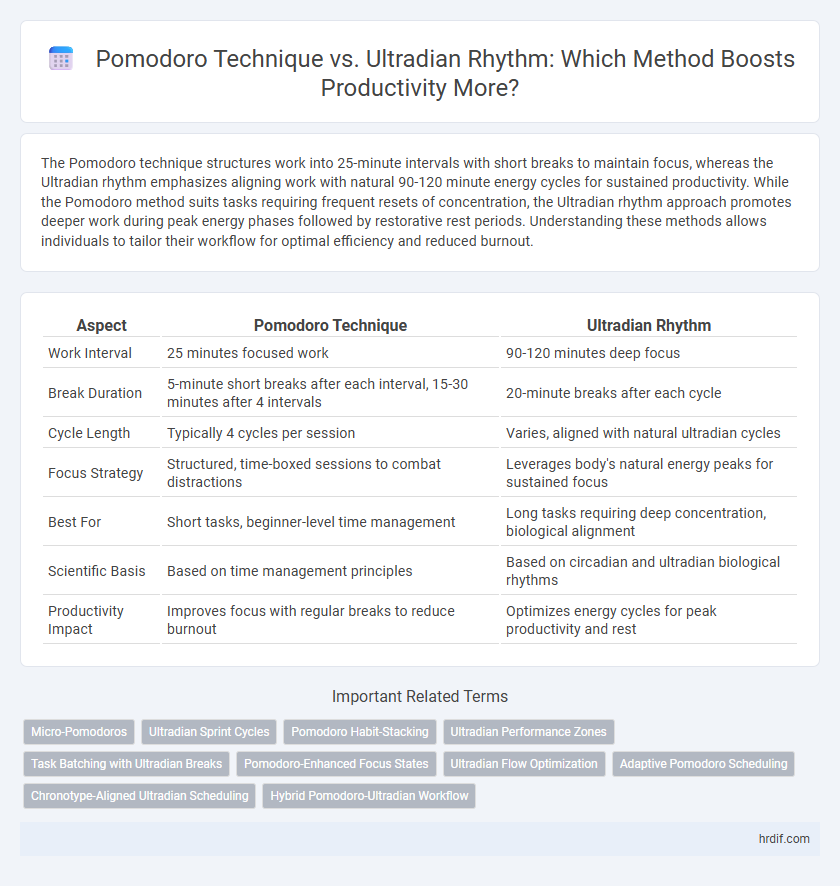
The Pomodoro technique structures work into 25-minute intervals with short breaks to maintain focus, whereas the Ultradian rhythm emphasizes aligning work with natural 90-120 minute energy cycles for sustained productivity. While the Pomodoro method suits tasks requiring frequent resets of concentration, the Ultradian rhythm approach promotes deeper work during peak energy phases followed by restorative rest periods. Understanding these methods allows individuals to tailor their workflow for optimal efficiency and reduced burnout.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pomodoro Technique | Ultradian Rhythm |
|---|---|---|
| Work Interval | 25 minutes focused work | 90-120 minutes deep focus |
| Break Duration | 5-minute short breaks after each interval, 15-30 minutes after 4 intervals | 20-minute breaks after each cycle |
| Cycle Length | Typically 4 cycles per session | Varies, aligned with natural ultradian cycles |
| Focus Strategy | Structured, time-boxed sessions to combat distractions | Leverages body's natural energy peaks for sustained focus |
| Best For | Short tasks, beginner-level time management | Long tasks requiring deep concentration, biological alignment |
| Scientific Basis | Based on time management principles | Based on circadian and ultradian biological rhythms |
| Productivity Impact | Improves focus with regular breaks to reduce burnout | Optimizes energy cycles for peak productivity and rest |
Understanding the Pomodoro Technique: Basics and Benefits
The Pomodoro Technique divides work into focused 25-minute intervals followed by short breaks, enhancing concentration and reducing mental fatigue. This time management method boosts productivity by leveraging structured sessions that align with natural attention spans. Its benefits include improved task completion, minimized distractions, and increased motivation through regular, manageable work periods.
