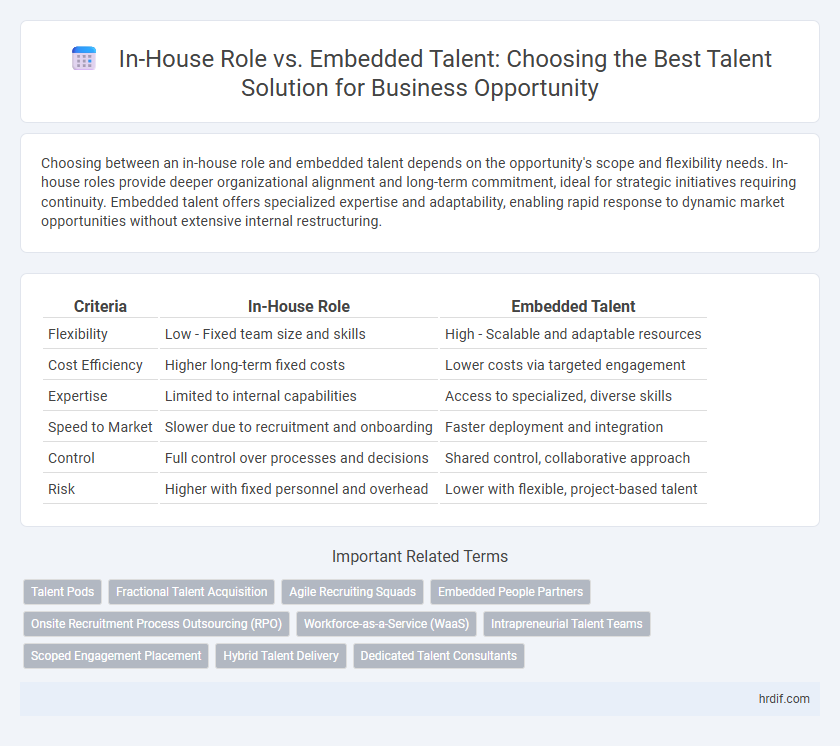
Choosing between an in-house role and embedded talent depends on the opportunity's scope and flexibility needs. In-house roles provide deeper organizational alignment and long-term commitment, ideal for strategic initiatives requiring continuity. Embedded talent offers specialized expertise and adaptability, enabling rapid response to dynamic market opportunities without extensive internal restructuring.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | In-House Role | Embedded Talent |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Low - Fixed team size and skills | High - Scalable and adaptable resources |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher long-term fixed costs | Lower costs via targeted engagement |
| Expertise | Limited to internal capabilities | Access to specialized, diverse skills |
| Speed to Market | Slower due to recruitment and onboarding | Faster deployment and integration |
| Control | Full control over processes and decisions | Shared control, collaborative approach |
| Risk | Higher with fixed personnel and overhead | Lower with flexible, project-based talent |
Defining In-House Roles and Embedded Talent
In-house roles refer to employees directly hired and managed within an organization, possessing deep institutional knowledge and long-term commitment to company goals. Embedded talent consists of external experts integrated into teams for specific projects, offering flexibility and specialized skills without permanent employment obligations. Understanding the distinctions enhances strategic workforce planning to maximize operational efficiency and innovation opportunities.
Key Differences Between In-House and Embedded Opportunities
In-house roles focus on deep organizational integration and long-term commitment, offering employees a stable environment with access to internal resources and direct influence on company culture. Embedded talent operates within client or partner organizations, providing specialized expertise and flexibility to adapt quickly to evolving project needs without the limitations of traditional employment structures. The key difference lies in control and scalability: in-house roles emphasize consistency and alignment with internal goals, while embedded talent excels in agility and rapid deployment across diverse opportunities.
Career Growth Potential: In-House vs Embedded Talent
In-house roles offer structured career growth with clear promotion paths and skill development aligned to the company's long-term goals, fostering deep organizational knowledge. Embedded talent provides rapid exposure to diverse projects and industries, accelerating skill acquisition and adaptability but may face limited upward mobility within a single entity. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing stability and internal advancement versus varied experience and flexible career trajectories.
Skill Development in In-House and Embedded Settings
In-house roles offer structured skill development through consistent training programs and deeper integration within company culture, fostering long-term expertise growth. Embedded talent gains diverse, project-specific skills by working across multiple teams or external clients, enhancing adaptability and broad industry knowledge. Both settings drive valuable skill development, but in-house roles emphasize specialized mastery while embedded talent cultivates versatile capabilities.
Access to Networking and Professional Connections
In-house roles offer employees direct access to a company's internal networks and established professional relationships, facilitating smoother collaboration and faster opportunity identification. Embedded talent, working within client environments, gains diverse external connections across industries, enhancing cross-sector networking potential and broadening opportunity pipelines. Both approaches provide unique advantages in expanding professional connections critical for career and business growth.
Job Stability: Which Offers Greater Security?
In-house roles typically offer greater job stability due to long-term contracts and clear career progression within a single organization, reducing the risk of sudden job loss. Embedded talent, while flexible and often project-based, faces variability in contract duration and continuity, posing potential instability. Companies valuing consistent operational control often prefer in-house roles to maximize employee retention and institutional knowledge.
