Email communication often leads to frequent interruptions and slow decision-making, reducing overall productivity. Async work allows team members to respond at their own pace, fostering deeper focus and more thoughtful contributions. Prioritizing async communication can streamline workflows and enhance project efficiency in the modern workplace.
Table of Comparison
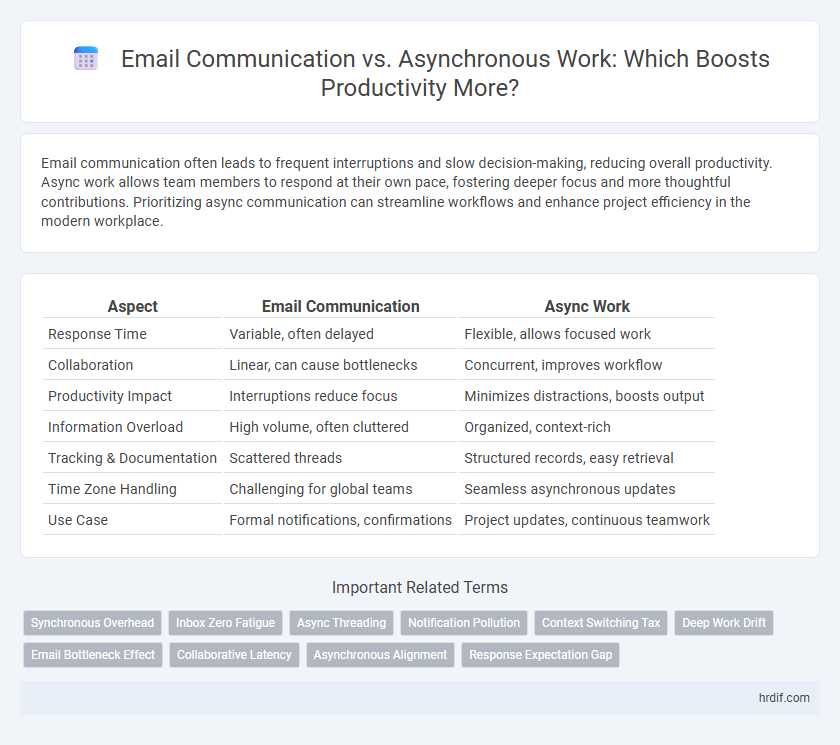
| Aspect | Email Communication | Async Work |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | Variable, often delayed | Flexible, allows focused work |
| Collaboration | Linear, can cause bottlenecks | Concurrent, improves workflow |
| Productivity Impact | Interruptions reduce focus | Minimizes distractions, boosts output |
| Information Overload | High volume, often cluttered | Organized, context-rich |
| Tracking & Documentation | Scattered threads | Structured records, easy retrieval |
| Time Zone Handling | Challenging for global teams | Seamless asynchronous updates |
| Use Case | Formal notifications, confirmations | Project updates, continuous teamwork |
The Evolution of Workplace Communication: Email vs Async Work
Email has been a foundational tool in workplace communication, enabling quick information exchange and task coordination across teams. However, async work models prioritize flexibility and focused productivity by allowing employees to respond at their own pace without the interruptions caused by constant email checking. The evolution from email-centric workflows to async communication platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams enhances team collaboration while minimizing time lost to email overload.
Defining Email Communication and Async Work
Email communication involves exchanging messages through electronic mail platforms, allowing for direct yet often delayed responses, which can interrupt workflow and reduce focus. Asynchronous work emphasizes completing tasks independently of real-time interaction, enabling individuals to manage their schedules and prioritize deep work without immediate digital interruptions. Both methods influence productivity by balancing the need for communication with the benefits of uninterrupted concentration.
The Impact of Email on Workplace Productivity
Email communication often leads to frequent interruptions, decreasing overall workplace productivity by diverting attention from deep, focused work. Studies show that employees spend up to 28% of their workweek managing emails, reducing time available for critical tasks. Async work models mitigate these disruptions by allowing individuals to prioritize tasks, enhancing efficiency and output quality.
Async Workflows: Advantages for Focus and Flexibility
Async workflows enhance productivity by minimizing constant email interruptions, allowing individuals to concentrate deeply on tasks without frequent context switching. This method offers flexibility to manage work on personalized schedules, accommodating diverse time zones and peak focus periods. Companies adopting async communication report improved efficiency, reduced stress, and higher employee satisfaction compared to traditional email-heavy environments.
Bottlenecks and Distractions: Limitations of Email
Email communication often creates bottlenecks due to delayed responses and overloaded inboxes, which significantly hinder workflow efficiency. Frequent email notifications disrupt deep focus, leading to increased distractions and reduced productivity in asynchronous work environments. Limiting reliance on email in favor of structured async collaboration tools can minimize these interruptions and streamline task management.
