Productivity levels often improve by adopting structured time management methods, with the Pomodoro Technique standing out for its ability to enhance focus through short, timed work intervals followed by breaks. This technique minimizes burnout and maintains high mental clarity by balancing concentrated work periods with regular rest. Many find that combining productivity goals with Pomodoro cycles leads to sustained attention and increased task completion rates.
Table of Comparison
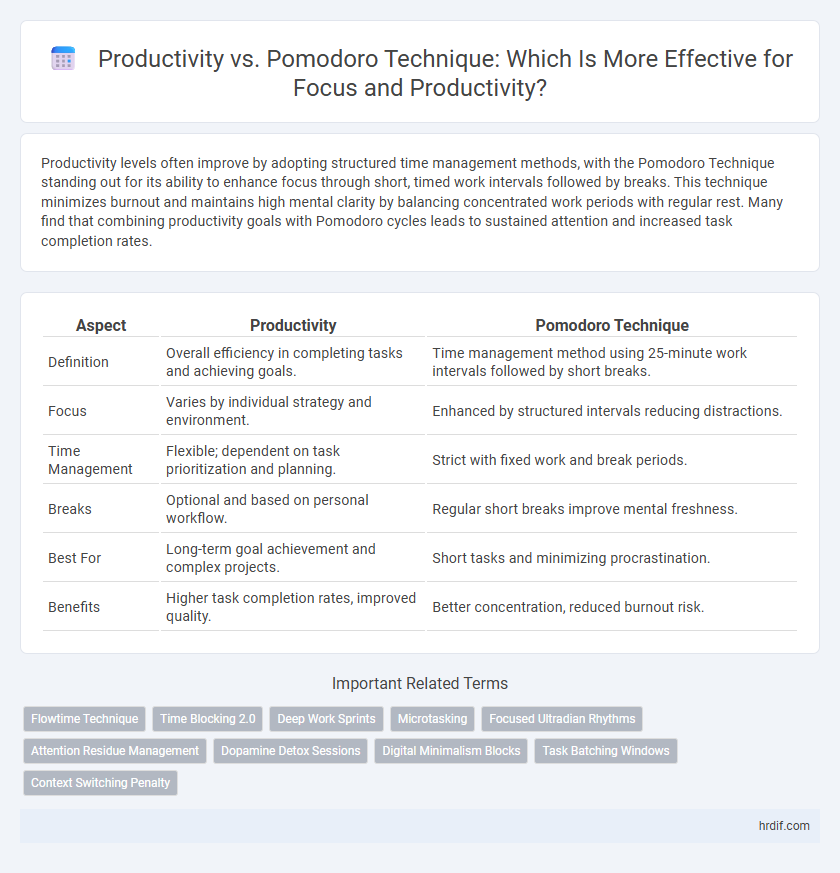
| Aspect | Productivity | Pomodoro Technique |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overall efficiency in completing tasks and achieving goals. | Time management method using 25-minute work intervals followed by short breaks. |
| Focus | Varies by individual strategy and environment. | Enhanced by structured intervals reducing distractions. |
| Time Management | Flexible; dependent on task prioritization and planning. | Strict with fixed work and break periods. |
| Breaks | Optional and based on personal workflow. | Regular short breaks improve mental freshness. |
| Best For | Long-term goal achievement and complex projects. | Short tasks and minimizing procrastination. |
| Benefits | Higher task completion rates, improved quality. | Better concentration, reduced burnout risk. |
Understanding Productivity in the Workplace
Productivity in the workplace is measured by output quality and efficiency, driven by effective time management and sustained concentration. The Pomodoro Technique breaks work into 25-minute intervals with short breaks, enhancing focus by reducing mental fatigue and preventing burnout. This method aligns with cognitive science principles, optimizing attention spans and improving overall task execution.
What Is the Pomodoro Technique?
The Pomodoro Technique is a time management method developed by Francesco Cirillo that involves breaking work into focused intervals of 25 minutes, called pomodoros, followed by short breaks. This approach enhances productivity by maintaining high levels of concentration and preventing burnout during tasks. Research shows that using structured intervals like pomodoros can significantly improve task completion and mental clarity compared to traditional work methods.
Key Differences: General Productivity vs Pomodoro
General productivity strategies encompass a broad range of methods aimed at enhancing overall efficiency and time management through prioritization, goal-setting, and eliminating distractions. The Pomodoro Technique specifically segments work into focused intervals of 25 minutes followed by short breaks, optimizing concentration and preventing burnout. Unlike general productivity approaches, the Pomodoro Technique provides a structured timing system that promotes sustained focus and task completion in discrete, manageable units.
How Pomodoro Enhances Focus
Pomodoro Technique enhances focus by breaking work into 25-minute intervals called Pomodoros, reducing mental fatigue and preventing burnout. This time management method leverages short, regular breaks to maintain high levels of concentration and sustain cognitive performance throughout the day. Studies show that Pomodoro increases task efficiency compared to traditional productivity methods by promoting disciplined work-rest cycles.
Pros and Cons of the Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro Technique enhances productivity by breaking work into 25-minute focused intervals, reducing mental fatigue and increasing concentration. However, its rigid timing may disrupt deep work flow and does not suit tasks requiring extended periods of uninterrupted focus. While fostering regular breaks promotes mental rejuvenation, frequent interruptions can hinder complex problem-solving and creative thinking.
