Networking skills provide foundational knowledge critical for career growth, while Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) offers practical, scalable experience in managing cloud-based network infrastructures. Mastery of traditional networking concepts combined with proficiency in NaaS platforms enhances adaptability in evolving IT environments. Professionals leveraging both approaches gain a competitive edge, enabling smoother transitions across diverse roles and industries.
Table of Comparison
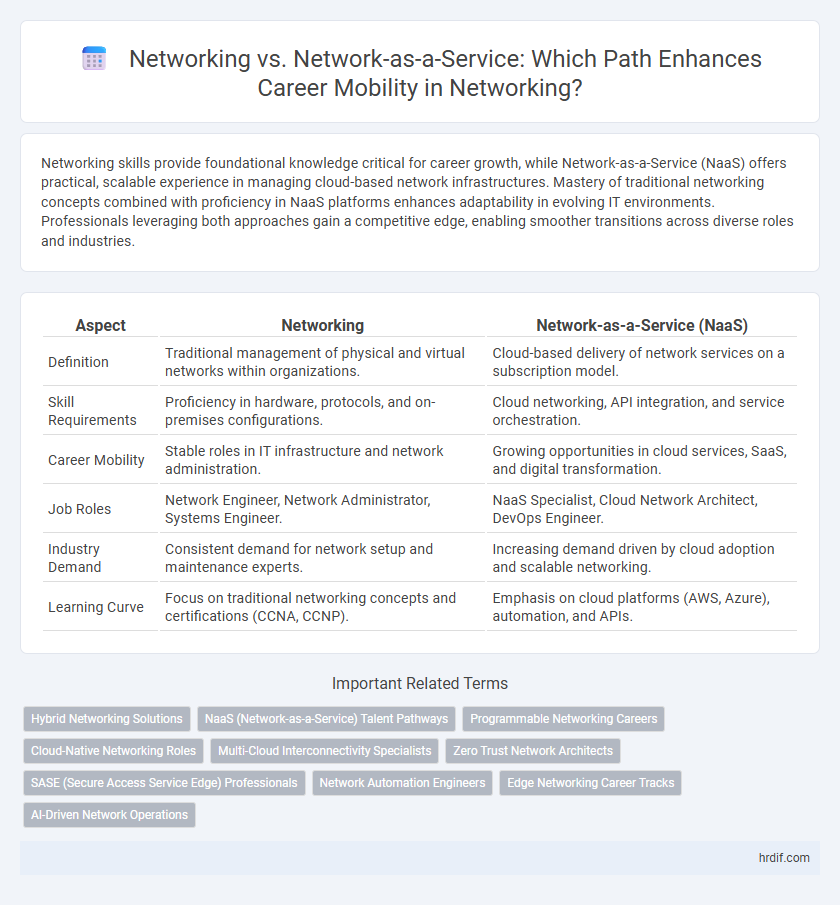
| Aspect | Networking | Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional management of physical and virtual networks within organizations. | Cloud-based delivery of network services on a subscription model. |
| Skill Requirements | Proficiency in hardware, protocols, and on-premises configurations. | Cloud networking, API integration, and service orchestration. |
| Career Mobility | Stable roles in IT infrastructure and network administration. | Growing opportunities in cloud services, SaaS, and digital transformation. |
| Job Roles | Network Engineer, Network Administrator, Systems Engineer. | NaaS Specialist, Cloud Network Architect, DevOps Engineer. |
| Industry Demand | Consistent demand for network setup and maintenance experts. | Increasing demand driven by cloud adoption and scalable networking. |
| Learning Curve | Focus on traditional networking concepts and certifications (CCNA, CCNP). | Emphasis on cloud platforms (AWS, Azure), automation, and APIs. |
Understanding Networking in Career Development
Understanding traditional networking involves building in-person connections and professional relationships, which enhances trust and long-term career growth. Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) leverages cloud-based solutions to provide scalable, on-demand networking infrastructure, aligning with digital transformation trends in IT careers. Mastering both interpersonal networking skills and NaaS technologies increases adaptability and broadens opportunities in evolving career paths within the tech industry.
What is Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) in Professional Growth?
Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) offers professionals scalable, cloud-based networking solutions that enhance flexibility and reduce infrastructure management complexities, making it a pivotal skill in modern IT careers. Mastery of NaaS platforms such as Cisco Meraki, AWS Transit Gateway, and Microsoft Azure Virtual Network enables network engineers to design, deploy, and manage virtualized networks efficiently, positioning them for roles in cloud architecture and network automation. Proficiency in NaaS technology aligns with industry trends toward Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV), providing significant career mobility in the evolving digital landscape.
Key Differences Between Traditional Networking and NaaS
Traditional networking relies on physical hardware and manual configuration, whereas Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) offers cloud-based, on-demand network access through subscription models. NaaS enables greater scalability, flexibility, and automation, facilitating quicker deployment and management compared to the static nature of traditional setups. Career mobility benefits from NaaS proficiency as it aligns with emerging cloud technologies and software-defined networking skills increasingly demanded in modern IT roles.
The Role of Networking in Building Career Opportunities
Networking cultivates professional relationships that open doors to new job opportunities and industry insights, essential for career mobility. Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) leverages cloud-based technologies to streamline connectivity and collaboration, enhancing access to remote and global job markets. Mastering both traditional networking skills and NaaS platforms increases adaptability and visibility in an evolving digital job landscape.