The Science Behind Ultradian Rhythms and Productivity
Ultradian rhythms are natural cycles in the body that last about 90-120 minutes, influencing energy levels and cognitive performance throughout the day. Aligning work sessions with these biological peaks can enhance focus and productivity compared to fixed-interval methods like the Pomodoro technique, which uses 25-minute work segments. Research shows that syncing tasks with ultradian cycles supports sustained attention, reduces burnout, and improves overall work output.
Pomodoro Technique Workflow: Structure and Implementation
The Pomodoro Technique structures productivity into focused 25-minute work intervals followed by 5-minute breaks, optimizing mental stamina and reducing burnout. This workflow encourages consistent concentration bursts and frequent rest periods, which helps maintain high levels of efficiency throughout the day. Implementing the Pomodoro Technique requires using a timer to track sessions, prioritizing tasks, and taking short, scheduled breaks to sustain attention and prevent fatigue.
Ultradian Rhythm Cycles: Harnessing Natural Energy Peaks
Ultradian rhythm cycles align with the body's natural 90- to 120-minute energy fluctuations, optimizing productivity by encouraging focused work periods followed by restorative breaks. This approach taps into inherent biological patterns, enhancing mental clarity and sustained concentration beyond rigid time blocks like the Pomodoro technique. By synchronizing tasks with ultradian peaks, individuals experience improved efficiency and reduced cognitive fatigue throughout the workday.
Task Management: Pomodoro vs Ultradian Rhythms in Action
The Pomodoro Technique structures work into 25-minute intervals followed by short breaks, optimizing focus through timeboxing, while Ultradian Rhythms leverage natural 90-120 minute cycles of alertness to align tasks with peak energy levels. Task management using Pomodoro is ideal for tasks requiring sustained concentration and minimizing distractions, whereas Ultradian Rhythms offer flexibility by promoting breaks when cognitive fatigue naturally occurs. Effective productivity results from matching task demands with either Pomodoro's rigid intervals or the body's inherent alertness cycles in Ultradian Rhythms.
Focus and Breaks: Comparing Rest Intervals for Maximum Output
The Pomodoro Technique employs fixed 25-minute work intervals followed by 5-minute breaks to maintain high focus while preventing burnout. In contrast, the Ultradian rhythm suggests work periods of 90-120 minutes aligned with natural body energy cycles, followed by 20-minute rest intervals to optimize cognitive performance. Research indicates that aligning work and break intervals with individual physiological rhythms, such as the Ultradian cycles, may enhance productivity and mental clarity more effectively than rigid time blocks.
Personalization: Customizing Productivity Methods to Fit Your Work Style
The Pomodoro technique segments work into fixed 25-minute intervals with short breaks, promoting focus through structured time blocks, while the Ultradian rhythm aligns work periods with natural 90-120 minute energy cycles, enhancing sustained productivity based on biological rhythms. Customizing productivity methods to fit individual work styles involves assessing personal energy patterns and task demands to choose either time-fixed sessions or rhythm-based pacing. Tailoring these approaches improves concentration, reduces burnout, and optimizes overall work efficiency by respecting unique cognitive and physiological needs.
Workplace Applications: Which Technique Suits Your Job Role?
The Pomodoro Technique, involving 25-minute work intervals followed by short breaks, enhances focus and time management in roles with task-oriented workflows such as administrative support and software development. Ultradian rhythm scheduling aligns work phases with natural 90-120 minute energy cycles, benefiting creative and analytical jobs like design, research, and strategic planning by optimizing cognitive stamina. Choosing between these methods depends on job demands: Pomodoro suits repetitive or time-sensitive tasks, while Ultradian rhythms better support prolonged periods of deep concentration.
Potential Pitfalls: Common Mistakes in Using Pomodoro and Ultradian Techniques
Common pitfalls in using the Pomodoro technique include rigidly adhering to 25-minute work intervals without accounting for task complexity, leading to fragmented focus and burnout. With Ultradian rhythm-based productivity, misjudging the natural 90-120 minute energy cycles can result in working through fatigue phases, reducing efficiency and mental clarity. Both methods require flexibility and self-awareness to avoid overexertion and maintain sustained productivity.
