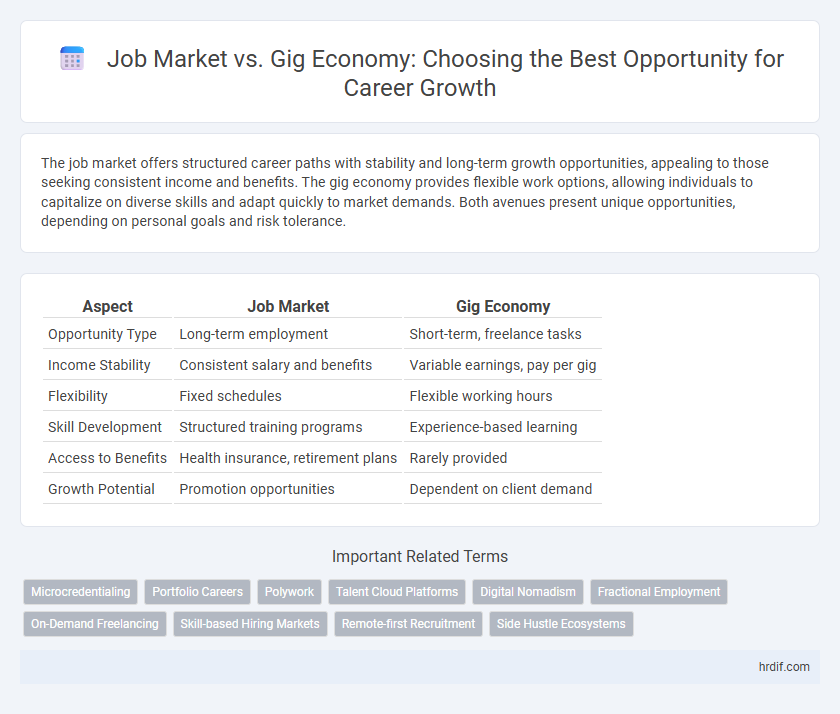
The job market offers structured career paths with stability and long-term growth opportunities, appealing to those seeking consistent income and benefits. The gig economy provides flexible work options, allowing individuals to capitalize on diverse skills and adapt quickly to market demands. Both avenues present unique opportunities, depending on personal goals and risk tolerance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Job Market | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Opportunity Type | Long-term employment | Short-term, freelance tasks |
| Income Stability | Consistent salary and benefits | Variable earnings, pay per gig |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedules | Flexible working hours |
| Skill Development | Structured training programs | Experience-based learning |
| Access to Benefits | Health insurance, retirement plans | Rarely provided |
| Growth Potential | Promotion opportunities | Dependent on client demand |
Job Market Stability vs Gig Economy Flexibility
The traditional job market offers stability through consistent income, benefits, and long-term career growth, making it ideal for individuals seeking financial security. In contrast, the gig economy provides unparalleled flexibility, allowing workers to choose projects, control schedules, and diversify income sources. Balancing stability and flexibility is crucial for maximizing opportunities in today's evolving employment landscape.
Income Potential: Traditional Jobs vs Gig Work
Traditional jobs offer stable, predictable income with benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, appealing to those seeking long-term financial security. Gig economy work provides flexible opportunities to increase earnings through multiple short-term projects, but income can be inconsistent and lacks traditional job benefits. Evaluating income potential requires balancing steady paychecks against the scalability and variability of gig work earnings.
Skills Development in the Job Market vs Gig Economy
The job market offers structured skills development through formal training programs and clear career progression, enabling employees to build and refine expertise over time. In contrast, the gig economy promotes on-the-fly learning by requiring workers to adapt quickly and diversify skills across multiple short-term projects. Leveraging opportunities in both environments can enhance adaptability and expand a skill set tailored to evolving labor demands.
Career Advancement Opportunities Compared
The traditional job market offers structured career advancement opportunities through promotions, skill development programs, and long-term growth paths within organizations. In contrast, the gig economy provides flexibility and diverse project experiences but often lacks clear pathways for consistent career progression and formal recognition. Professionals seeking steady upward mobility may find traditional employment more conducive, while gig workers benefit from varied experiences that can enhance adaptability and entrepreneurial skills.
Work-Life Balance: Employment vs Gig Opportunities
The job market often provides structured work hours and benefits that promote a stable work-life balance, offering employees predictable schedules and paid time off. In contrast, gig economy opportunities allow for flexible work arrangements, enabling individuals to set their own hours but often lack traditional benefits, which can lead to inconsistent income and work-life boundaries. Evaluating work-life balance in employment versus gig roles involves considering stability, flexibility, and the presence or absence of employer-sponsored benefits.
Benefits and Security: Jobs vs Gig Economy
Traditional jobs provide stable income, healthcare benefits, and retirement plans, offering long-term financial security and legal protections. The gig economy offers flexible work hours and diverse income streams but often lacks benefits such as paid leave, health insurance, and job security. Workers in the gig economy must manage inconsistent earnings and bear the burden of self-employment taxes and expenses.
