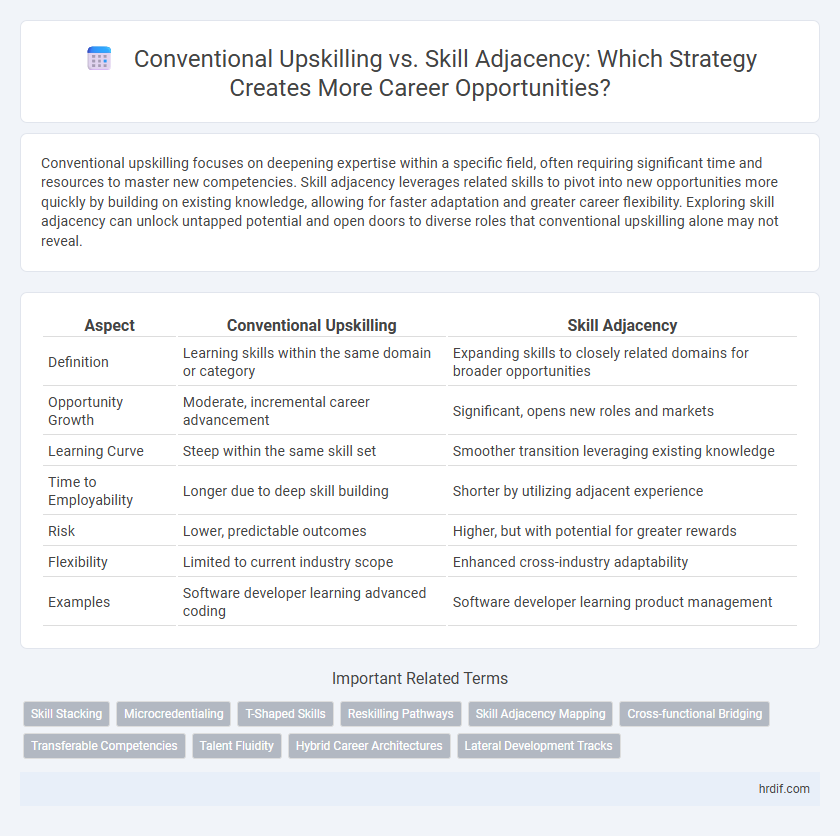
Conventional upskilling focuses on deepening expertise within a specific field, often requiring significant time and resources to master new competencies. Skill adjacency leverages related skills to pivot into new opportunities more quickly by building on existing knowledge, allowing for faster adaptation and greater career flexibility. Exploring skill adjacency can unlock untapped potential and open doors to diverse roles that conventional upskilling alone may not reveal.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Conventional Upskilling | Skill Adjacency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning skills within the same domain or category | Expanding skills to closely related domains for broader opportunities |
| Opportunity Growth | Moderate, incremental career advancement | Significant, opens new roles and markets |
| Learning Curve | Steep within the same skill set | Smoother transition leveraging existing knowledge |
| Time to Employability | Longer due to deep skill building | Shorter by utilizing adjacent experience |
| Risk | Lower, predictable outcomes | Higher, but with potential for greater rewards |
| Flexibility | Limited to current industry scope | Enhanced cross-industry adaptability |
| Examples | Software developer learning advanced coding | Software developer learning product management |
Understanding Conventional Upskilling
Conventional upskilling involves acquiring additional knowledge and competencies within the same functional area, emphasizing depth over breadth in skill development. This traditional approach often requires formal training programs, certifications, and structured learning paths tailored to enhance existing expertise. Understanding conventional upskilling highlights its role in maintaining technical proficiency and improving efficiency within established roles, yet it may limit exposure to adjacent opportunities that drive innovation and career flexibility.
Exploring Skill Adjacency Concepts
Exploring skill adjacency concepts reveals opportunities for accelerated career growth by leveraging related capabilities rather than relying solely on conventional upskilling methods. Skill adjacency emphasizes identifying and acquiring competencies that align closely with existing expertise, enabling seamless transitions and enhanced proficiency in new domains. This approach unlocks broader professional possibilities by strategically expanding skill sets within adjacent areas.
Traditional Upskilling: Advantages and Drawbacks
Traditional upskilling focuses on deepening expertise within a specific domain, enhancing proficiency and productivity in well-defined roles. Its advantages include structured learning paths and clear skill benchmarks, promoting mastery and career advancement. However, its drawbacks involve slower adaptability to rapidly changing industries and limited exposure to diverse skill sets, which can hinder agility in seizing emerging opportunities.
The Power of Skill Adjacency in Career Growth
Skill adjacency leverages existing competencies by expanding into related areas, enabling faster and more efficient career growth than conventional upskilling methods that often require starting from scratch. This approach maximizes the use of transferable skills, increasing employability and opening doors to new opportunities with less effort and time investment. Emphasizing skill adjacency leads to agile career development aligned with evolving industry demands and innovation trends.
Comparing Employment Outcomes: Upskilling vs Skill Adjacency
Conventional upskilling focuses on deepening existing skills within a specific domain, often resulting in incremental employment growth within the same industry. Skill adjacency leverages transferable skills to pivot into related fields, producing more diverse job opportunities and higher adaptability in dynamic markets. Studies show workers pursuing skill adjacency experience faster employment gains and greater resilience against automation threats compared to those solely engaged in traditional upskilling.