Choosing the Right Productivity Method for Career Advancement
The Pomodoro Technique, which breaks work into 25-minute focused intervals followed by short breaks, enhances concentration and reduces mental fatigue for tasks requiring sustained attention. In contrast, the Ultradian Rhythm method aligns work periods with natural 90- to 120-minute cycles of high cognitive energy, optimizing productivity by leveraging the body's biological clock. Selecting the right productivity method depends on individual work patterns and job demands, with the Pomodoro Technique suited for structured tasks and the Ultradian Rhythm beneficial for roles requiring creative or prolonged mental engagement.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Pomodoros
Micro-Pomodoros, short work intervals typically lasting 5 to 10 minutes, leverage focused bursts of productivity aligned with the brain's natural attention span, contrasting with the Ultradian rhythm's 90-120 minute cycles of heightened alertness and rest. This technique enhances task engagement by minimizing cognitive fatigue through frequent breaks, optimizing productivity in fast-paced or fragmented work environments.
Ultradian Sprint Cycles
Ultradian Sprint Cycles leverage natural 90- to 120-minute energy rhythms to maximize sustained focus, contrasting with the fixed 25-minute intervals of the Pomodoro technique. Aligning work sessions with these biological cycles enhances productivity by synchronizing task intensity with peak cognitive performance periods.
Pomodoro Habit-Stacking
The Pomodoro Technique enhances productivity by breaking work into 25-minute focused intervals followed by short breaks, aligning well with habit-stacking to build consistent routines. Unlike Ultradian rhythms, which recommend 90-120 minute work cycles, Pomodoro's shorter sessions are more adaptable for integrating with multiple daily habits and improving sustained focus.
Ultradian Performance Zones
The Pomodoro technique cycles productivity into fixed 25-minute intervals followed by 5-minute breaks, while Ultradian Performance Zones align work with natural 90-120 minute body rhythms for deeper focus and sustained energy. Leveraging Ultradian rhythms enables enhanced cognitive function by syncing tasks with peak alertness phases, improving overall productivity more effectively than rigid Pomodoro timing.
Task Batching with Ultradian Breaks
Task batching within the Ultradian rhythm framework leverages natural 90-120 minute energy cycles to enhance productivity by aligning focused work periods with biological highs. Unlike the rigid 25-minute intervals of the Pomodoro technique, Ultradian breaks optimize concentration and rest, reducing cognitive fatigue and improving task completion efficiency.
Pomodoro-Enhanced Focus States
The Pomodoro technique enhances focus by structuring work into 25-minute intervals followed by short breaks, aligning with the brain's natural attention span to reduce fatigue and maintain high productivity. In comparison, Ultradian rhythm leverages 90-120 minute cycles of heightened alertness, but Pomodoro's time-boxed approach provides more frequent rest periods, optimizing sustained concentration and task completion.
Ultradian Flow Optimization
Ultradian rhythm-based flow optimization leverages natural 90- to 120-minute energy cycles to enhance productivity by aligning work periods with innate cognitive peaks, unlike the rigid 25-minute intervals of the Pomodoro technique. Aligning deep work sessions with ultradian cycles maximizes focus, reduces burnout, and sustains high performance throughout the day.
Adaptive Pomodoro Scheduling
Adaptive Pomodoro Scheduling tailors work intervals based on Ultradian rhythm cycles, enhancing productivity by aligning task focus with natural 90-120 minute energy fluctuations instead of fixed 25-minute sessions. This synergy optimizes cognitive performance and reduces burnout, leveraging biological rhythms for sustained concentration and efficient task management.
Chronotype-Aligned Ultradian Scheduling
Aligning work intervals with your chronotype using Chronotype-Aligned Ultradian Scheduling capitalizes on natural energy fluctuations occurring roughly every 90-120 minutes, enhancing sustained focus and productivity compared to the fixed 25-minute intervals of the Pomodoro Technique. This method synchronizes task engagement with ultradian rhythm peaks and rest periods during troughs, optimizing cognitive performance and reducing burnout.
Hybrid Pomodoro-Ultradian Workflow
The Hybrid Pomodoro-Ultradian Workflow leverages 25-minute focused Pomodoro intervals aligned with 90-minute Ultradian rhythm cycles to maximize mental energy and reduce fatigue. Integrating timely breaks within natural productivity peaks optimizes cognitive function and sustains high performance throughout the workday.
Pomodoro technique vs Ultradian rhythm for productivity. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com