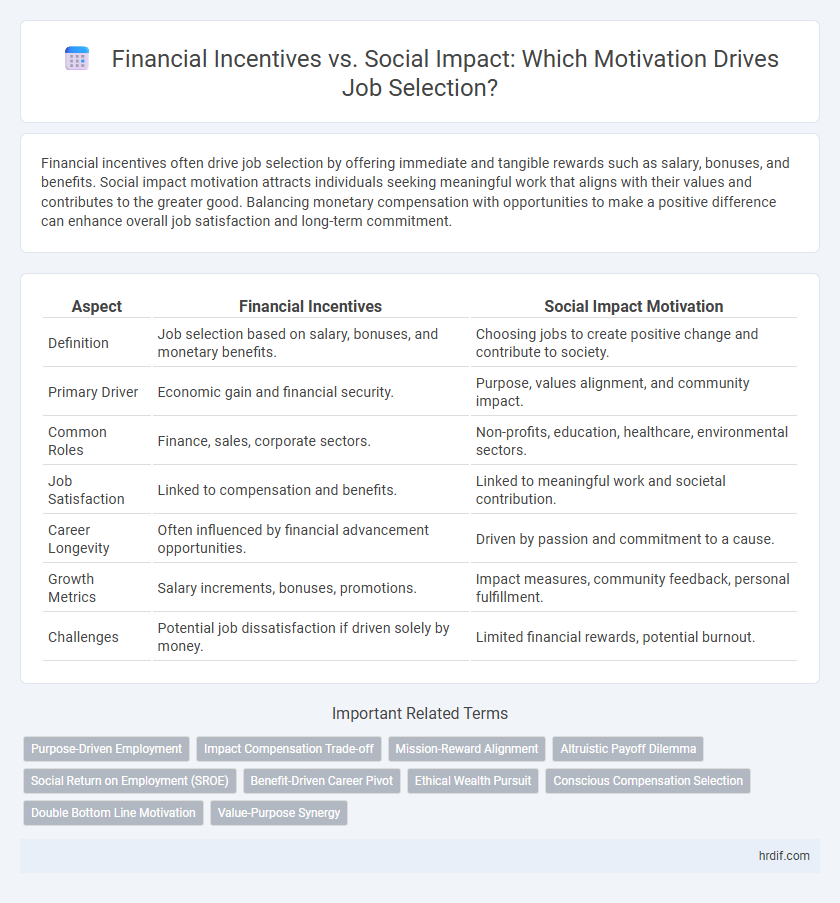
Financial incentives often drive job selection by offering immediate and tangible rewards such as salary, bonuses, and benefits. Social impact motivation attracts individuals seeking meaningful work that aligns with their values and contributes to the greater good. Balancing monetary compensation with opportunities to make a positive difference can enhance overall job satisfaction and long-term commitment.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Financial Incentives | Social Impact Motivation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Job selection based on salary, bonuses, and monetary benefits. | Choosing jobs to create positive change and contribute to society. |
| Primary Driver | Economic gain and financial security. | Purpose, values alignment, and community impact. |
| Common Roles | Finance, sales, corporate sectors. | Non-profits, education, healthcare, environmental sectors. |
| Job Satisfaction | Linked to compensation and benefits. | Linked to meaningful work and societal contribution. |
| Career Longevity | Often influenced by financial advancement opportunities. | Driven by passion and commitment to a cause. |
| Growth Metrics | Salary increments, bonuses, promotions. | Impact measures, community feedback, personal fulfillment. |
| Challenges | Potential job dissatisfaction if driven solely by money. | Limited financial rewards, potential burnout. |
Understanding Job Motivation: Money vs. Meaning
Job motivation is often influenced by financial incentives and social impact, with many workers weighing salary against meaningful work that contributes to society. Studies reveal that individuals motivated by social impact experience higher job satisfaction and long-term engagement compared to those driven primarily by monetary rewards. Employers aiming to attract and retain talent should balance competitive compensation with opportunities for employees to make a positive difference.
The Power of Pay: Financial Incentives in Career Choices
Financial incentives play a crucial role in career selection by directly influencing job seekers' decisions through salary, bonuses, and benefits that meet their economic needs and lifestyle goals. Competitive pay structures enhance employee retention and attract top talent by aligning compensation with industry standards and individual performance. Companies leveraging financial rewards often experience higher productivity and motivation, emphasizing the undeniable power of pay in shaping professional paths.
Purpose-Driven Work: The Appeal of Social Impact Roles
Purpose-driven work attracts employees seeking meaningful social impact rather than solely financial rewards, fostering higher job satisfaction and long-term commitment. Studies show that roles aligned with personal values and societal contribution increase intrinsic motivation and overall productivity. Organizations emphasizing social impact benefits often experience lower turnover rates and stronger employee engagement compared to those focusing primarily on financial incentives.
Weighing Salary Against Social Value
Choosing a job often involves weighing salary against social value, where financial incentives provide immediate economic security and tangible rewards. Social impact motivation drives individuals seeking meaningful work that contributes to societal well-being and personal fulfillment. Research indicates employees prioritizing social value exhibit higher long-term engagement, while those focused on salary may experience greater short-term satisfaction but less overall job commitment.