Measuring Productivity Outcomes
Measuring productivity outcomes reveals distinct advantages between traditional productivity methods and the Pomodoro Technique, with the latter providing precise time-blocked intervals that enhance task completion rates and reduce cognitive fatigue. Empirical studies show that employees using the Pomodoro Technique report a 25-30% increase in focused work segments, directly correlating with improved measurable deliverables. Quantifying output through task completion metrics and time efficiency highlights the Pomodoro Technique's effectiveness in sustaining high productivity levels over extended periods.
Adapting Pomodoro for Different Careers
Adapting the Pomodoro Technique for different careers maximizes productivity by aligning work intervals with specific job demands, such as using shorter cycles for creative roles requiring frequent brainstorming and longer sessions for analytical tasks needing deep concentration. Careers in education, programming, and design benefit from tailored Pomodoro lengths, breaks, and task segmentation, enhancing focus and reducing burnout. Customizing Pomodoro timing based on individual workflow patterns significantly improves task completion rates and maintains sustained mental clarity across professions.
Common Productivity Barriers and Solutions
Common productivity barriers include distractions, lack of clear goals, and mental fatigue, which hinder sustained focus and task completion. The Pomodoro Technique combats these challenges by breaking work into focused intervals of 25 minutes, followed by short breaks, facilitating mental clarity and reducing burnout. Implementing time management tools alongside prioritized task lists can further enhance productivity and maintain consistent focus throughout work sessions.
When to Use Pomodoro vs Traditional Methods
The Pomodoro Technique excels in tasks requiring sustained focus and frequent breaks, enhancing mental clarity and preventing burnout during intensive work sessions. Traditional productivity methods, such as time blocking or to-do lists, are better suited for complex projects demanding flexibility and longer periods of uninterrupted concentration. Choosing Pomodoro for routine, repetitive tasks and traditional methods for strategic planning optimizes overall efficiency and focus management.
Tips for Maximizing Focus and Productivity
Maximizing focus and productivity requires balancing deep work sessions with strategic breaks to maintain mental clarity and prevent burnout. Implementing the Pomodoro Technique--25-minute focused intervals followed by 5-minute breaks--enhances concentration by leveraging short bursts of intense work while allowing time for recovery. Prioritizing task lists, minimizing distractions, and adjusting interval lengths based on personal energy cycles further optimize sustained productivity throughout the day.
Related Important Terms
Flowtime Technique
The Flowtime Technique enhances productivity by allowing flexible work intervals based on natural concentration levels, unlike the rigid Pomodoro Technique that enforces fixed 25-minute sessions and breaks. This adaptive method reduces interruptions and promotes sustained focus, leading to higher quality output and better alignment with individual work rhythms.
Time Blocking 2.0
Time Blocking 2.0 enhances productivity by allocating specific, uninterrupted time slots for tasks, reducing decision fatigue and maximizing focus compared to the Pomodoro Technique's rigid intervals. This advanced method integrates buffer periods and priority shifts, allowing greater flexibility and sustained deep work throughout the day.
Deep Work Sprints
The Pomodoro Technique, with its 25-minute focused intervals, enhances productivity by creating structured Deep Work sprints that minimize distractions and maximize concentration. Leveraging timed sessions aligns with cognitive rhythms, fostering sustained immersion in complex tasks critical for high-impact results.
Microtasking
Productivity increases significantly when microtasking is combined with the Pomodoro Technique, as breaking work into focused 25-minute intervals enhances concentration and reduces cognitive fatigue. Microtasking within these time blocks allows for manageable goal setting, improving task completion rates and maintaining consistent momentum throughout the day.
Focused Ultradian Rhythms
Focused Ultradian Rhythms leverage natural 90-120 minute cycles of heightened brain activity to optimize productivity by aligning work periods with peak focus. Unlike the Pomodoro Technique's fixed 25-minute intervals, ultradian rhythm-based productivity encourages longer, more intense focus sessions followed by restorative breaks to enhance cognitive performance and sustain attention.
Attention Residue Management
The Pomodoro Technique minimizes attention residue by encouraging focused 25-minute work intervals followed by short breaks, preventing task-switching fatigue and cognitive overload. Managing attention residue effectively boosts productivity by maintaining mental clarity and enhancing sustained concentration on single tasks.
Dopamine Detox Sessions
Dopamine detox sessions enhance productivity by temporarily reducing overstimulation, allowing the brain to reset its reward system and improve focus more sustainably than the Pomodoro Technique. Unlike timed work intervals, dopamine detox emphasizes minimizing all pleasurable distractions, leading to deeper cognitive clarity and prolonged attention span.
Digital Minimalism Blocks
Digital Minimalism Blocks enhance productivity by limiting digital distractions, enabling deeper focus compared to the Pomodoro Technique's structured intervals. This method leverages extended, distraction-free work periods to improve task engagement and workflow efficiency.
Task Batching Windows
Task batching windows enhance productivity by grouping similar tasks into fixed time blocks, minimizing context switching and increasing focus. Unlike the Pomodoro Technique's uniform intervals, task batching tailors work periods to task complexity, optimizing cognitive flow and reducing mental fatigue.
Context Switching Penalty
Productivity often declines due to the context switching penalty, where shifting between tasks disrupts cognitive flow and increases time spent reorienting. The Pomodoro Technique minimizes this penalty by structuring work into focused intervals, reducing distractions and maintaining sustained attention.
Productivity vs Pomodoro Technique for focus Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com