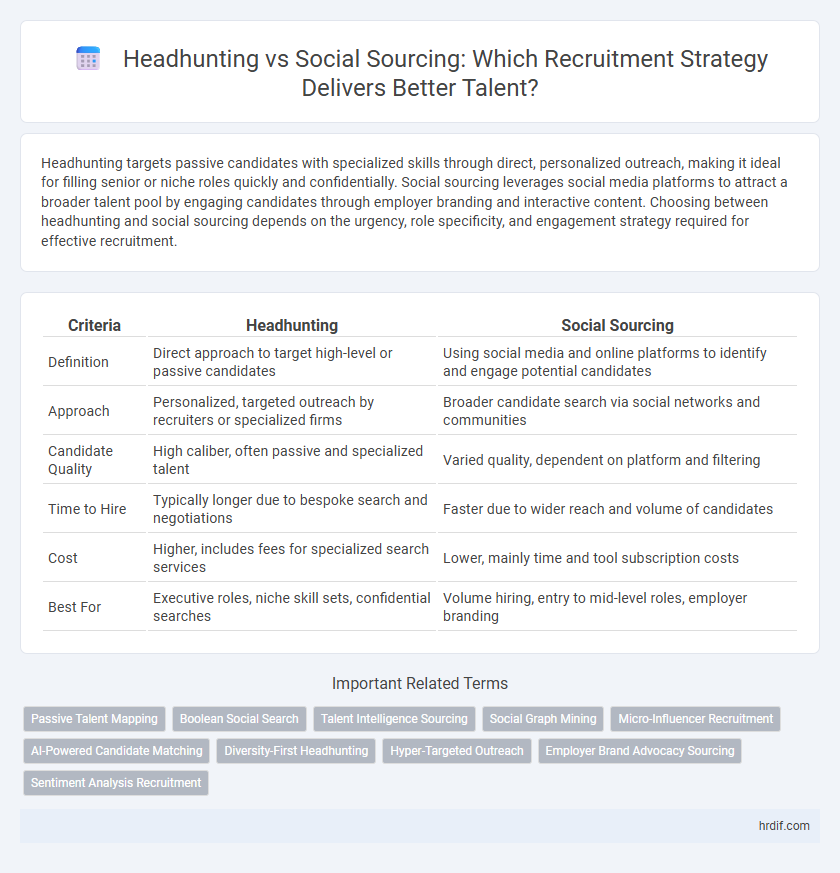
Headhunting targets passive candidates with specialized skills through direct, personalized outreach, making it ideal for filling senior or niche roles quickly and confidentially. Social sourcing leverages social media platforms to attract a broader talent pool by engaging candidates through employer branding and interactive content. Choosing between headhunting and social sourcing depends on the urgency, role specificity, and engagement strategy required for effective recruitment.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Headhunting | Social Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct approach to target high-level or passive candidates | Using social media and online platforms to identify and engage potential candidates |
| Approach | Personalized, targeted outreach by recruiters or specialized firms | Broader candidate search via social networks and communities |
| Candidate Quality | High caliber, often passive and specialized talent | Varied quality, dependent on platform and filtering |
| Time to Hire | Typically longer due to bespoke search and negotiations | Faster due to wider reach and volume of candidates |
| Cost | Higher, includes fees for specialized search services | Lower, mainly time and tool subscription costs |
| Best For | Executive roles, niche skill sets, confidential searches | Volume hiring, entry to mid-level roles, employer branding |
Defining Headhunting and Social Sourcing
Headhunting involves proactively identifying and approaching highly qualified candidates for specific executive or specialized roles, often relying on direct outreach and personalized engagement. Social sourcing leverages social media platforms and online professional networks to discover potential candidates, facilitating broader talent engagement through organic interactions and community building. Both strategies optimize talent acquisition by targeting passive candidates, but headhunting emphasizes exclusivity while social sourcing capitalizes on expansive digital ecosystems.
Key Differences Between Headhunting and Social Sourcing
Headhunting involves actively targeting and approaching highly specialized candidates, often in niche industries, through direct outreach and personalized engagement. Social sourcing leverages social media platforms and online networks to identify and attract potential candidates more broadly, emphasizing volume and reach. The key differences lie in headhunting's focus on exclusivity and precision versus social sourcing's emphasis on accessibility and scalability in recruitment strategies.
Pros and Cons of Headhunting in Recruitment
Headhunting excels in targeting highly specialized and passive candidates, ensuring access to top-tier talent often unavailable through traditional methods, but it can be costly and time-consuming due to the extensive research and personalized approach required. This method offers a higher success rate for executive and niche roles by leveraging expert networks and deep market insights, though it may limit candidate diversity by focusing primarily on known professionals within specific industries. Headhunting's precision reduces hiring risks but demands a significant investment in recruiter expertise and relationship management, making it less scalable for high-volume recruitment needs.
Advantages and Challenges of Social Sourcing
Social sourcing accelerates talent acquisition by leveraging personal networks and social media platforms, enabling recruiters to access passive candidates often overlooked by traditional headhunting. The advantage lies in cost-effectiveness and increased candidate diversity through broader outreach and real-time engagement. Challenges include maintaining candidate data privacy, managing high-volume responses, and ensuring consistent employer branding across multiple social channels.
When to Choose Headhunting Over Social Sourcing
Headhunting is ideal for filling highly specialized or executive roles where candidates are not actively seeking new opportunities and require targeted, confidential approaches. Social sourcing excels in volume hiring and when building diverse talent pools from active candidates on digital platforms. Choose headhunting when the role demands top-tier expertise, niche skills, or when immediate impact on company strategy is critical.
