Job satisfaction plays a crucial role in fostering intrinsic motivation, as employees who find fulfillment in their work are more likely to remain engaged and productive. Motivational design strategically enhances this effect by structuring tasks and environments that align with employees' values and goals, thereby increasing commitment and performance. Prioritizing both job satisfaction and motivational design creates a synergistic environment that drives sustained motivation and organizational success.
Table of Comparison
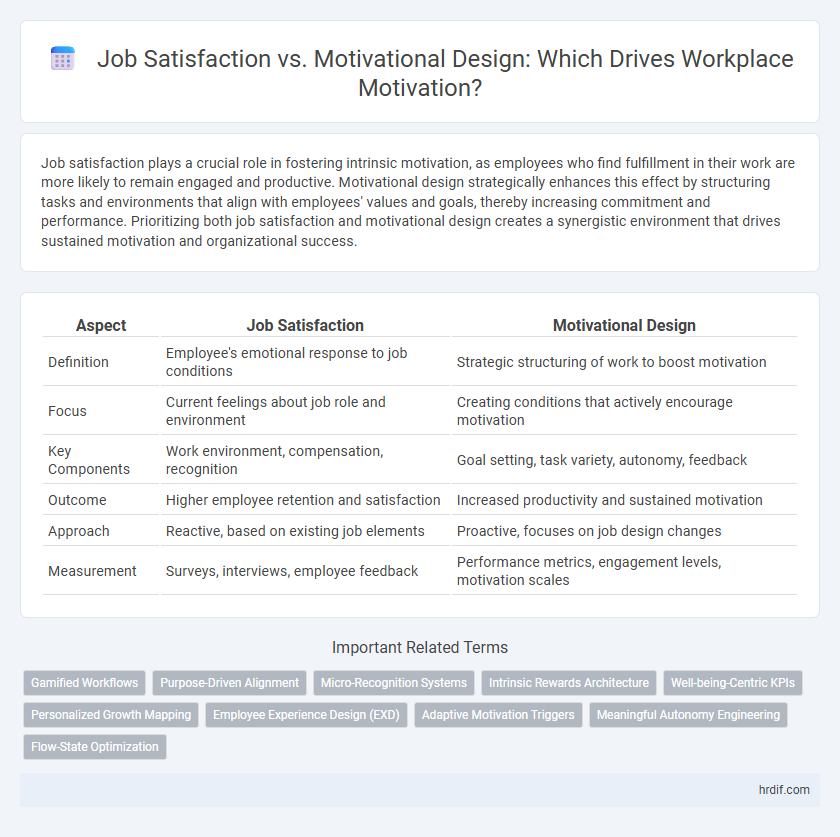
| Aspect | Job Satisfaction | Motivational Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee's emotional response to job conditions | Strategic structuring of work to boost motivation |
| Focus | Current feelings about job role and environment | Creating conditions that actively encourage motivation |
| Key Components | Work environment, compensation, recognition | Goal setting, task variety, autonomy, feedback |
| Outcome | Higher employee retention and satisfaction | Increased productivity and sustained motivation |
| Approach | Reactive, based on existing job elements | Proactive, focuses on job design changes |
| Measurement | Surveys, interviews, employee feedback | Performance metrics, engagement levels, motivation scales |
Understanding Job Satisfaction: Core Concepts
Job satisfaction reflects an employee's emotional response to their job, driven by factors such as work environment, recognition, and role clarity. Motivational design employs structured strategies like goal setting, autonomy, and feedback systems to enhance intrinsic motivation. Understanding job satisfaction's core concepts helps organizations tailor motivational design that aligns employees' personal values with organizational objectives.
Defining Motivational Design in the Workplace
Motivational design in the workplace refers to creating job roles, tasks, and environments that inherently drive employee engagement and productivity by aligning work conditions with intrinsic and extrinsic motivators. Unlike job satisfaction, which measures employees' contentment with their current roles, motivational design proactively shapes work experiences to foster sustained motivation and performance. Key elements include meaningful task variety, autonomy, recognition, and opportunities for professional growth tailored to individual and organizational goals.
Key Differences Between Job Satisfaction and Motivation
Job satisfaction reflects an employee's contentment with their current role, encompassing factors like work environment, compensation, and job security, while motivational design focuses on structuring tasks and rewards to actively enhance employee drive and performance. Job satisfaction is often a passive outcome influenced by external conditions, whereas motivational design is an intentional strategy aimed at fostering intrinsic motivation through goal-setting, feedback, and autonomy. Understanding these key differences helps organizations create environments that not only satisfy employees but also stimulate sustained motivation and productivity.
How Job Satisfaction Impacts Employee Performance
Job satisfaction significantly influences employee performance by enhancing engagement, reducing turnover, and fostering a positive work environment. Employees with high job satisfaction demonstrate increased productivity, better teamwork, and greater commitment to organizational goals. Integrating motivational design elements such as clear goals, recognition, and autonomy further amplifies these positive outcomes, driving overall business success.
The Science of Motivational Design Strategies
Job satisfaction primarily addresses employees' contentment with their current roles, whereas motivational design strategically integrates psychological principles like autonomy, mastery, and purpose to drive sustained engagement and performance. The science of motivational design leverages intrinsic motivators identified by Deci and Ryan's Self-Determination Theory to enhance both productivity and well-being. Implementing evidence-based strategies such as goal setting, feedback loops, and task variety optimizes motivation more effectively than traditional job satisfaction measures alone.
