The gig economy offers flexible opportunities that traditional employment often lacks, allowing individuals to choose when and how they work. Unlike conventional jobs with fixed schedules and roles, gig work provides a diverse range of income streams and skills development. This shift empowers workers to adapt rapidly to market demands and create personalized career paths.
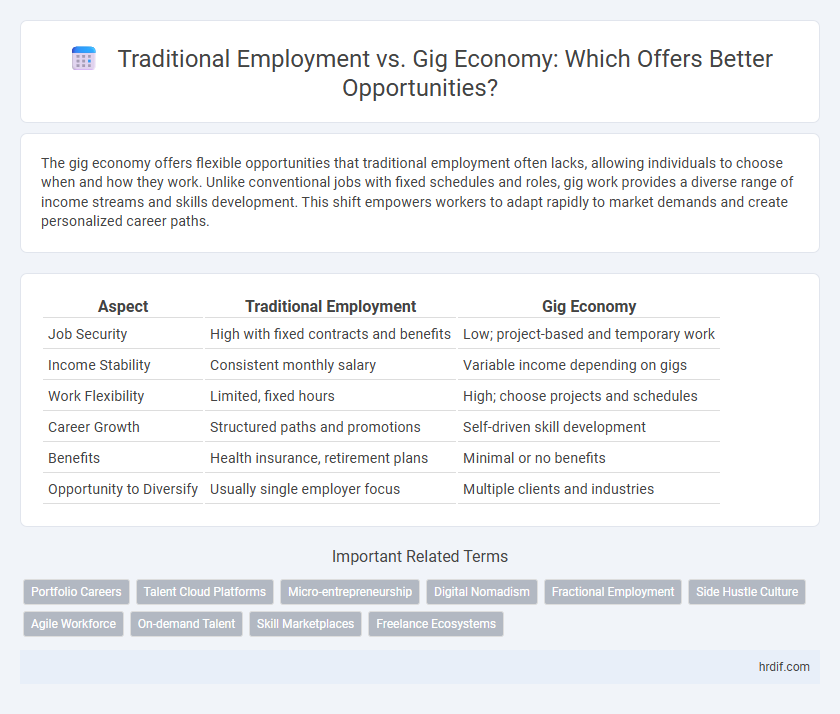
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Employment | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Job Security | High with fixed contracts and benefits | Low; project-based and temporary work |
| Income Stability | Consistent monthly salary | Variable income depending on gigs |
| Work Flexibility | Limited, fixed hours | High; choose projects and schedules |
| Career Growth | Structured paths and promotions | Self-driven skill development |
| Benefits | Health insurance, retirement plans | Minimal or no benefits |
| Opportunity to Diversify | Usually single employer focus | Multiple clients and industries |
Defining Traditional Employment and the Gig Economy
Traditional employment typically involves long-term contracts with a single employer, offering stable income, benefits, and structured work hours. The gig economy is characterized by short-term, flexible jobs often facilitated through digital platforms, allowing workers to engage in multiple projects. These contrasting models provide diverse opportunities, with traditional employment prioritizing security and the gig economy emphasizing autonomy and adaptability.
Career Growth Potential: Gig Economy vs Traditional Jobs
Gig economy roles offer flexible career paths with opportunities to develop diverse skills across multiple projects, fostering rapid personal growth and adaptability. Traditional jobs provide structured career advancement with clear hierarchies, performance metrics, and defined promotion tracks, ensuring long-term stability and incremental skill development. Balancing gig economy flexibility with traditional employment's growth frameworks can optimize overall career progression.
Financial Stability: Comparing Income Opportunities
Traditional employment often provides consistent financial stability through regular salaries, benefits, and predictable income streams, appealing to those seeking long-term security. The gig economy offers flexible income opportunities with potential for higher earnings based on skill, demand, and hours worked, but lacks guaranteed pay and benefits. Income volatility in gig work contrasts with the steady paycheck of traditional roles, influencing individual decisions based on financial risk tolerance and lifestyle preferences.
Flexibility and Work-Life Balance: Which Offers More?
The gig economy offers greater flexibility by allowing individuals to choose their working hours and projects, which significantly enhances work-life balance compared to traditional employment's fixed schedules and structured environments. Traditional employment provides stability and predictable income but often limits personal time due to rigid office hours and commute demands. Studies reveal gig workers report higher satisfaction in managing family commitments and leisure activities, making gig work more suitable for those prioritizing flexibility.
Skill Development and Advancement Opportunities
Traditional employment offers structured skill development programs and clear advancement pathways through promotions and certifications, providing long-term career growth. The gig economy enables rapid skill acquisition across diverse projects, fostering adaptability and entrepreneurial abilities but often lacks formal progression routes. Both models present unique opportunities for developing expertise, with traditional roles favoring stability and the gig economy prioritizing flexibility and breadth of experience.
