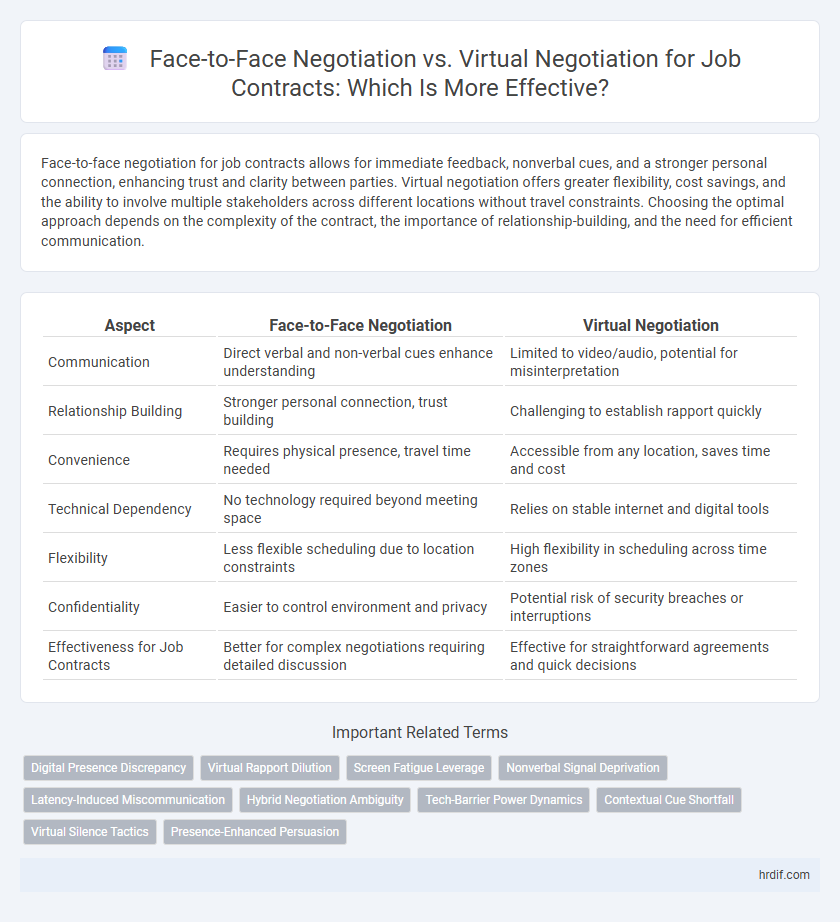
Face-to-face negotiation for job contracts allows for immediate feedback, nonverbal cues, and a stronger personal connection, enhancing trust and clarity between parties. Virtual negotiation offers greater flexibility, cost savings, and the ability to involve multiple stakeholders across different locations without travel constraints. Choosing the optimal approach depends on the complexity of the contract, the importance of relationship-building, and the need for efficient communication.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Face-to-Face Negotiation | Virtual Negotiation |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Direct verbal and non-verbal cues enhance understanding | Limited to video/audio, potential for misinterpretation |
| Relationship Building | Stronger personal connection, trust building | Challenging to establish rapport quickly |
| Convenience | Requires physical presence, travel time needed | Accessible from any location, saves time and cost |
| Technical Dependency | No technology required beyond meeting space | Relies on stable internet and digital tools |
| Flexibility | Less flexible scheduling due to location constraints | High flexibility in scheduling across time zones |
| Confidentiality | Easier to control environment and privacy | Potential risk of security breaches or interruptions |
| Effectiveness for Job Contracts | Better for complex negotiations requiring detailed discussion | Effective for straightforward agreements and quick decisions |
Introduction: The Evolution of Job Contract Negotiations
Job contract negotiations have evolved from predominantly face-to-face interactions to increasingly virtual formats, driven by technological advancements and global workforce trends. Face-to-face negotiations offer rich non-verbal cues and immediate rapport, enhancing trust and clarity during contract discussions. Virtual negotiations leverage digital platforms to provide flexibility, wider accessibility, and efficient scheduling, reshaping how employers and candidates finalize job agreements.