Networking and Professional Growth in Each Sector
The traditional job market offers structured networking opportunities through company events, professional associations, and mentorship programs that foster long-term career growth. In contrast, the gig economy relies heavily on digital platforms and social media for networking, providing flexibility but often limited access to sustained professional development. Both sectors present unique opportunities for expanding connections, with the job market emphasizing stability and the gig economy prioritizing diverse, project-based engagements.
Entry Barriers: Job Market versus Gig Economy
Entry barriers in the traditional job market often include stringent educational requirements, extensive experience, and formal application processes, creating obstacles for many job seekers. In contrast, the gig economy lowers entry barriers by offering flexible opportunities that typically require minimal qualifications and allow workers to start quickly through digital platforms. This accessibility expands opportunities for individuals seeking immediate income and skill development without the constraints of conventional employment.
Navigating Uncertainty in Both Career Paths
Navigating uncertainty in both the traditional job market and the gig economy requires adaptability and proactive skill development. Professionals must continuously assess market trends, leveraging platforms like LinkedIn for jobs and Upwork or Fiverr for freelance gigs to maximize opportunities. Emphasizing flexibility and building a diverse portfolio enhances resilience against economic fluctuations and job instability in either career path.
Long-Term Career Prospects: Jobs vs Gigs
Long-term career prospects significantly differ between the job market and the gig economy. Traditional jobs often provide stability, benefits, and opportunities for professional growth within a structured environment. Conversely, gig economy roles offer flexibility and diverse experiences but may lack consistent income and formal career advancement pathways.
Related Important Terms
Microcredentialing
Microcredentialing enhances opportunities in both the traditional job market and gig economy by providing verified, skill-specific credentials that increase employability and project acquisition. These compact qualifications bridge the gap between formal education and practical demand, enabling workers to swiftly adapt to evolving industry needs and monetize specialized skills.
Portfolio Careers
Portfolio careers offer a flexible approach in the evolving job market, allowing professionals to combine multiple gigs, freelance projects, and part-time roles to diversify income streams and enhance skill sets. This model leverages the gig economy's demand for specialized talents while providing stability and growth opportunities typically found in traditional employment.
Polywork
Polywork leverages the gig economy by enabling professionals to showcase diverse skills and multiple income streams beyond traditional job market constraints. This platform maximizes opportunity by connecting users with flexible projects and collaborative roles, fostering career growth in a dynamic labor landscape.
Talent Cloud Platforms
Talent cloud platforms revolutionize opportunity by seamlessly connecting professionals with flexible gigs and traditional jobs, enhancing market accessibility and workforce agility. These platforms leverage advanced algorithms and data analytics to match talent with real-time demand, driving efficiency and expanding economic potential in both the job market and gig economy.
Digital Nomadism
The rise of the gig economy offers digital nomads unparalleled flexibility and diverse income streams compared to traditional job markets, enabling professionals to work remotely across global time zones. Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr empower location-independent workers to capitalize on skills in web development, content creation, and digital marketing, driving economic opportunity beyond conventional employment structures.
Fractional Employment
Fractional employment bridges the job market and gig economy by offering flexible, project-based roles that allow professionals to work for multiple companies simultaneously. This model increases opportunity by providing diversified income streams and access to specialized skills without full-time commitments.
On-Demand Freelancing
On-demand freelancing within the gig economy offers unparalleled flexibility and immediate income opportunities compared to traditional job markets, enabling workers to leverage digital platforms to connect with clients globally. This shift toward gig-based opportunities emphasizes project-based engagement and real-time demand fulfillment, disrupting conventional employment models by prioritizing autonomy and decentralized work structures.
Skill-based Hiring Markets
Skill-based hiring markets in the job market prioritize long-term career growth and stability by matching candidates' expertise with specialized roles, fostering sustained professional development. In contrast, the gig economy emphasizes flexible, project-based opportunities that leverage specific skills for short-term contracts, enabling rapid entry and diverse experience accumulation.
Remote-first Recruitment
The remote-first recruitment model significantly expands opportunity by bridging the traditional job market with the gig economy, enabling access to a broader talent pool regardless of location. This approach leverages digital platforms to offer flexible, project-based roles alongside full-time positions, driving workforce diversity and increased employment options globally.
Side Hustle Ecosystems
The job market offers structured opportunities with stable income and benefits, while the gig economy thrives on flexible, project-based roles fueling side hustle ecosystems that connect freelancers, platforms, and clients seamlessly. Side hustle ecosystems leverage digital platforms like Upwork and Fiverr, enabling individuals to diversify income streams and foster entrepreneurial growth outside traditional employment channels.
Job Market vs Gig Economy for Opportunity Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com