Passion fuels motivation by igniting deep interest and emotional commitment to a goal, driving sustained effort over time. The flow state enhances motivation by immersing individuals fully in the task, creating a sense of timeless focus and intrinsic reward. Combining passion with flow maximizes productivity and personal fulfillment, as passion provides purpose while flow delivers optimal engagement.
Table of Comparison
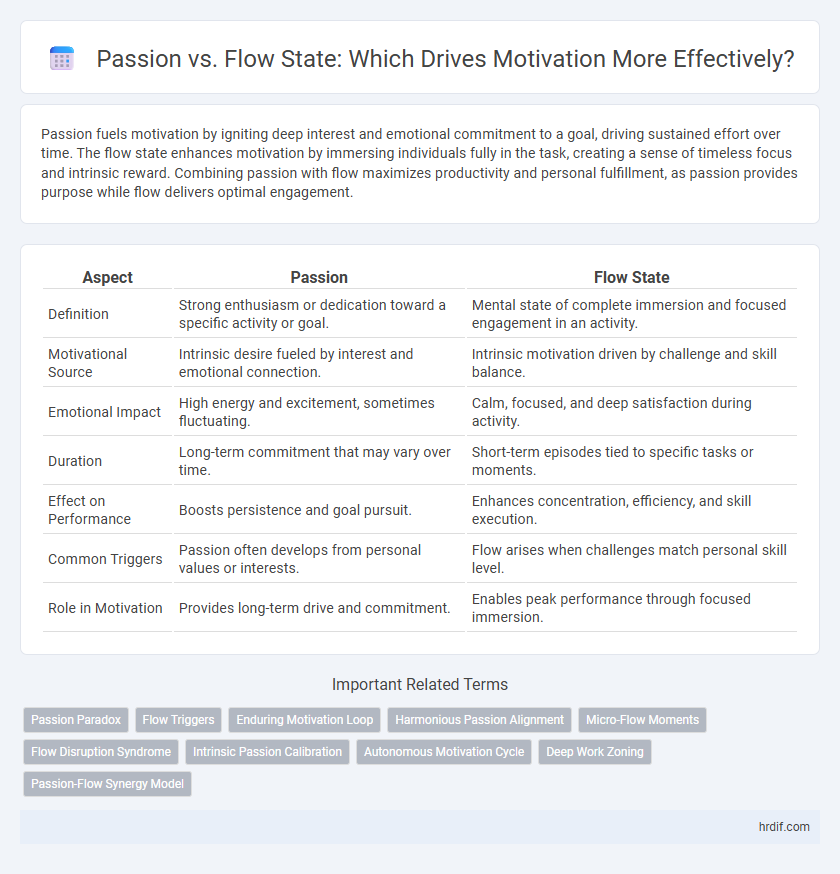
| Aspect | Passion | Flow State |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strong enthusiasm or dedication toward a specific activity or goal. | Mental state of complete immersion and focused engagement in an activity. |
| Motivational Source | Intrinsic desire fueled by interest and emotional connection. | Intrinsic motivation driven by challenge and skill balance. |
| Emotional Impact | High energy and excitement, sometimes fluctuating. | Calm, focused, and deep satisfaction during activity. |
| Duration | Long-term commitment that may vary over time. | Short-term episodes tied to specific tasks or moments. |
| Effect on Performance | Boosts persistence and goal pursuit. | Enhances concentration, efficiency, and skill execution. |
| Common Triggers | Passion often develops from personal values or interests. | Flow arises when challenges match personal skill level. |
| Role in Motivation | Provides long-term drive and commitment. | Enables peak performance through focused immersion. |
Understanding Passion: The Fuel for Career Motivation
Passion serves as the foundational fuel for career motivation, driving individuals to pursue their goals with relentless energy and commitment. Unlike the flow state, which represents a temporary cognitive immersion in tasks, passion provides a sustained emotional connection that underpins long-term perseverance and resilience. Understanding passion's role enables professionals to align their work with intrinsic values, fostering continuous motivation and career fulfillment.
Flow State: The Psychology Behind Peak Performance
Flow state represents a psychological condition characterized by complete immersion and energized focus on the task at hand, often leading to peak performance. This state enhances motivation by aligning intrinsic rewards with task execution, reducing self-consciousness, and increasing creativity and productivity. Neuroscientific research links flow to optimal dopamine regulation and transient hypofrontality, which support sustained attention and seamless skill integration during motivated performance.
Key Differences Between Passion and Flow in the Workplace
Passion in the workplace is a strong emotional drive that fuels long-term commitment and enthusiasm toward goals, often linked to personal values and identity. Flow state occurs when an individual is fully immersed and focused on a task, experiencing peak productivity and intrinsic motivation without distractions. The key difference lies in passion being a sustained motivational force, while flow is a transient cognitive state that maximizes performance during specific activities.
Passion-Driven Careers: Benefits and Potential Pitfalls
Passion-driven careers fuel intrinsic motivation by aligning work with deeply held interests, often leading to greater job satisfaction and perseverance. However, excessive reliance on passion can cause burnout and unrealistic expectations when challenges arise or initial excitement fades. Balancing passion with adaptability and skill development ensures sustainable motivation and career growth.
