Traditional careers offer stability and clear advancement paths but can limit exposure to diverse skills and industries. Portfolio careers provide opportunities to develop a broad skill set through varied projects and roles, enhancing adaptability in a rapidly changing job market. Embracing a portfolio career can unlock unique opportunities by leveraging multiple talents and networks simultaneously.
Table of Comparison
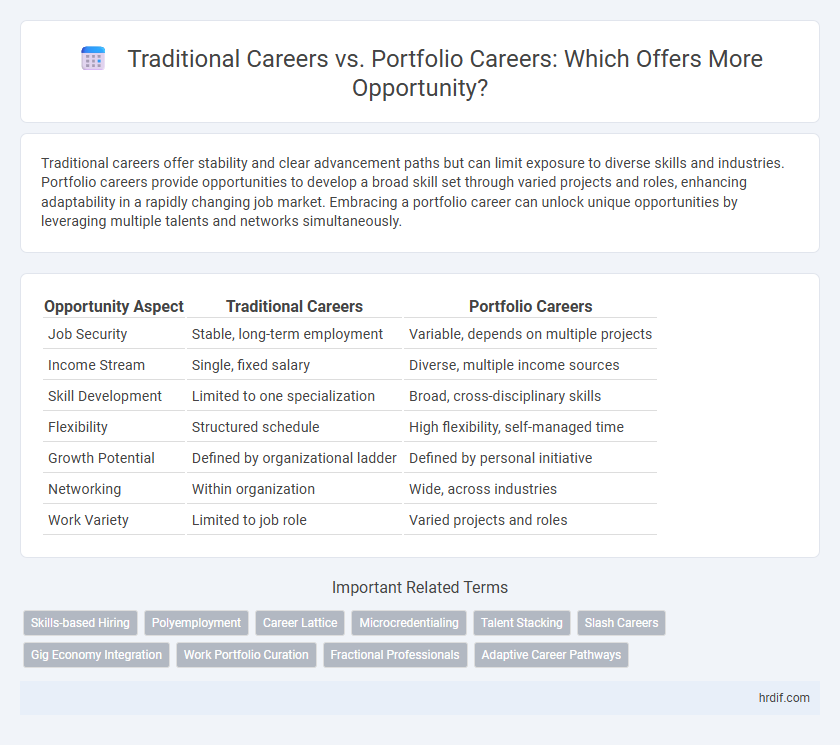
| Opportunity Aspect | Traditional Careers | Portfolio Careers |
|---|---|---|
| Job Security | Stable, long-term employment | Variable, depends on multiple projects |
| Income Stream | Single, fixed salary | Diverse, multiple income sources |
| Skill Development | Limited to one specialization | Broad, cross-disciplinary skills |
| Flexibility | Structured schedule | High flexibility, self-managed time |
| Growth Potential | Defined by organizational ladder | Defined by personal initiative |
| Networking | Within organization | Wide, across industries |
| Work Variety | Limited to job role | Varied projects and roles |
Defining Traditional Careers and Portfolio Careers
Traditional careers emphasize long-term employment within a single industry or organization, often featuring linear progression and job stability. Portfolio careers involve managing multiple simultaneous roles or projects across various fields, promoting skill diversity and flexible income streams. Opportunity in traditional careers lies in job security and specialization, while portfolio careers capitalize on adaptability and broad expertise to unlock diverse professional pathways.
Historical Evolution of Career Paths
Traditional careers historically emphasized long-term employment within a single organization, offering job security and steady progression but limited flexibility. Portfolio careers, emerging prominently in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, reflect a shift towards diverse skill sets and multiple income streams, driven by gig economies and digital transformation. This evolution highlights increasing opportunities for professionals to tailor careers around personal strengths and market demands rather than linear advancement.
Job Stability: Traditional vs Portfolio Approaches
Traditional careers often provide greater job stability through long-term employment contracts and predictable income streams, offering employees structured growth and benefits. Portfolio careers, characterized by multiple part-time roles or freelance projects, present greater flexibility but less income certainty, requiring continuous skill adaptation and proactive opportunity seeking. The choice between stability and adaptability defines how professionals navigate opportunities in evolving job markets.
Income Diversification and Financial Security
Portfolio careers offer significant income diversification by combining multiple revenue streams from diverse skills and projects, reducing dependency on a single employer or industry. Traditional careers typically provide more predictable but limited financial security through steady salaries and benefits, yet lack the flexibility to adapt swiftly to economic shifts. Embracing a portfolio career can enhance financial resilience by leveraging varied opportunities that adapt to market demands and mitigate income volatility.
Skill Development and Career Growth Opportunities
Traditional careers offer structured skill development through defined roles and clear promotion paths, fostering deep expertise in specific fields. Portfolio careers provide diverse skill acquisition by engaging in multiple roles or projects, enhancing adaptability and broadening professional capabilities. Combining varied experiences in a portfolio career can accelerate career growth by unlocking unique opportunities beyond conventional organizational hierarchies.