Generational Shifts: What Today’s Workers Prioritize
Younger generations, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, increasingly prioritize social impact motivation over financial incentives when selecting jobs, valuing purpose-driven work and corporate social responsibility. Studies indicate that 72% of Millennials prefer jobs with a mission aligned to their values, while older generations more often emphasize salary and benefits as primary motivators. Employers adapting to this generational shift incorporate social impact initiatives to attract and retain top talent from younger demographics.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Both Paths
Case studies reveal that employees motivated by financial incentives often achieve rapid career advancement and increased productivity, as seen in tech giants like Google and Apple where bonuses and stock options drive performance. Conversely, social impact motivation fuels long-term job satisfaction and retention, exemplified by organizations like TOMS and Patagonia that prioritize mission-driven work and community engagement. Both paths demonstrate distinct success metrics: financial incentives boost short-term gains, while social impact fosters enduring employee commitment and brand loyalty.
Navigating Trade-offs: Can You Have Both?
Balancing financial incentives and social impact motivation requires evaluating personal values alongside tangible rewards, as research shows job satisfaction correlates strongly with alignment to intrinsic motivations despite competitive salaries. Studies reveal professionals increasingly seek roles that offer meaningful contributions to society while providing financial stability, indicating that hybrid models with performance-based pay and social missions enhance retention. Strategic employers design compensation packages that integrate monetary benefits with opportunities for social impact, effectively attracting talent motivated by both economic factors and purpose-driven work.
Long-Term Satisfaction: Which Motivation Lasts?
Financial incentives provide immediate gratification but often lead to diminishing returns in long-term job satisfaction, as monetary rewards alone may fail to fulfill intrinsic desires. Social impact motivation fosters enduring fulfillment by aligning work with personal values and purpose, enhancing sustained engagement and well-being over time. Research consistently shows employees driven by social impact report higher long-term job satisfaction compared to those motivated primarily by financial gain.
Company Strategies: Attracting Talent with Pay and Purpose
Companies aiming to attract top talent balance competitive financial incentives with meaningful social impact initiatives to satisfy diverse employee motivations. Offering performance-based bonuses and equity shares appeals to candidates driven by monetary rewards, while promoting corporate social responsibility programs attracts those who prioritize purpose and values. Integrating pay and purpose in recruitment strategies enhances employer branding and increases retention by aligning individual goals with organizational mission.
Making Your Choice: Tips for Aligning Career with Values
Choosing between financial incentives and social impact motivation requires a clear understanding of personal values and long-term goals. Evaluating job roles based on salary benefits alongside the potential for meaningful community contribution helps in making an informed decision. Prioritizing career paths that resonate with individual ethics enhances job satisfaction and overall well-being.
Related Important Terms
Purpose-Driven Employment
Purpose-driven employment emphasizes intrinsic motivation where social impact often outweighs financial incentives in job selection, fostering long-term commitment and job satisfaction. Employees motivated by meaningful work demonstrate increased productivity and organizational loyalty compared to those driven primarily by salary.
Impact Compensation Trade-off
Employees often face an impact compensation trade-off where choosing jobs with higher financial incentives may reduce opportunities for social impact, while roles emphasizing social value typically offer lower monetary rewards. Understanding this balance can help organizations design compensation packages that attract talent motivated by both competitive salaries and meaningful societal contributions.
Mission-Reward Alignment
Employees who perceive strong alignment between their personal values and a company's mission demonstrate higher engagement and job satisfaction, especially when social impact motivation complements financial incentives. Organizations that integrate mission-reward alignment by balancing competitive salaries with meaningful social impact opportunities attract and retain talent driven by purpose and monetary benefits.
Altruistic Payoff Dilemma
Employees often face the Altruistic Payoff Dilemma when choosing jobs, weighing financial incentives against social impact motivation. Research shows that while competitive salaries attract talent, many individuals prioritize roles aligned with altruistic values, seeking intrinsic rewards over monetary gain to achieve personal fulfillment and societal benefit.
Social Return on Employment (SROE)
Social Return on Employment (SROE) emphasizes the broader societal benefits generated by job roles that prioritize social impact motivation over financial incentives. Employees driven by SROE contribute to community well-being and sustainable development, aligning personal fulfillment with organizational and social value creation.
Benefit-Driven Career Pivot
Benefit-driven career pivots often prioritize social impact motivation over financial incentives, as individuals seek meaningful work that aligns with personal values and long-term fulfillment. Studies show that employees motivated by contributing to social good exhibit higher job satisfaction and increased organizational commitment compared to those driven primarily by monetary rewards.
Ethical Wealth Pursuit
Financial incentives often drive job selection by offering tangible rewards and security, while social impact motivation appeals to individuals seeking ethical wealth pursuit through meaningful contributions. Balancing monetary gain with a commitment to social responsibility enhances long-term job satisfaction and aligns career goals with personal values.
Conscious Compensation Selection
Conscious Compensation Selection emphasizes balancing financial incentives with social impact motivation to attract employees aligned with a company's values and purpose. This approach enhances job satisfaction and long-term engagement by integrating meaningful work with competitive pay structures.
Double Bottom Line Motivation
Double Bottom Line Motivation integrates financial incentives with social impact goals, driving job selection by balancing profit generation and meaningful societal contribution. Employees motivated by this dual approach often exhibit higher engagement and retention, as they seek roles that fulfill both economic needs and ethical values.
Value-Purpose Synergy
Employees who experience value-purpose synergy often prioritize social impact motivation over financial incentives when selecting jobs, as meaningful work aligns with intrinsic values and long-term fulfillment. This alignment enhances job satisfaction and productivity by fostering a sense of purpose that transcends monetary rewards.
Financial incentives vs Social impact motivation for job selection. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com