Employee roles provide consistent, deep engagement with company culture and long-term objectives, fostering stability and specialized expertise. Fractional work offers flexible, cost-effective access to diverse skills and perspectives for specific projects or periods. Balancing both approaches can maximize opportunity by aligning resource allocation with evolving business needs.
Table of Comparison
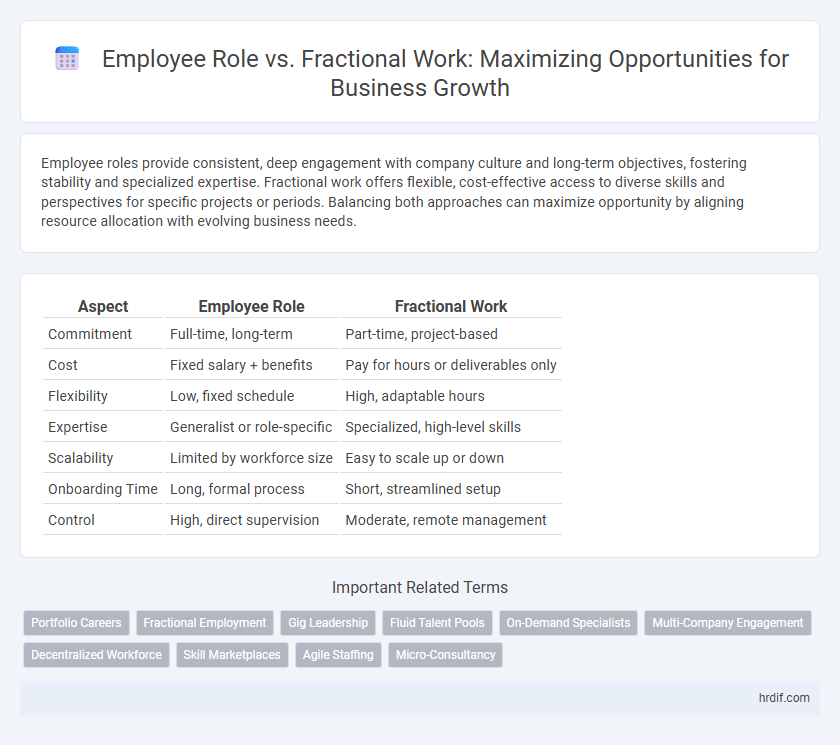
| Aspect | Employee Role | Fractional Work |
|---|---|---|
| Commitment | Full-time, long-term | Part-time, project-based |
| Cost | Fixed salary + benefits | Pay for hours or deliverables only |
| Flexibility | Low, fixed schedule | High, adaptable hours |
| Expertise | Generalist or role-specific | Specialized, high-level skills |
| Scalability | Limited by workforce size | Easy to scale up or down |
| Onboarding Time | Long, formal process | Short, streamlined setup |
| Control | High, direct supervision | Moderate, remote management |
Understanding Employee Roles in Today’s Job Market
Understanding employee roles in today's job market requires recognizing the growing importance of flexibility and specialized skills, where fractional work offers opportunities for businesses to access expert talent without full-time commitments. Employees increasingly seek roles that provide autonomy and project-based assignments, aligning with organizational needs for agility and cost efficiency. Embracing fractional roles can enhance innovation and productivity by leveraging diverse expertise tailored to specific business objectives.
Exploring the Rise of Fractional Work Opportunities
The rise of fractional work opportunities challenges traditional employee roles by offering flexible, project-based engagements that align with evolving business needs. Companies benefit from accessing specialized skills without long-term commitments, while professionals gain diverse experiences and work-life balance. This shift emphasizes strategic workforce agility and optimized resource allocation in a competitive market.
Key Differences: Traditional Employment vs. Fractional Work
Traditional employment offers employees defined roles, consistent hours, and full integration within organizational structures, fostering long-term career growth and job security. Fractional work provides flexible, project-based engagements with specialized tasks, allowing professionals to contribute their expertise to multiple companies without the constraints of a full-time position. Key differences include commitment level, compensation models, and scope of responsibilities, with traditional employees benefiting from company culture immersion while fractional workers gain variety and autonomy.
Advantages of Employee Roles for Career Growth
Employee roles offer structured career progression through consistent skill development, performance evaluations, and access to internal training programs. Full-time employees benefit from mentorship opportunities and clearer pathways to leadership positions within the company. Employer investment in permanent staff enhances job security and long-term professional growth compared to the variable nature of fractional work.
Benefits of Fractional Work for Skill Expansion
Fractional work offers employees the chance to engage with diverse projects across multiple industries, accelerating skill expansion and adaptability. This flexible model allows professionals to develop specialized expertise while balancing various roles, enhancing their marketability and career growth. Employers benefit from access to a broad range of talents without long-term commitments, fostering innovation and agility within teams.