Work-Life Balance and Flexibility
Traditional careers often provide stable income but may limit work-life balance due to fixed schedules and less flexibility. Portfolio careers offer diverse income streams and greater control over time, enabling better adjustment to personal and professional needs. Emphasizing flexibility, portfolio careers present increased opportunities for tailored work arrangements that support overall well-being.
Networking and Professional Relationships
Traditional careers rely heavily on established networks within a single industry or organization, offering stability but limited diversity in professional relationships. Portfolio careers foster expansive networking across multiple fields, enhancing opportunities for collaboration and innovation. Building diverse professional connections through portfolio careers significantly increases access to new opportunities and career growth.
Adaptability in a Changing Job Market
Traditional careers provide stability but often lack flexibility, limiting adaptability in a rapidly evolving job market. Portfolio careers, combining multiple skills and roles, enhance resilience by allowing professionals to pivot and seize diverse opportunities. Embracing a portfolio approach enables continuous learning and agility, key factors for success amid technological advancements and shifting industry demands.
Personal Fulfillment and Job Satisfaction
Traditional careers often offer stability and a clear advancement path, but can limit personal fulfillment due to rigid roles and repetitive tasks. Portfolio careers provide diverse opportunities that align with varied interests, increasing job satisfaction through creative freedom and skill variety. Emphasizing personal fulfillment, portfolio careers enable individuals to tailor their work life to intrinsic motivations rather than external expectations.
Future Trends in Career Opportunities
Future career opportunities increasingly favor portfolio careers, allowing individuals to leverage diverse skills across multiple industries rather than relying on a single traditional career path. Technological advancements and the gig economy drive demand for adaptability, continuous learning, and multidisciplinary expertise. Data from the World Economic Forum indicates that 50% of all employees will need reskilling by 2025, highlighting a shift toward flexible, portfolio-based work models.
Related Important Terms
Skills-based Hiring
Skills-based hiring drives opportunity by valuing diverse competencies over fixed job roles, aligning more naturally with portfolio careers that showcase varied expertise across multiple projects. Traditional careers often emphasize linear progression and rigid qualifications, whereas portfolio careers unlock broader opportunities by highlighting adaptable, demonstrable skills in dynamic market environments.
Polyemployment
Polyemployment, a key aspect of portfolio careers, amplifies opportunity by enabling individuals to diversify income streams and skill sets across multiple roles simultaneously. This dynamic approach contrasts with traditional careers that rely on single-track employment, limiting exposure to varied professional experiences and market adaptability.
Career Lattice
Exploring career lattices reveals that portfolio careers offer greater opportunity for skill diversification and lateral movement compared to traditional linear careers, enabling professionals to adapt to evolving job markets more effectively. Embracing a career lattice through portfolio careers fosters continuous learning and cross-industry experience, maximizing long-term career growth and resilience.
Microcredentialing
Microcredentialing enhances opportunity by equipping professionals with targeted skills that bridge gaps in both traditional and portfolio careers. This flexible approach increases employability and adaptability, enabling seamless transitions and growth in dynamic job markets.
Talent Stacking
Talent stacking enhances opportunity by combining diverse skills, making portfolio careers more adaptable and resilient than traditional careers focused on a single specialization. This approach leverages multiple talents to create unique value propositions, increasing employability and entrepreneurial potential in dynamic job markets.
Slash Careers
Slash careers, characterized by professionals juggling multiple roles such as writer-entrepreneur or designer-consultant, create greater opportunity by diversifying income streams and skill sets compared to traditional careers with a single focus. This approach enhances adaptability in a fluctuating job market and maximizes personal growth by blending passions and expertise into a cohesive portfolio.
Gig Economy Integration
Traditional careers offer stability and long-term growth within a single industry, while portfolio careers leverage gig economy integration by combining multiple freelance and contract roles to maximize diverse income streams and skill development. The gig economy enables portfolio careerists to access flexible opportunities across platforms, enhancing adaptability and resilience in a rapidly changing job market.
Work Portfolio Curation
Work portfolio curation enhances opportunity by showcasing diverse skills and projects, making candidates adaptable to evolving job markets compared to traditional careers limited to singular roles. Portfolio careers leverage curated work samples to attract employers seeking multifaceted talent and increased flexibility.
Fractional Professionals
Fractional professionals illustrate the shift from traditional careers to portfolio careers by leveraging diverse skills across multiple part-time roles, maximizing opportunity and flexibility. This model enhances professional growth and income potential, contrasting with the fixed trajectory of traditional full-time employment.
Adaptive Career Pathways
Adaptive career pathways embrace portfolio careers by combining diverse skills and roles, enabling individuals to seize multiple opportunities in evolving job markets. Traditional careers offer stability but limit flexibility, while portfolio careers enhance resilience and growth through adaptive, skill-based opportunities across industries.
Traditional Careers vs Portfolio Careers for opportunity. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com