Exploring Compensation and Benefits Packages
In-house roles typically offer structured compensation packages, including fixed salaries, comprehensive health benefits, retirement plans, and potential bonuses, creating financial predictability for employees. Embedded talent arrangements often provide more flexible remuneration models, such as project-based pay or equity stakes, appealing to professionals seeking performance-driven earnings. Comparing these options requires evaluating total rewards, including non-monetary benefits like professional development opportunities and work-life balance tailored to individual career goals.
Work Culture: Integrating in In-House vs Embedded Roles
Work culture integration significantly differs between in-house roles and embedded talent, with in-house employees often benefiting from a cohesive environment aligned with company values and long-term goals. Embedded talent operates within client environments, requiring adaptability to diverse cultures and communication styles, which may challenge seamless collaboration but fosters flexibility and specialized expertise. Organizations optimize opportunity by balancing the stability of in-house roles with the dynamic integration of embedded talent to enhance innovation and operational efficiency.
Advancing Your Career Pathway: Opportunity Analysis
Evaluating in-house roles versus embedded talent reveals distinct opportunities for advancing your career pathway through skill diversification and organizational influence. In-house positions offer sustained growth within a single corporate culture, fostering deep expertise and strong internal networks essential for leadership roles. Embedded talent, often positioned within multiple projects across varied teams, accelerates adaptability and cross-functional experience, enhancing marketability and strategic impact in dynamic industries.
Choosing the Right Fit: In-House Role or Embedded Talent?
Choosing the right fit between in-house roles and embedded talent hinges on a company's strategic goals, budget constraints, and project scope. In-house roles offer deeper organizational alignment and long-term commitment, while embedded talent provides specialized skills and flexibility for targeted initiatives. Evaluating factors such as scalability, expertise requirements, and integration challenges ensures optimal opportunity capture and resource allocation.
Related Important Terms
Talent Pods
Talent Pods offer a flexible blend of in-house role stability and embedded talent's adaptability, optimizing opportunity capture by fostering focused collaboration and rapid scalability. Leveraging Talent Pods enhances project efficiency and innovation, ensuring businesses can quickly respond to evolving market demands while maintaining core expertise internally.
Fractional Talent Acquisition
Fractional Talent Acquisition offers a flexible opportunity to optimize workforce capabilities by integrating specialized embedded talent without the long-term commitment of expanding an in-house team. This approach enables companies to access industry-specific expertise and scalability while maintaining cost-efficiency and agility in talent management.
Agile Recruiting Squads
Agile recruiting squads enhance opportunity capture by embedding talent directly within business units, accelerating decision-making and aligning skills with dynamic project needs more effectively than traditional in-house roles. This embedded approach leverages cross-functional expertise and real-time collaboration to swiftly address talent gaps, optimize workforce agility, and increase the precision of candidate placements in fast-evolving markets.
Embedded People Partners
Embedded People Partners drive opportunity by integrating deeply within business units to provide tailored talent solutions that align with strategic goals, enhancing agility and responsiveness. This approach leverages real-time insights and close collaboration, outperforming traditional in-house roles by fostering proactive workforce planning and dynamic employee engagement.
Onsite Recruitment Process Outsourcing (RPO)
Onsite Recruitment Process Outsourcing (RPO) maximizes hiring efficiency by embedding talent directly within the client's operations, allowing seamless alignment with company culture and immediate access to talent acquisition expertise. In-house roles may offer familiarity but often lack the scalability and specialized recruitment technology that embedded RPO teams provide, driving faster, cost-effective talent acquisition and stronger workforce agility.
Workforce-as-a-Service (WaaS)
Workforce-as-a-Service (WaaS) combines the agility of embedded talent with the reliability of in-house roles, allowing organizations to scale their workforce on demand while maintaining control over core competencies. This hybrid approach optimizes operational efficiency and agility by leveraging specialized external expertise without the overhead of full-time employment.
Intrapreneurial Talent Teams
In-house intrapreneurial talent teams drive opportunity by fostering innovation within the organizational culture, leveraging deep company knowledge to identify and pursue new growth avenues. Embedded talent, while agile and externally sourced, often lacks the intrinsic alignment and long-term commitment that in-house teams bring to sustained opportunity development.
Scoped Engagement Placement
Scoped engagement placements provide clear parameters and deliverables that optimize opportunity realization by aligning embedded talent directly with project-specific needs, unlike in-house roles that often encompass broader, less defined responsibilities. Leveraging embedded talent through scoped engagements enhances agility and focus, ensuring targeted expertise drives measurable impact within defined timeframes.
Hybrid Talent Delivery
Hybrid talent delivery leverages both in-house roles and embedded talent to maximize flexibility and expertise within a single opportunity framework. Combining permanent staff with strategically integrated external professionals enhances innovation, reduces costs, and accelerates project outcomes by aligning specialized skills directly with business needs.
Dedicated Talent Consultants
Dedicated Talent Consultants enhance opportunity realization by merging in-house role expertise with embedded talent agility, ensuring tailored recruitment strategies that align closely with company culture and immediate business needs. Leveraging deep industry knowledge, they streamline talent acquisition processes, reduce time-to-hire, and drive higher retention rates by fostering authentic candidate engagement within the organizational ecosystem.
In-House Role vs Embedded Talent for opportunity. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com