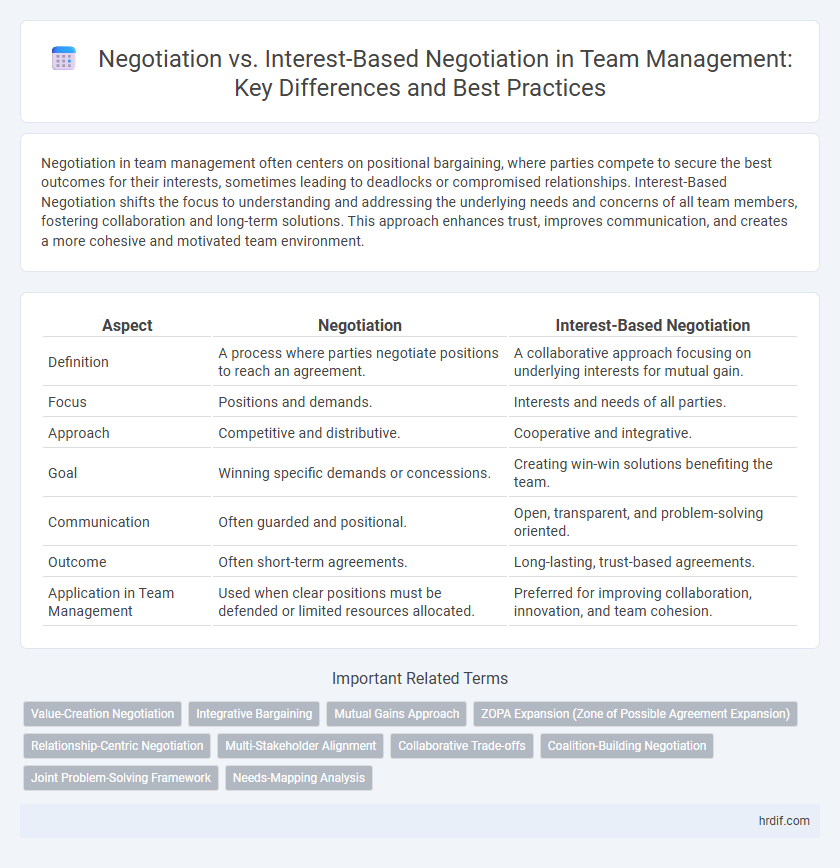
Negotiation in team management often centers on positional bargaining, where parties compete to secure the best outcomes for their interests, sometimes leading to deadlocks or compromised relationships. Interest-Based Negotiation shifts the focus to understanding and addressing the underlying needs and concerns of all team members, fostering collaboration and long-term solutions. This approach enhances trust, improves communication, and creates a more cohesive and motivated team environment.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Negotiation | Interest-Based Negotiation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A process where parties negotiate positions to reach an agreement. | A collaborative approach focusing on underlying interests for mutual gain. |
| Focus | Positions and demands. | Interests and needs of all parties. |
| Approach | Competitive and distributive. | Cooperative and integrative. |
| Goal | Winning specific demands or concessions. | Creating win-win solutions benefiting the team. |
| Communication | Often guarded and positional. | Open, transparent, and problem-solving oriented. |
| Outcome | Often short-term agreements. | Long-lasting, trust-based agreements. |
| Application in Team Management | Used when clear positions must be defended or limited resources allocated. | Preferred for improving collaboration, innovation, and team cohesion. |
Understanding Negotiation in Team Management
Negotiation in team management involves balancing competing interests to reach agreements that enhance collaboration and productivity. Interest-Based Negotiation prioritizes understanding underlying needs and motivations of team members, fostering solutions that satisfy all parties and build long-term trust. Mastery of these negotiation styles enables managers to effectively resolve conflicts and align team goals with organizational objectives.
What Is Interest-Based Negotiation?
Interest-based negotiation prioritizes understanding and addressing the underlying needs and concerns of all parties rather than focusing solely on positions or demands. This approach fosters collaboration and joint problem-solving, leading to mutually beneficial outcomes and stronger team relationships. In team management, interest-based negotiation empowers open communication and trust, enhancing commitment to agreed solutions and long-term success.
Key Differences: Traditional vs Interest-Based Approaches
Traditional negotiation centers on positional bargaining, where parties compete over fixed resources, often leading to win-lose outcomes and strained team dynamics. Interest-Based Negotiation emphasizes understanding underlying interests and collaborative problem-solving, promoting win-win solutions that enhance trust and cohesion within teams. This approach leverages open communication and shared goals, resulting in more sustainable agreements and improved team performance.
Benefits of Interest-Based Negotiation for Teams
Interest-Based Negotiation enhances team management by prioritizing mutual interests over fixed positions, fostering collaboration and trust among team members. This approach leads to more creative problem-solving and sustainable agreements, reducing conflicts and improving overall team cohesion. Emphasizing shared goals and open communication also boosts morale and aligns individual efforts with organizational objectives.
Common Challenges in Team Negotiations
Negotiation in team management often faces challenges such as conflicting priorities, lack of trust, and communication barriers that hinder effective resolution. Interest-based negotiation addresses these issues by focusing on underlying needs and collaborative problem-solving, fostering mutual understanding and long-term relationships. Overcoming common obstacles requires aligning team goals with individual interests to create win-win outcomes and enhance overall team performance.