Opportunity for Advancement: Employee vs. Fractional Worker
Employees often experience greater opportunities for advancement due to structured career paths, access to training programs, and internal networking within an organization. Fractional workers, while gaining diverse experiences across multiple industries, generally face limited upward mobility within a single company due to the part-time nature of their roles. Companies typically prioritize full-time employees for leadership development and long-term growth initiatives, enhancing their potential for career progression.
Flexibility and Work-Life Balance: A Comparative Analysis
Employee roles typically provide structured schedules and consistent responsibilities, supporting stability but often limiting flexibility. Fractional work offers adaptable hours and diverse projects, enhancing work-life balance by allowing employees to tailor workloads and time commitments. This flexibility fosters opportunities for personal priorities and professional growth without the constraints of full-time employment.
Financial Outlook: Salary vs. Fractional Income Potential
Employee roles offer stable salaries and predictable benefits, providing consistent financial security and long-term career growth. Fractional work presents flexible income potential, often leading to higher earnings through multiple simultaneous contracts but with variable cash flow and limited benefits. Evaluating financial outlook requires balancing guaranteed salary stability against the entrepreneurial opportunity and income scalability of fractional roles.
Navigating Job Security and Stability in Both Models
Employees in traditional roles often benefit from greater job security and structured career development, while fractional work offers flexibility but may lack long-term stability. Understanding contract terms and company policies is essential for navigating employment risks and securing consistent income streams. Strategic networking and continuous skill development are crucial for maximizing opportunity regardless of the employment model.
Choosing the Right Fit: Employee Role or Fractional Work for Your Career
Choosing between an employee role and fractional work depends on career goals, work-life balance, and desired flexibility. Employee roles offer stability, consistent income, and opportunities for long-term growth within a company, while fractional work provides varied projects, autonomy, and the chance to develop diverse skills across industries. Evaluating your personal priorities and the specific demands of your field will help determine the optimal path for professional development and opportunity maximization.
Related Important Terms
Portfolio Careers
Portfolio careers leveraging fractional work enable professionals to diversify skillsets and income streams while balancing multiple projects simultaneously, increasing overall marketability and resilience. Employee roles typically offer stability and defined responsibilities, but portfolio careers provide greater flexibility and opportunities for continuous growth and innovation.
Fractional Employment
Fractional employment offers businesses flexible access to specialized skills without the long-term commitment and overhead associated with full-time employee roles. This model enables organizations to capitalize on project-based opportunities, optimize costs, and rapidly scale talent according to evolving needs.
Gig Leadership
Gig leadership in fractional work environments enhances opportunity by enabling employees to take on specialized, project-based roles that drive innovation and agility. This model maximizes talent utilization and fosters dynamic leadership, contrasting with traditional employee roles that often limit flexibility and scope of influence.
Fluid Talent Pools
Fluid talent pools enable organizations to leverage fractional work by matching specialized skills with project-based opportunities, maximizing workforce flexibility and efficiency. Employee roles often lack this adaptability, limiting the ability to rapidly redeploy talent across evolving business needs and reducing overall organizational agility.
On-Demand Specialists
On-demand specialists offer businesses flexible access to expert skills without the long-term commitment of full-time employee roles, optimizing cost-efficiency and project-specific expertise. This shift toward fractional work creates opportunities for companies to scale quickly, tap into niche talent pools, and respond dynamically to market demands.
Multi-Company Engagement
Employee roles foster deeper organizational alignment and long-term commitment, enabling consistent performance and strategic growth within a single company. Fractional work offers flexibility and diverse expertise across multiple companies simultaneously, maximizing opportunities for innovation and cross-industry collaboration.
Decentralized Workforce
Decentralized workforce models leverage fractional work, enabling organizations to tap into specialized talent on-demand without the constraints of permanent employee roles. This flexibility enhances opportunity-driven agility, allowing companies to scale swiftly and optimize resource allocation across diverse projects and geographies.
Skill Marketplaces
Skill marketplaces expand opportunity by connecting specialized fractional workers with employers seeking specific expertise for project-based roles, enhancing flexibility beyond traditional employee roles. These platforms enable companies to tap into a diverse talent pool, optimizing workforce agility and cost-efficiency in rapidly changing markets.
Agile Staffing
Agile staffing embraces fractional work by enabling businesses to rapidly allocate specialized talent for specific projects, boosting flexibility and reducing overhead compared to traditional full-time employee roles. This dynamic approach maximizes opportunity by aligning expert skills with evolving business needs while maintaining cost-efficiency and scalability.
Micro-Consultancy
Micro-consultancy within fractional work offers companies targeted expertise and flexibility, enabling businesses to address specific challenges without the long-term commitment of full-time employees. Opportunity in this model arises from leveraging specialized skills on-demand, optimizing resource allocation and accelerating project outcomes.
Employee Role vs Fractional Work for Opportunity Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com