Identifying Skill Gaps and Adjacency Opportunities
Conventional upskilling targets existing skill gaps by enhancing proficiency within defined roles, often relying on training programs that address current job demands. Skill adjacency uncovers new growth opportunities by identifying complementary skills that expand an employee's capabilities beyond their core expertise, fostering agility in evolving markets. Leveraging skill adjacency alongside traditional methods enables organizations to strategically bridge gaps while unlocking untapped potential for innovation and career progression.
Industry Demand: What Employers Prefer
Employers increasingly prioritize skill adjacency over conventional upskilling, valuing professionals who can leverage existing expertise to quickly adapt to related roles. Industry demand favors candidates with versatile, transferable skills that align with emerging technologies and evolving market needs. This shift underscores the importance of strategic skill expansion tailored to adjacent sectors rather than repetitive training within the same discipline.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Both Approaches
Case studies reveal that conventional upskilling programs often lead to measurable improvements in employee productivity within the same role, as exemplified by IBM's workforce development initiatives. Conversely, skill adjacency strategies, such as AT&T's implementation of cross-functional training in adjacent tech domains, enable faster transitions into emerging markets and roles, driving innovation and agility. Both approaches demonstrate quantifiable business growth, with upskilling enhancing depth in core competencies and skill adjacency expanding breadth across complementary skill sets.
Strategic Planning for Lifelong Learning
Conventional upskilling focuses on deepening expertise within a specific domain, enhancing proficiency to meet current job demands effectively. Skill adjacency involves diversifying competencies by acquiring related skills that expand professional versatility and open new pathways for career growth. Strategic planning for lifelong learning integrates both approaches, leveraging core skill enhancement alongside adjacent skill acquisition to maximize adaptability and future opportunity potential.
Choosing the Right Path for Career Advancement
Conventional upskilling often involves deepening expertise within a current skill set, enhancing proficiency through targeted training and certifications to improve job performance and promotion prospects. Skill adjacency focuses on acquiring complementary skills that broaden professional versatility, enabling individuals to pivot into related roles or industries with greater ease. Selecting between these paths depends on career goals, industry demands, and the potential for growth, making strategic alignment essential for maximizing long-term career opportunities.
Related Important Terms
Skill Stacking
Skill stacking leverages skill adjacency by combining complementary competencies, creating unique value beyond traditional conventional upskilling that often emphasizes deepening a single skill set. This approach multiplies opportunity potential, enabling professionals to adapt quickly in dynamic markets by integrating diverse expertise.
Microcredentialing
Microcredentialing enables targeted skill adjacency by offering concise, industry-relevant courses that expand existing competencies, providing a faster route to new opportunities compared to conventional upskilling's broader, time-intensive programs. This agile approach aligns workforce development with evolving market demands, maximizing employability and career growth through specialized, stackable credentials.
T-Shaped Skills
T-shaped skills, combining deep expertise in a core area with broad abilities across related fields, enable greater opportunity seizing compared to conventional upskilling, which often narrows focus without enhancing cross-functional adaptability. Skill adjacency leverages related competencies to open pathways in emerging roles, fostering innovation and career growth beyond traditional, siloed skill development.
Reskilling Pathways
Conventional upskilling focuses on deepening existing expertise within a specific domain, whereas skill adjacency opens new opportunities by leveraging related competencies across fields, accelerating reskilling pathways and enhancing career mobility. Prioritizing skill adjacency enables professionals to swiftly adapt to evolving job markets by building on transferable skills, facilitating broader access to emerging roles and industries.
Skill Adjacency Mapping
Skill adjacency mapping identifies complementary skills closely related to an individual's current expertise, enabling targeted upskilling that maximizes career growth opportunities faster than conventional broad training methods. This strategic approach leverages skill overlap analysis to pinpoint high-value competencies, enhancing adaptability and opening new professional pathways efficiently.
Cross-functional Bridging
Skill adjacency accelerates opportunity creation by leveraging cross-functional bridging, enabling employees to apply related competencies across different domains more effectively than conventional upskilling, which often focuses narrowly on specific skill enhancements. This approach fosters innovation and adaptability, driving organizational growth through diversified expertise and collaborative problem-solving.
Transferable Competencies
Conventional upskilling often targets specialized knowledge within a specific domain, limiting the scope of transferable competencies across industries. Skill adjacency leverages transferable competencies such as critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving to create broader opportunities by enabling professionals to pivot across related fields with greater agility.
Talent Fluidity
Conventional upskilling focuses on deepening expertise within a specific role, while skill adjacency leverages related competencies to accelerate talent fluidity and unlock broader career opportunities. Emphasizing skill adjacency enables organizations to adapt quickly to evolving market demands by deploying versatile talent across diverse functions.
Hybrid Career Architectures
Conventional upskilling focuses on deepening expertise within a specific domain, while skill adjacency leverages related competencies to unlock new career pathways and innovative roles. Hybrid career architectures blend these approaches, enabling professionals to seamlessly transition across functions by combining core skills with adjacent capabilities, maximizing opportunity in dynamic job markets.
Lateral Development Tracks
Conventional upskilling focuses on deepening expertise within a single domain, limiting opportunity by narrowing skill sets, whereas skill adjacency leverages lateral development tracks to broaden competencies across related fields, unlocking greater potential for career mobility and innovation. Emphasizing skill adjacency accelerates opportunity creation by enabling professionals to apply diverse skills in new contexts, fostering adaptability and cross-functional collaboration.
Conventional upskilling vs Skill adjacency for opportunity. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com