Skills Required for Effective Interest-Based Negotiation
Effective interest-based negotiation in team management requires strong active listening skills to fully understand underlying needs and concerns. Empathy and emotional intelligence enable negotiators to build trust and foster collaboration among team members. Additionally, critical thinking and problem-solving skills are essential to identify mutually beneficial solutions that align with the interests of all parties involved.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Team Settings
Case studies reveal that interest-based negotiation fosters higher team cohesion by prioritizing mutual goals and collaborative problem-solving, leading to sustainable agreements and enhanced productivity. Traditional negotiation often focuses on position-based tactics, resulting in short-term gains but potential conflicts or reduced trust within teams. Teams employing interest-based approaches report improved communication, increased commitment to outcomes, and measurable success in complex project management scenarios.
When to Use Traditional Negotiation Methods
Traditional negotiation methods are most effective when clear, fixed positions dominate the discussion, such as in deadline-driven projects or budget approvals. These approaches excel in situations where quick decisions are required and the scope for creative problem-solving is limited. Managers benefit from using traditional negotiation during contract renewals or resource allocations where defined terms are non-negotiable.
Building a Collaborative Team Culture Through Interest-Based Negotiation
Interest-based negotiation fosters a collaborative team culture by prioritizing mutual interests and open communication, leading to more sustainable agreements and stronger team cohesion. This approach shifts the focus from positional bargaining to understanding underlying needs, enabling creative problem-solving and increased trust among team members. Implementing interest-based negotiation techniques in team management enhances cooperation, reduces conflicts, and drives collective success.
Practical Steps to Implement Interest-Based Negotiation in Teams
Implementing Interest-Based Negotiation in teams requires identifying underlying needs and priorities through open dialogue, fostering mutual understanding and collaboration. Encourage team members to share their interests explicitly, then jointly develop creative solutions that satisfy shared goals while respecting individual concerns. Establish clear communication protocols and continuous feedback loops to maintain alignment and adapt strategies as the negotiation evolves.
Related Important Terms
Value-Creation Negotiation
Value-creation negotiation emphasizes collaborative problem-solving and mutual benefits, contrasting with traditional negotiation's often competitive approach focused on individual positions. Implementing interest-based negotiation in team management enhances trust and innovation by aligning underlying interests, leading to more sustainable and productive agreements.
Integrative Bargaining
Integrative bargaining in team management emphasizes collaboration by focusing on shared interests rather than positional demands, resulting in mutually beneficial outcomes and strengthened team relationships. Interest-based negotiation fosters open communication and creative problem-solving, enhancing trust and long-term cooperation within teams.
Mutual Gains Approach
Negotiation in team management can follow traditional positional tactics or the Interest-Based Negotiation method, which prioritizes understanding underlying interests to create value for all parties. The Mutual Gains Approach emphasizes collaboration, fostering trust and innovative solutions that satisfy shared and individual team goals more effectively than adversarial negotiation.
ZOPA Expansion (Zone of Possible Agreement Expansion)
Traditional negotiation often restricts outcomes within fixed positions, limiting the Zone of Possible Agreement (ZOPA), while interest-based negotiation expands ZOPA by uncovering underlying interests and creating value through collaborative problem-solving. This approach encourages team management to identify shared goals and integrate diverse perspectives, resulting in more flexible agreements and sustainable, mutually beneficial solutions.
Relationship-Centric Negotiation
Relationship-centric negotiation emphasizes building trust and long-term collaboration by addressing the underlying interests and emotions of team members rather than merely dividing resources or positions. This approach fosters a cooperative team environment, enhances communication, and facilitates sustainable agreements aligned with collective goals.
Multi-Stakeholder Alignment
Negotiation often centers on positional bargaining, where parties prioritize individual demands, potentially leading to conflicts in multi-stakeholder alignment. Interest-Based Negotiation fosters collaboration by addressing underlying needs and shared interests, enabling diverse team members to co-create solutions that align collective goals and enhance overall team cohesion.
Collaborative Trade-offs
Negotiation involves traditional bargaining where parties often prioritize positions, while Interest-Based Negotiation focuses on underlying needs, fostering collaborative trade-offs that enhance team management effectiveness. Emphasizing shared interests and mutual gains promotes trust and long-term cooperation, optimizing team dynamics and project outcomes.
Coalition-Building Negotiation
Coalition-building negotiation fosters collaborative alliances within teams by aligning individual interests and leveraging collective power to achieve common goals, contrasting with traditional negotiation that often centers on positional bargaining. Interest-based negotiation emphasizes understanding underlying needs and priorities, enabling team managers to build trust and facilitate integrative solutions that enhance group cohesion and long-term success.
Joint Problem-Solving Framework
Negotiation typically emphasizes positional bargaining where each party aims to maximize their own outcomes, while Interest-Based Negotiation prioritizes understanding underlying needs through a joint problem-solving framework that fosters collaboration and mutual gain. This approach enhances team management by creating shared value and encouraging open communication, leading to sustainable agreements and strengthened relationships.
Needs-Mapping Analysis
Negotiation often relies on positional bargaining, where each party defends their stance, while Interest-Based Negotiation centers on uncovering underlying needs and mutual interests, facilitating collaborative solutions. Needs-Mapping Analysis in Interest-Based Negotiation identifies core concerns and priorities, enabling teams to align strategies and enhance conflict resolution effectively.
Negotiation vs Interest-Based Negotiation for team management. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com