Key Differences Between Face-to-Face and Virtual Negotiations
Face-to-face negotiation enables real-time reading of non-verbal cues such as body language and facial expressions, fostering stronger rapport and trust, which are crucial in job contract discussions. Virtual negotiation relies heavily on digital communication tools, which can limit spontaneous interactions and increase the risk of misunderstandings due to technical issues or lack of physical presence. The immediacy and emotional connection in face-to-face settings often lead to more nuanced agreement terms, whereas virtual negotiations demand clearer, more explicit communication protocols.
The Role of Communication Cues in Negotiation Effectiveness
Face-to-face negotiation allows for the full range of nonverbal communication cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice, which significantly enhance understanding and trust in job contract discussions. Virtual negotiation often limits these cues, relying heavily on verbal communication and digital body language like eye contact through a screen, potentially causing misunderstandings or reduced rapport. Effective negotiators adapt by using clear verbal signals and confirming interpretations to overcome the communication barriers inherent in virtual settings.
Building Trust: In-Person vs Virtual Settings
Building trust in face-to-face negotiation for job contracts is enhanced by direct eye contact, body language, and immediate feedback, fostering stronger interpersonal connections. Virtual negotiation risks misunderstandings due to limited non-verbal cues and potential technical issues, but can still build trust through clear communication and consistent follow-up. Research indicates that in-person meetings increase perceived trustworthiness by 30% compared to virtual settings, crucial for finalizing job agreements.
Technological Barriers and Opportunities in Virtual Negotiations
Virtual negotiations for job contracts often face technological barriers such as unstable internet connections, software glitches, and limited access to advanced communication tools, which can hinder real-time interaction and trust-building. These challenges contrast with face-to-face negotiations, where non-verbal cues and immediate feedback facilitate clearer understanding and rapport. However, virtual platforms present opportunities for enhanced scheduling flexibility, digital document sharing, and the integration of AI-driven analytics to support data-informed decision-making in contract discussions.
Impact on Negotiation Outcomes: Salary, Benefits, and Flexibility
Face-to-face negotiations for job contracts often result in higher salary offers due to enhanced personal rapport and nonverbal cues that build trust and credibility. Virtual negotiations, while convenient, may lead to more conservative benefit packages as limited emotional connection hinders relationship-building and nuanced communication. Flexibility tends to be negotiated more effectively in virtual settings where both parties have easier access to digital tools and can explore remote work options in real-time.
Time Efficiency and Scheduling Flexibility
Face-to-face negotiation for job contracts often requires coordinating specific times and locations, potentially causing delays and limiting scheduling flexibility compared to virtual negotiation. Virtual negotiation platforms enable real-time communication across different time zones, significantly improving time efficiency by reducing travel and waiting periods. This flexibility supports quicker decision-making and accommodates diverse schedules, enhancing overall negotiation productivity.
Managing Power Dynamics and Influence
Face-to-face negotiation allows for better management of power dynamics through direct observation of body language, tone, and immediate feedback, enhancing influence and trust during job contract discussions. Virtual negotiation limits these non-verbal cues, requiring more deliberate communication strategies and digital tools to assert power and build rapport effectively. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing negotiation outcomes and maintaining balance in influence between parties.
Strategies for Success in Both Negotiation Environments
Effective strategies for success in both face-to-face and virtual negotiations for job contracts include thorough preparation, clear communication, and active listening to understand the other party's priorities. Building rapport and trust are crucial in face-to-face settings through body language and eye contact, while in virtual negotiations, leveraging technology features such as video calls and screen sharing enhances engagement and clarity. Maintaining flexibility and adapting negotiation tactics to the specific environment increases the likelihood of mutually beneficial agreements.