How NaaS is Transforming Career Mobility
Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) is revolutionizing career mobility by enabling professionals to develop expertise in scalable, cloud-based network solutions that align with modern IT infrastructures. Unlike traditional networking roles that often require deep hardware knowledge, NaaS focuses on software-defined networking, automation, and on-demand services, opening new pathways for career growth in emerging technology fields. Mastery of NaaS platforms and concepts enhances employability by positioning individuals at the forefront of digital transformation and hybrid cloud networking trends.
Advantages of Networking for Career Advancement
Networking offers direct access to industry professionals and decision-makers, enhancing opportunities for mentorship, referrals, and insider knowledge critical for career advancement. Building genuine relationships through networking fosters trust and credibility, often leading to unadvertised job openings and career growth. This personalized interaction allows professionals to tailor their personal brand and market expertise effectively, boosting career mobility.
Benefits of Adopting Network-as-a-Service for Professionals
Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) offers professionals increased career mobility by enabling access to scalable and flexible network solutions without the need for deep hardware management expertise. It allows IT specialists to focus on high-level network design, security, and optimization, fostering skill development aligned with current industry trends. Leveraging NaaS empowers professionals to rapidly adapt to evolving technological demands and enhances employability across diverse industries.
Challenges and Limitations: Networking vs NaaS
Traditional networking careers face challenges including complex hardware management, limited scalability, and slower adaptation to new technologies. Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) offers greater flexibility and rapid deployment but introduces limitations such as dependency on third-party providers and potential security concerns. Professionals must weigh these factors when considering career mobility between on-premises networking roles and cloud-based NaaS environments.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Career Path
Choosing between traditional networking and Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) depends on your career goals in IT infrastructure and cloud computing. Traditional networking expertise offers foundational skills in hardware and protocols, essential for roles in network administration and security. In contrast, mastering NaaS prepares professionals for modern cloud-based environments, emphasizing scalability and automation, which are highly valued in emerging network engineering positions.
Future Trends: Networking and NaaS in Career Mobility
Future trends in networking emphasize the shift towards Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) as businesses demand scalable, cloud-based solutions that enhance agility and reduce infrastructure costs. Career mobility in this domain requires professionals to develop skills in software-defined networking (SDN), cloud integration, and cybersecurity to adapt to these evolving technologies. Mastery of NaaS platforms, combined with traditional networking knowledge, positions individuals for advanced roles in network architecture, cloud engineering, and IT service management.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Networking Solutions
Hybrid networking solutions combine traditional networking with Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) to enhance career mobility by offering professionals expertise in both physical infrastructure and cloud-based services. Mastery of hybrid models enables networking specialists to design scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient systems, positioning them for in-demand roles that integrate on-premise hardware and virtualized network functions.
NaaS (Network-as-a-Service) Talent Pathways
Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) offers a dynamic career mobility pathway by enabling professionals to specialize in cloud-based network provisioning, automation, and virtualized infrastructure management, aligning with the growing demand for scalable and flexible network solutions. Talent pathways in NaaS emphasize skills in software-defined networking (SDN), network function virtualization (NFV), and cloud orchestration platforms, positioning experts for roles in cloud-native networking and service provider environments.
Programmable Networking Careers
Programmable networking careers emphasize skills in software-defined networking (SDN) and network automation, offering greater career mobility compared to traditional networking roles that rely on manual configuration. Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) platforms amplify this trend by providing cloud-based programmable infrastructure, enabling professionals to develop expertise in API-driven network management and orchestration, critical for future-proof career growth.
Cloud-Native Networking Roles
Cloud-native networking roles emphasize mastering Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) platforms, which streamline infrastructure management and enhance automation compared to traditional networking practices. Proficiency in NaaS technologies like SD-WAN, cloud orchestration, and API-driven network configuration significantly boosts career mobility by aligning with modern enterprise cloud adoption trends.
Multi-Cloud Interconnectivity Specialists
Multi-Cloud Interconnectivity Specialists gain enhanced career mobility by mastering Networking fundamentals and Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) platforms, enabling seamless integration across hybrid cloud environments. Proficiency in NaaS accelerates deployment times and scalability, positioning professionals as key assets in evolving cloud infrastructure landscapes.
Zero Trust Network Architects
Zero Trust Network Architects benefit from Network-as-a-Service by gaining scalable, cloud-based infrastructure that simplifies policy enforcement and continuous verification, enhancing career mobility through expertise in cutting-edge, decentralized security models. Traditional networking roles emphasize hardware management and on-premises configurations, whereas mastering NaaS platforms aligns professionals with evolving market demands for agility and zero trust security frameworks.
SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) Professionals
Networking professionals focusing on SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) enhance career mobility by mastering integrated security and network services that support cloud-native architectures. Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) offers scalable, on-demand network resources, empowering SASE experts to rapidly deploy secure access solutions and adapt to evolving enterprise security demands.
Network Automation Engineers
Network Automation Engineers benefit from Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) by leveraging cloud-based platforms that simplify infrastructure management, improving scalability and reducing manual configuration efforts compared to traditional networking. This shift enhances career mobility by fostering expertise in programmable network environments, API integration, and automation frameworks essential for modern enterprise networking.
Edge Networking Career Tracks
Edge networking career tracks offer hands-on experience in designing and managing decentralized networks, enhancing skills in hardware, protocols, and security essential for on-premises roles. Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) careers emphasize cloud-based overlay networks and software-defined networking, providing agility and scalability knowledge that aligns with evolving virtualized infrastructure demands.
AI-Driven Network Operations
AI-driven Network Operations enhance automation and predictive analytics, offering real-time optimization beyond traditional networking methods. Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) provides scalable, on-demand infrastructure, accelerating career mobility by enabling professionals to manage and deploy AI-integrated solutions without extensive hardware expertise.
Networking vs Network-as-a-Service for career mobility Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com