Async Work: Reducing Response Time Pressure
Async work significantly reduces response time pressure by allowing employees to process and respond to tasks at their own pace, enhancing focus and minimizing distractions caused by constant email checks. Unlike email communication, which often demands immediate replies and leads to task switching, async work supports deep concentration and improves overall productivity. Tools such as project management platforms and asynchronous messaging apps enable clear, organized, and time-flexible collaboration, further driving efficiency.
Collaboration Quality: Synchronous vs Asynchronous Approaches
Synchronous email communication enables real-time feedback, fostering immediate clarification and dynamic problem-solving that enhance collaboration quality. Asynchronous work promotes thoughtful responses and flexibility, reducing interruptions and allowing team members to manage their focus effectively. Balancing both methods optimizes productivity by combining the immediacy of synchronous exchanges with the depth and flexibility of asynchronous collaboration.
Managing Information Overload: Email Inboxes vs Async Platforms
Email inboxes often contribute to information overload by bombarding users with real-time notifications and cluttered threads, reducing focus and efficiency. Async platforms enable better management of tasks by organizing communications into categorized channels, allowing users to prioritize and respond on their own schedule. This structured approach to information flow minimizes distractions and enhances overall productivity in managing work-related communication.
Choosing the Right Tool: Matching Communication Methods to Task Types
Email communication suits tasks requiring detailed information exchange and formal documentation, enhancing clarity and accountability. Async work excels in collaborative projects needing flexible timing and reduces interruptions, boosting focus and deep work. Matching communication methods to the nature of the task optimizes productivity by leveraging the strengths of both tools effectively.
Best Practices for Integrating Email and Async Work for Maximum Productivity
Integrating email communication with asynchronous work requires strategic management of response times and clear prioritization to enhance productivity. Utilizing tools like shared task boards and setting specific email-checking intervals minimizes interruptions and ensures actionable items are addressed promptly. Establishing clear guidelines for which communications warrant immediate response versus those best handled asynchronously optimizes workflow efficiency and reduces cognitive load.
Related Important Terms
Synchronous Overhead
Email communication often introduces synchronous overhead due to immediate response expectations and frequent interruptions, which can significantly reduce productivity by fragmenting focus. In contrast, async work minimizes these disruptions by allowing individuals to manage their time effectively, leading to deeper concentration and higher-quality outputs.
Inbox Zero Fatigue
Email communication often leads to inbox zero fatigue as constant message checking disrupts focus, whereas async work minimizes interruptions, allowing deeper concentration and sustained productivity. Prioritizing asynchronous methods reduces cognitive load and prevents burnout associated with managing overwhelming email volumes.
Async Threading
Async threading in email communication significantly enhances productivity by allowing team members to respond at their convenience, reducing context-switching and minimizing immediate interruptions. This approach streamlines collaboration, improves focus, and facilitates clearer, more organized exchanges compared to traditional synchronous email exchanges.
Notification Pollution
Email communication often leads to notification pollution, disrupting focus with frequent alerts that fragment work sessions and reduce overall productivity. Async work minimizes these interruptions by consolidating messages into manageable batches, allowing deeper concentration and more efficient task completion.
Context Switching Tax
Email communication increases the context switching tax by frequently interrupting deep work, leading to reduced productivity and higher cognitive load. Async work minimizes disruptions, allowing individuals to maintain focus and complete tasks more efficiently by batching communication at optimal times.
Deep Work Drift
Email communication often disrupts focus by creating frequent interruptions, causing deep work drift that reduces overall productivity. Async work minimizes these distractions, allowing sustained concentration and more effective task completion.
Email Bottleneck Effect
Email communication often creates a bottleneck effect by accumulating unread messages, causing delays and reducing overall productivity. Async work minimizes interruptions by enabling team members to respond at their own pace, streamlining workflows and enhancing focus.
Collaborative Latency
Email communication often increases collaborative latency due to delayed responses and fragmented threads, which hinder real-time decision-making and workflow momentum. Async work reduces this latency by allowing team members to contribute at their own pace while maintaining continuous progress and clear documentation.
Asynchronous Alignment
Asynchronous work enhances productivity by enabling employees to align on tasks and objectives without the interruptions caused by real-time email communication. Leveraging async tools fosters focused work, reduces cognitive load, and supports a flexible workflow that scales across different time zones and teams.
Response Expectation Gap
Email communication often creates a response expectation gap that diminishes productivity by interrupting deep work and increasing cognitive load. Async work minimizes this gap by allowing individuals to manage their time efficiently, fostering focused tasks and reducing the pressure for immediate replies.
Email Communication vs Async Work for productivity. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com