Ideal Roles for Headhunting vs Social Sourcing
Headhunting is ideal for filling executive, senior leadership, and highly specialized technical roles that require discreet approaches and a deep industry network to access passive candidates. Social sourcing excels in identifying mid-level positions and volume hiring needs by leveraging social media platforms and online communities to engage a broader, active talent pool. Both strategies complement each other, with headhunting targeting niche expertise while social sourcing capitalizes on dynamic and diverse candidate pipelines.
Cost Implications: Headhunting vs Social Sourcing
Headhunting typically involves higher costs due to agency fees and exclusive search processes, often ranging from 20% to 30% of the candidate's first-year salary. Social sourcing leverages online platforms and social networks, significantly reducing expenses by minimizing reliance on third-party recruiters and enabling in-house recruitment teams to engage candidates directly. Organizations aiming to optimize recruitment budgets should consider social sourcing for lower-cost candidate acquisition while reserving headhunting for specialized or executive-level roles requiring bespoke search efforts.
Impact on Candidate Experience and Employer Branding
Headhunting in recruitment offers a highly personalized approach, enhancing candidate experience through tailored engagement and demonstrating exclusivity, which positively influences employer branding by portraying the company as selective and premium. Social sourcing leverages broad networks and digital platforms, allowing for increased candidate diversity and quicker response times, contributing to a dynamic employer brand seen as innovative and accessible. Both strategies impact employer branding and candidate experience differently, with headhunting fostering deeper individual connections and social sourcing maximizing reach and inclusivity.
Technology Tools Enhancing Both Methods
Technology tools such as AI-driven candidate matching software and advanced CRM platforms significantly enhance both headhunting and social sourcing by streamlining talent identification and engagement processes. Headhunting benefits from predictive analytics and targeted outreach automation, enabling recruiters to focus on high-potential passive candidates efficiently. Social sourcing is amplified through social media monitoring tools and algorithmic candidate segmentation, increasing reach and interaction with diverse talent pools in real time.
Future Trends in Recruitment: Headhunting or Social Sourcing?
Future recruitment trends indicate a growing integration of AI-driven social sourcing platforms that leverage data analytics to identify passive candidates efficiently. Headhunting maintains its value for executive and niche roles requiring personalized assessment and high-level negotiation skills. Companies balancing technological innovation with strategic human insight will lead the recruitment landscape.
Related Important Terms
Passive Talent Mapping
Headhunting targets specialized passive candidates through direct outreach and personalized engagement, excelling in mapping high-value talent unavailable via traditional channels. Social sourcing leverages social media platforms and digital networks to identify and nurture passive talent pools, enhancing recruitment agility and broadening access to diverse candidate segments.
Boolean Social Search
Boolean social search in recruitment leverages advanced Boolean operators to filter and target specific candidate profiles across social media platforms, enhancing the precision of social sourcing. Compared to traditional headhunting, Boolean social search significantly expands candidate reach and reduces time-to-hire by systematically mining online social networks for talent with desired skills and experience.
Talent Intelligence Sourcing
Headhunting leverages targeted outreach and deep industry networks to identify high-caliber candidates, while social sourcing utilizes platforms like LinkedIn and Twitter to gather real-time talent intelligence and engage passive prospects. Combining talent intelligence sourcing tools enhances both methods by analyzing candidate data patterns, skills, and market trends to optimize recruitment strategies and improve candidate matching precision.
Social Graph Mining
Social Graph Mining leverages relationships within professional networks to identify passive candidates more effectively than traditional headhunting, uncovering hidden talent pools through patterns of connections and interactions. This data-driven approach enhances recruitment precision by analyzing social behaviors and endorsements, resulting in higher-quality candidate matches.
Micro-Influencer Recruitment
Headhunting targets high-level candidates with specialized skills through direct outreach, while social sourcing leverages platforms like LinkedIn and Instagram to engage micro-influencers who can attract niche talent via authentic networks. Micro-influencer recruitment enhances employer branding and widens candidate pools by tapping into trusted community voices within specific industries or skill sets.
AI-Powered Candidate Matching
AI-powered candidate matching enhances headhunting by analyzing comprehensive data patterns and executive profiles to identify high-potential passive candidates with precision. Social sourcing leverages AI algorithms to scan vast social networks and online communities, enabling recruiters to discover and engage talent pools based on real-time skills and behavioral insights.
Diversity-First Headhunting
Diversity-first headhunting leverages targeted outreach and personalized engagement to identify underrepresented talent pools, ensuring a more inclusive recruitment pipeline compared to broader social sourcing strategies that often rely on algorithms and existing networks. By prioritizing cultural fit and diverse skill sets, diversity-first headhunting enhances organizational innovation and drives equitable hiring outcomes.
Hyper-Targeted Outreach
Hyper-targeted outreach in recruitment leverages headhunting by directly identifying and engaging high-value candidates with specialized skills through personalized contact, maximizing talent acquisition efficiency. In contrast, social sourcing utilizes advanced algorithms and platforms like LinkedIn to broadly scan and filter potential candidates, enabling scalable yet precise recruitment within niche markets.
Employer Brand Advocacy Sourcing
Headhunting targets high-caliber candidates through direct outreach, enhancing employer brand advocacy by showcasing selective recruitment practices that emphasize quality and exclusivity. Social sourcing leverages employee networks and social media platforms to amplify employer brand advocacy, fostering authentic engagement and expanding reach through genuine candidate referrals.
Sentiment Analysis Recruitment
Headhunting leverages targeted identification of high-potential candidates, enhancing recruitment precision through sentiment analysis to gauge candidate interest and cultural fit. Social sourcing utilizes broad social media engagement and sentiment data to identify emerging talent trends and uncover passive candidates with aligned employer values.
Headhunting vs Social Sourcing for Recruitment Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com