Integrating Motivational Design for Enhanced Job Satisfaction
Integrating motivational design in the workplace directly boosts job satisfaction by aligning tasks with employees' intrinsic needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness. Research indicates that environments emphasizing motivational design principles lead to higher engagement, improved performance, and sustained employee retention. Organizations prioritizing tailored motivational strategies experience significant increases in overall job satisfaction metrics and organizational commitment.
Factors Driving Job Satisfaction in Modern Careers
Key factors driving job satisfaction in modern careers include meaningful work aligned with personal values, opportunities for professional growth, and recognition of achievements. Motivational design emphasizes creating work environments that foster autonomy, mastery, and purpose to enhance employee engagement. Integrating these elements leads to higher productivity, reduced turnover, and sustained motivation in the workplace.
Motivational Design Techniques for Employee Engagement
Motivational design techniques for employee engagement focus on creating work environments that fulfill intrinsic needs such as autonomy, competence, and relatedness, which significantly enhance motivation beyond basic job satisfaction. Strategies like goal setting, providing meaningful feedback, and fostering skill development directly influence employees' emotional commitment and productivity. Implementing these techniques leads to sustained engagement by aligning organizational objectives with individual purpose.
Measuring Success: Job Satisfaction vs. Motivational Outcomes
Measuring success in motivation requires distinguishing job satisfaction from motivational design outcomes, as job satisfaction reflects employees' contentment while motivational design targets behavioral change and performance improvement. Job satisfaction metrics often include employee surveys capturing happiness and engagement levels, whereas motivational outcomes assess goal attainment, productivity, and intrinsic drive. Organizations leveraging both qualitative satisfaction data and quantitative motivational performance indicators achieve a comprehensive understanding of workforce motivation.
Choosing the Right Approach: Job Satisfaction or Motivational Design?
Choosing between job satisfaction and motivational design hinges on aligning workplace strategies with employee needs and organizational goals. Job satisfaction centers on fulfilling employees' basic needs through a positive work environment, fair compensation, and recognition, while motivational design focuses on intrinsic factors such as autonomy, mastery, and purpose to drive engagement and productivity. Data from organizational behavior studies suggest that integrating motivational design principles often yields higher long-term commitment and innovation compared to solely focusing on job satisfaction metrics.
Related Important Terms
Gamified Workflows
Gamified workflows enhance job satisfaction by integrating motivational design elements such as rewards, feedback loops, and challenges that align with employees' intrinsic and extrinsic motivators. These game-like features drive engagement and productivity, making work more enjoyable and fostering a deeper commitment to organizational goals.
Purpose-Driven Alignment
Job satisfaction primarily depends on employees finding their tasks fulfilling and aligned with personal values, but motivational design enhances this by strategically embedding purpose-driven alignment within job roles to foster intrinsic motivation and sustained engagement. Purpose-driven alignment connects individual goals with organizational mission, amplifying motivation beyond basic satisfaction through meaningful contribution and clear impact.
Micro-Recognition Systems
Micro-recognition systems significantly enhance job satisfaction by providing frequent, personalized acknowledgment that aligns with intrinsic motivational design principles. These systems leverage real-time praise and small rewards to sustainably boost employee engagement and performance within organizational motivation frameworks.
Intrinsic Rewards Architecture
Job satisfaction stems from a positive Intrinsic Rewards Architecture that aligns individual values with meaningful work, fostering internal motivation and sustained engagement. Motivational design leverages intrinsic rewards such as autonomy, mastery, and purpose to enhance job satisfaction, driving intrinsic motivation and improved performance.
Well-being-Centric KPIs
Job satisfaction directly influences employee retention and productivity, but motivational design centered on well-being-centric KPIs such as stress levels, work-life balance, and emotional resilience drives sustained engagement and performance. Integrating well-being metrics with motivational strategies enables organizations to create environments that foster intrinsic motivation and holistic employee flourishing.
Personalized Growth Mapping
Personalized Growth Mapping enhances job satisfaction by aligning individual career goals with motivational design strategies, fostering intrinsic motivation and sustained engagement. This tailored approach boosts productivity and retention by addressing unique employee aspirations and development needs.
Employee Experience Design (EXD)
Job satisfaction reflects employees' current feelings about their roles, while motivational design proactively shapes the work environment to enhance engagement and productivity; Employee Experience Design (EXD) integrates these elements by creating personalized, meaningful interactions that foster intrinsic motivation and long-term commitment. Leveraging EXD strategies such as feedback loops, autonomy support, and recognition systems drives higher job satisfaction and aligns organizational goals with individual purpose.
Adaptive Motivation Triggers
Job satisfaction stems from fulfilled needs and positive work conditions, but adaptive motivation triggers dynamically tailor incentives to individual preferences and evolving roles, enhancing long-term employee engagement. Integrating adaptive motivational design leverages real-time feedback and personalized rewards, promoting sustained productivity and deeper organizational commitment.
Meaningful Autonomy Engineering
Meaningful Autonomy Engineering prioritizes job satisfaction by designing roles that empower employees with control and purposeful decision-making, directly enhancing intrinsic motivation. By integrating autonomy with meaningful work, organizations foster higher engagement, productivity, and long-term commitment.
Flow-State Optimization
Job satisfaction enhances overall well-being, but motivational design specifically targets flow-state optimization by structuring tasks to balance challenge and skill, fostering deep engagement and intrinsic motivation. This approach improves productivity and creativity more effectively than general job satisfaction alone.
Job satisfaction vs Motivational design for motivation. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com