Harnessing Flow State for Productivity and Engagement
Harnessing the flow state significantly boosts productivity and engagement by immersing individuals in tasks with intense focus and intrinsic motivation. Unlike passion, which can fluctuate and sometimes lead to burnout, flow provides a sustainable experience of deep concentration where challenges match skill levels perfectly. Cultivating environments that facilitate flow enables individuals to achieve peak performance and maintain long-term motivation.
Balancing Passion and Flow for Sustainable Motivation
Balancing passion and flow is essential for sustainable motivation, as passion provides the initial drive while flow maintains deep focus and engagement over time. Passion without flow can lead to burnout, whereas flow without passion may result in a lack of long-term commitment. Cultivating both enables continuous motivation by aligning emotional energy with peak productivity states.
Signs You’re Motivated by Passion vs Flow at Work
Signs you're motivated by passion at work include persistent enthusiasm for tasks and a deep emotional connection to your role, often driving you to invest extra time voluntarily. In contrast, flow state motivation is characterized by intense concentration, a loss of self-awareness, and effortless action that makes challenging projects feel seamless. Both passion and flow enhance productivity, but passion fuels sustained commitment while flow optimizes moment-to-moment performance.
How to Cultivate Flow State in Your Professional Life
Cultivating flow state in your professional life requires focusing on tasks that align with your skills and challenge your abilities just enough to maintain engagement without causing overwhelming stress. Prioritize setting clear goals, eliminating distractions, and maintaining deep concentration to enter and sustain this optimal state of motivation and productivity. Regularly practicing mindfulness and seeking feedback can enhance your ability to reach flow, ultimately boosting job satisfaction and performance.
When Passion Fades: Relying on Flow for Continued Success
Passion often ignites initial motivation, but sustaining success requires harnessing the flow state, where deep focus and intrinsic engagement drive consistent performance. Unlike passion, which can fluctuate, flow fosters a seamless connection between challenge and skill, maintaining motivation even when initial enthusiasm wanes. Cultivating flow enables individuals to achieve continuous progress and resilience in the face of motivational decline.
Integrating Passion and Flow for Long-Term Career Satisfaction
Integrating passion and flow creates sustained motivation by aligning deep personal interests with immersive, focused work experiences, enhancing long-term career satisfaction. Passion drives initial enthusiasm and commitment, while flow facilitates optimal performance and intrinsic reward during tasks. Balancing both allows professionals to maintain engagement and resilience throughout evolving career challenges.
Related Important Terms
Passion Paradox
Passion often drives initial motivation but can lead to the Passion Paradox, where intense enthusiasm results in burnout or decreased persistence. In contrast, cultivating a flow state enhances sustained motivation by fostering deep engagement without the emotional volatility linked to passion.
Flow Triggers
Flow triggers such as clear goals, immediate feedback, and a balanced challenge-skill ratio create an optimal state of focus and immersion that fuels intrinsic motivation beyond mere passion. These psychological conditions enhance productivity and satisfaction by aligning actions with deep engagement, making flow a powerful catalyst for sustained motivation.
Enduring Motivation Loop
Passion ignites initial motivation while flow state sustains it by creating immersive focus and intrinsic reward, forming a continuous and enduring motivation loop. This loop enhances productivity and resilience by balancing emotional drive with deep engagement in tasks.
Harmonious Passion Alignment
Harmonious passion fosters intrinsic motivation by aligning personal interests with flow state experiences, enhancing sustained engagement and performance. This alignment balances emotional intensity and cognitive control, promoting well-being and resilience in goal pursuit.
Micro-Flow Moments
Passion ignites initial motivation by fueling deep interest, while the flow state sustains it through complete immersion and heightened focus during Micro-Flow Moments. These brief intervals of intense concentration optimize productivity and reinforce intrinsic motivation by seamlessly blending challenge and skill.
Flow Disruption Syndrome
Flow state enhances motivation by fully immersing individuals in tasks, boosting productivity and satisfaction, whereas passion alone can lead to Flow Disruption Syndrome, characterized by anxiety and decreased focus due to emotional volatility. Recognizing the signs of Flow Disruption Syndrome allows for strategic interventions to restore deep engagement and maintain consistent motivational rhythms.
Intrinsic Passion Calibration
Intrinsic passion calibration enhances motivation by aligning personal interests with optimal challenges, fostering a flow state where deep engagement and productivity naturally occur. This balance between passion and flow ensures sustained intrinsic motivation, minimizing burnout and maximizing creative output.
Autonomous Motivation Cycle
Passion fuels the Autonomous Motivation Cycle by igniting intrinsic desire, while flow state sustains motivation through deep immersion and optimal challenge balance. This synergy enhances persistence, creativity, and self-driven goal attainment in personal and professional growth.
Deep Work Zoning
Passion ignites initial motivation by driving interest and emotional engagement, but achieving a flow state during deep work zoning maximizes productivity and sustained focus by fully immersing the mind in challenging tasks. Neuroscientific studies highlight that flow triggers optimal dopamine release, enhancing cognitive performance and long-term motivation beyond the fluctuating intensity of passion.
Passion-Flow Synergy Model
The Passion-Flow Synergy Model reveals that motivation peaks when an individual's passionate interests align seamlessly with their flow state activities, creating a powerful feedback loop that enhances intrinsic drive and sustained engagement. This synergy fosters heightened focus, deep immersion, and resilience, crucial for achieving long-term goals and personal fulfillment.
Passion vs Flow state for motivation. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com