Choosing the Right Negotiation Mode for Your Career
Choosing the right negotiation mode for job contracts significantly impacts outcomes and relationship-building. Face-to-face negotiation allows for richer communication through body language and immediate feedback, fostering trust and rapport crucial for long-term career opportunities. Virtual negotiation offers flexibility and efficiency, making it ideal for remote positions or global companies, but may require enhanced clarity and digital communication skills to avoid misunderstandings.
Related Important Terms
Digital Presence Discrepancy
Face-to-face negotiation offers nuanced communication through body language and immediate feedback, minimizing digital presence discrepancy that can obscure intent during virtual job contract discussions. Virtual negotiation often risks misunderstandings due to limited non-verbal cues and technical issues, impacting trust and clarity in finalizing job agreements.
Virtual Rapport Dilution
Virtual negotiation for job contracts often suffers from virtual rapport dilution, where the lack of physical presence and limited nonverbal cues hinder trust-building and nuanced communication compared to face-to-face interactions. This reduction in emotional connection can lead to misunderstandings, decreased mutual engagement, and slower consensus during contract discussions.
Screen Fatigue Leverage
Face-to-face negotiation allows for clearer non-verbal communication and reduces screen fatigue, enhancing focus and rapport during job contract discussions. Virtual negotiation, while convenient, often increases cognitive strain due to prolonged screen exposure, potentially diminishing decision-making effectiveness and leverage.
Nonverbal Signal Deprivation
Face-to-face negotiation for job contracts offers rich nonverbal cues such as body language, eye contact, and facial expressions, which enhance mutual understanding and trust. Virtual negotiation often suffers from nonverbal signal deprivation, leading to potential misinterpretations and weakened rapport between parties.
Latency-Induced Miscommunication
Latency-induced miscommunication in virtual negotiations often leads to misunderstandings and delayed responses, impacting the clarity and effectiveness of job contract discussions more than face-to-face negotiations. Real-time, in-person interactions minimize latency effects, allowing for immediate feedback and nuanced communication crucial for complex contract terms.
Hybrid Negotiation Ambiguity
Hybrid negotiation ambiguity arises when job contract discussions blend face-to-face and virtual formats, leading to challenges in interpreting non-verbal cues and digital communication nuances. This ambiguity can impact trust-building and mutual understanding, requiring negotiators to develop adaptive strategies that leverage both in-person presence and technological tools effectively.
Tech-Barrier Power Dynamics
Face-to-face negotiation for job contracts often provides clearer communication cues and stronger power dynamics due to physical presence, which can influence outcomes favorably for both parties. Virtual negotiation introduces tech-barrier challenges such as connectivity issues and reduced nonverbal signals, potentially diminishing perceived authority and altering traditional power balances.
Contextual Cue Shortfall
Face-to-face negotiation for job contracts provides rich contextual cues such as body language, tone, and immediate feedback, which enhance mutual understanding and trust. Virtual negotiation often suffers from contextual cue shortfall, leading to potential misinterpretations and reduced emotional connection between parties.
Virtual Silence Tactics
Virtual silence tactics in job contract negotiations leverage intentional pauses and non-responsiveness to create pressure and elicit concessions from counterparts, capitalizing on the screen-mediated communication gap. Unlike face-to-face settings, where body language and immediate feedback guide responses, virtual silence demands heightened psychological awareness and strategic patience to interpret unspoken cues and maintain negotiation leverage.
Presence-Enhanced Persuasion
Face-to-face negotiation leverages nonverbal cues such as body language, eye contact, and vocal tone to enhance presence and build trust, significantly boosting persuasive impact during job contract discussions. Virtual negotiation often limits these sensory inputs, potentially reducing emotional connection and the effectiveness of influence but can be supplemented with video conferencing tools that simulate real-time interaction to partially restore presence-enhanced persuasion.
Face-to-face negotiation vs Virtual negotiation for job contracts. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com