Job Security: Long-term Prospects in Both Models
Traditional employment offers greater job security through steady income, benefits, and long-term contracts that foster career development. The gig economy provides flexible opportunities but often lacks consistent income and retirement benefits, leading to uncertain long-term prospects. Evaluating these models requires balancing stability against flexibility to match individual career goals and risk tolerance.
Benefits and Perks: What Each Employment Type Offers
Traditional employment offers benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, and job security, providing financial stability and long-term career growth opportunities. The gig economy provides flexibility, diverse income streams, and the ability to choose projects, appealing to those seeking autonomy and entrepreneurial experience. Access to perks depends on individual priorities, with traditional roles favoring structured benefits and gig roles emphasizing freedom and variety.
Networking and Professional Connections
Traditional employment offers structured networking opportunities through company events, mentorship programs, and established professional hierarchies that foster long-term relationships. The gig economy provides flexible, diverse connections across multiple clients and industries, enabling rapid expansion of a freelance professional's network. Both pathways present unique chances to build valuable contacts, but the gig economy demands proactive effort to sustain and leverage these relationships effectively.
Accessibility and Barriers to Entry
Traditional employment often has higher barriers to entry, requiring formal qualifications, lengthy application processes, and rigid schedules that limit accessibility for many individuals. In contrast, the gig economy offers lower entry barriers by enabling flexible work arrangements and minimal upfront requirements, making it more accessible to a diverse range of workers. This accessibility fosters opportunities for people with varying skill sets, geographic locations, and time availability to participate in the labor market.
Future Outlook: Evolving Opportunities in Both Sectors
The future outlook for opportunities in traditional employment and the gig economy highlights rapid evolution driven by technological advancements and shifting workforce preferences. Traditional employment continues to offer stability and structured career paths, while the gig economy expands flexible work options and diversified income streams through digital platforms like Uber, Fiverr, and Upwork. Emerging trends suggest hybrid models combining gig flexibility with traditional benefits will redefine workforce opportunities across industries by 2030.
Related Important Terms
Portfolio Careers
Portfolio careers offer greater opportunity by enabling individuals to combine multiple gig economy roles and freelance projects, diversifying income streams beyond traditional employment's single-source dependency. This flexible approach enhances skill development and adaptability, positioning workers advantageously in a rapidly evolving job market.
Talent Cloud Platforms
Talent Cloud Platforms revolutionize opportunity by bridging traditional employment's stability with the Gig economy's flexibility, enabling access to a diverse global talent pool. These platforms leverage advanced algorithms and real-time data to optimize job matching, maximizing both worker autonomy and employer reach in dynamic markets.
Micro-entrepreneurship
Micro-entrepreneurship thrives in the gig economy by offering flexible, diverse income streams and direct control over business growth, unlike traditional employment's fixed roles and limited advancement. This shift enables individuals to leverage digital platforms and personal skills for scalable, autonomous opportunities that bypass typical corporate constraints.
Digital Nomadism
Traditional employment offers stable income and structured career progression, but the gig economy fueled by digital nomadism provides unmatched flexibility and global work opportunities through platforms like Upwork and Fiverr. Digital nomads leverage remote work to access diverse projects across time zones, maximizing income potential while embracing lifestyle freedom.
Fractional Employment
Fractional employment in the gig economy offers flexible, skill-based opportunities that outperform traditional full-time roles by enabling professionals to work on multiple projects across industries, enhancing income diversity and career growth. This shift unlocks untapped potential for both workers seeking autonomy and companies aiming for specialized talent without long-term commitments.
Side Hustle Culture
Side hustle culture thrives in the gig economy, offering flexible opportunities for supplemental income beyond traditional employment's fixed schedules. This shift empowers individuals to diversify their income streams while leveraging digital platforms for freelance, part-time, or project-based work.
Agile Workforce
The gig economy offers unparalleled agility, enabling workers to seize diverse short-term opportunities and adapt quickly to market demands compared to traditional employment's fixed roles. This flexibility fosters an agile workforce that enhances innovation, productivity, and career growth in dynamic economic environments.
On-demand Talent
Traditional employment offers stability but limits flexibility, whereas the gig economy provides vast opportunities for on-demand talent to leverage diverse skills and access a global marketplace. Companies increasingly rely on gig workers to fill project-based roles quickly, maximizing efficiency and driving innovation in dynamic industries.
Skill Marketplaces
Skill marketplaces unlock new opportunities by connecting gig workers with diverse, short-term projects, offering flexible income streams that traditional employment often lacks. These platforms enable professionals to showcase specialized skills, accelerating job matching and expanding access to global markets beyond conventional full-time roles.
Freelance Ecosystems
Freelance ecosystems offer enhanced opportunities for flexible income streams and skill diversification compared to traditional employment, leveraging digital platforms that connect independent professionals to global markets. These ecosystems foster innovation and entrepreneurial growth by enabling individuals to capitalize on niche expertise and project-based work without long-term contractual obligations.
Traditional employment vs Gig economy for opportunity. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com