hire significantly improves when recruitment focuses on tailored assessments and cultural fit rather than sheer volume.
Cost Implications: Budgeting for Each Hiring Method
Mass hiring typically incurs higher overall costs due to large-scale outreach, broad advertising, and extensive candidate screening processes, resulting in variable quality and potential turnover. Micro-targeted hiring, while involving more upfront investment in specialized sourcing and personalized recruitment strategies, often leads to better candidate fit and reduced onboarding expenses. Budgeting for mass hiring requires allocating significant funds for volume-based activities, whereas micro-targeted hiring demands focused spending on precise talent pools, optimizing cost efficiency per hire.
Employer Branding Impact in Volume Recruitment Strategies
Mass hiring enhances employer branding through widespread visibility but risks diluting the company's unique culture message by targeting broad candidate pools. Micro-targeted hiring strengthens employer branding by delivering personalized, role-specific messaging that resonates with niche talent segments, fostering higher engagement and retention. Effective volume recruitment strategies balance these approaches to optimize brand perception and attract diverse, quality candidates.
Technological Tools Empowering Mass and Micro-targeted Hiring
Technological tools such as AI-driven applicant tracking systems (ATS) and data analytics platforms empower mass hiring by efficiently processing thousands of applications and automating candidate screening. Micro-targeted hiring leverages advanced algorithms and machine learning to identify niche candidates with specific skill sets, enhancing precision in volume recruitment campaigns. Cloud-based recruitment software integrates both strategies, optimizing talent acquisition by balancing speed and quality through scalable, technology-enabled workflows.
Choosing the Right Hiring Strategy for Your Recruitment Goals
Mass hiring accelerates the recruitment process by targeting large applicant pools, making it ideal for filling numerous entry-level positions quickly with standardized skill requirements. Micro-targeted hiring focuses on sourcing candidates with specific skill sets and cultural fits, enhancing quality and retention in specialized roles or strategic teams. Aligning your hiring strategy with organizational goals ensures efficient resource allocation and maximizes candidate-job alignment, balancing speed and precision in volume recruitment.
Related Important Terms
Hyperlocal Talent Sourcing
Mass hiring leverages broad talent pools to quickly fill high-volume positions, while micro-targeted hiring focuses on hyperlocal talent sourcing to match precise skill sets within specific geographic areas, improving retention and cultural fit. Hyperlocal approaches utilize advanced data analytics and community networks to identify candidates with relevant experience and reduce turnover costs in recruitment campaigns.
Programmatic Job Advertising
Programmatic job advertising enhances mass hiring efficiency by automating and optimizing large-scale ad placements across multiple platforms to reach diverse candidate pools rapidly. Micro-targeted hiring leverages data-driven audience segmentation within programmatic campaigns to attract niche talent, improving quality and reducing cost-per-hire in volume recruitment.
Talent Pool Segmentation
Mass hiring focuses on quickly filling large volumes of positions by casting a wide net, often resulting in a generic talent pool with varied skill levels. Micro-targeted hiring leverages talent pool segmentation to identify and engage specific candidate groups, enhancing recruitment precision and improving overall quality in volume hiring initiatives.
AI-driven Candidate Matching
AI-driven candidate matching enhances micro-targeted hiring by analyzing extensive data points such as skills, experience, and cultural fit, resulting in precise selection for specific roles. Mass hiring relies on generalized criteria, often leading to lower quality matches, whereas AI-powered micro-targeted recruitment optimizes volume hiring efficiency and candidate-job alignment.
Persona-based Recruitment
Mass hiring leverages broad candidate pools to fill numerous positions quickly, while micro-targeted hiring focuses on persona-based recruitment, tailoring job ads and outreach to specific candidate profiles for higher quality matches. Persona-based recruitment enhances engagement by aligning job requirements with candidate motivations, improving retention and reducing time-to-hire in volume recruitment scenarios.
Geo-targeted Hiring Campaigns
Geo-targeted hiring campaigns enable precise candidate sourcing by focusing recruitment efforts on specific locations, improving relevance and reducing costs compared to broad mass hiring approaches. Micro-targeted hiring increases quality and diversity by leveraging location-specific data to tailor job advertisements and attract local talent pools effectively.
Talent Funnel Automation
Mass hiring streamlines volume recruitment by automating the talent funnel to rapidly process large candidate pools, minimizing manual screening time and reducing time-to-hire. Micro-targeted hiring leverages precise data-driven strategies within talent funnel automation to attract niche skill sets, enhancing candidate quality and optimizing recruitment efficiency for specialized roles.
Data-Driven Sourcing
Data-driven sourcing enhances mass hiring efficiency by leveraging predictive analytics and AI algorithms to identify high-volume candidate pools with relevant skills and qualifications. Micro-targeted hiring, informed by precise data segmentation and behavioral insights, optimizes recruitment by focusing on niche talent clusters, improving quality and retention rates in volume recruitment campaigns.
Diversity Micro-targeting
Mass hiring streamlines volume recruitment but often overlooks diversity nuances, while micro-targeted hiring enhances inclusion by focusing on specific demographic segments and tailored outreach strategies. Leveraging diversity micro-targeting boosts organizational innovation and employee engagement by attracting varied skill sets and cultural perspectives in scalable volume recruitment campaigns.
Workforce Market Mapping
Mass hiring expedites volume recruitment by targeting broad candidate pools, while micro-targeted hiring leverages workforce market mapping to identify niche talent segments for precision recruitment outcomes. Effective workforce market mapping enhances micro-targeted hiring strategies by analyzing labor supply data, competitor workforce insights, and skill availability to optimize recruitment efficiency.
Mass Hiring vs Micro-targeted Hiring for volume recruitment. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com