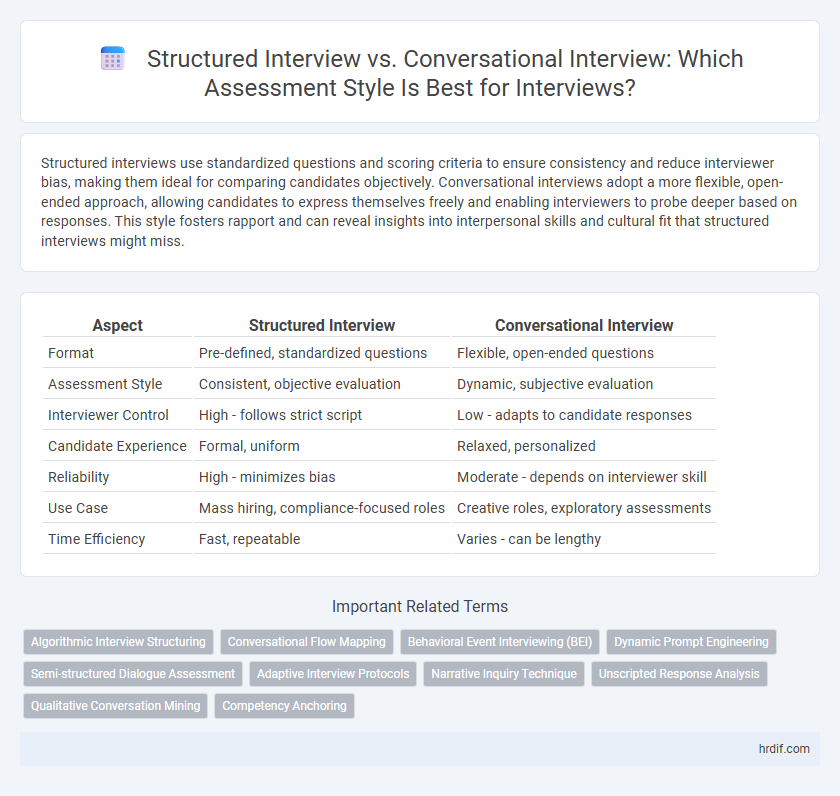
Structured interviews use standardized questions and scoring criteria to ensure consistency and reduce interviewer bias, making them ideal for comparing candidates objectively. Conversational interviews adopt a more flexible, open-ended approach, allowing candidates to express themselves freely and enabling interviewers to probe deeper based on responses. This style fosters rapport and can reveal insights into interpersonal skills and cultural fit that structured interviews might miss.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Structured Interview | Conversational Interview |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Pre-defined, standardized questions | Flexible, open-ended questions |
| Assessment Style | Consistent, objective evaluation | Dynamic, subjective evaluation |
| Interviewer Control | High - follows strict script | Low - adapts to candidate responses |
| Candidate Experience | Formal, uniform | Relaxed, personalized |
| Reliability | High - minimizes bias | Moderate - depends on interviewer skill |
| Use Case | Mass hiring, compliance-focused roles | Creative roles, exploratory assessments |
| Time Efficiency | Fast, repeatable | Varies - can be lengthy |
Introduction to Interview Assessment Styles
Structured interviews employ standardized questions ensuring consistent evaluation criteria, enhancing objectivity and reliability in candidate assessment. Conversational interviews offer flexibility, allowing interviewers to explore responses more deeply, which can reveal nuanced insights into candidates' personalities and problem-solving skills. Selecting the appropriate interview assessment style depends on the desired balance between consistency and adaptability in evaluating job applicants.
Defining Structured Interviews
Structured interviews are standardized assessment tools featuring predetermined questions and scoring criteria to ensure consistency and objectivity in candidate evaluation. They enhance reliability by minimizing interviewer bias and enabling direct comparison between candidates based on specific competencies. This method contrasts with conversational interviews, which rely on spontaneous dialogue and may lack uniform assessment metrics.
Understanding Conversational Interviews
Conversational interviews emphasize flexibility and natural dialogue, allowing interviewers to explore candidate responses in depth and adapt questions based on real-time answers. Unlike structured interviews with fixed questions and scoring criteria, conversational interviews foster rapport and provide richer insights into a candidate's problem-solving abilities and communication skills. This assessment style is particularly effective for roles requiring creativity, interpersonal skills, and adaptability.
Key Differences Between Structured and Conversational Interviews
Structured interviews use standardized questions and scoring systems to ensure consistency and objectivity in candidate assessment, improving reliability and comparability. Conversational interviews adopt a flexible, open-ended approach that encourages natural dialogue, allowing interviewers to explore candidate responses in-depth but risking variability in evaluation. Key differences include predictability, interviewer control, and scoring methods, impacting the accuracy and fairness of the assessment process.
Advantages of Structured Interviews
Structured interviews provide consistent and objective assessment by using standardized questions and scoring criteria, minimizing interviewer bias and ensuring reliability across candidates. They allow straightforward comparison of responses, enhancing the validity of hiring decisions and predicting job performance effectively. This assessment style supports legal defensibility and efficient data analysis, making it ideal for high-stakes recruitment.
Benefits of Conversational Interviews
Conversational interviews enhance candidate engagement by allowing a natural flow of dialogue, which helps reveal deeper insights into skills and cultural fit. This flexible approach adapts questions based on responses, uncovering personalized experiences that structured interviews might overlook. It fosters rapport-building, reducing candidate anxiety and promoting authentic communication for better assessment accuracy.
Limitations of Structured Interview Approaches
Structured interview approaches often limit the depth of candidate responses by adhering strictly to predetermined questions, reducing the ability to explore unique insights or clarify ambiguous answers. This rigidity can hinder the assessment of interpersonal skills and adaptability, which are better evaluated through more dynamic conversational interviews. Moreover, the standardized format risks overlooking contextual nuances that influence candidate performance and fit.
Challenges of Conversational Interviews
Conversational interviews face challenges such as inconsistent question delivery, making it difficult to ensure fairness and reliability across candidates. Interviewers may inadvertently introduce bias by varying question phrasing or probing differently, affecting the validity of assessment results. This lack of standardization complicates objective comparison and scoring, reducing the overall effectiveness of the evaluation process.
Choosing the Right Assessment Style for Your Hiring Process
Structured interviews offer standardized questions and scoring criteria, ensuring consistency and reducing bias in candidate evaluation. Conversational interviews allow for a more flexible, open-ended dialogue that can uncover deeper insights into a candidate's personality and problem-solving skills. Selecting the right assessment style depends on the role's requirements, with structured interviews favored for objective comparisons and conversational interviews suited for roles demanding creativity and interpersonal skills.
Best Practices for Effective Interview Assessments
Structured interviews enhance assessment reliability by using standardized questions, ensuring consistent evaluation criteria across candidates. Conversational interviews allow interviewers to adapt questions based on responses, fostering deeper insights into candidate fit and competencies. Combining structured frameworks with conversational flexibility promotes comprehensive and accurate hiring decisions.
Related Important Terms
Algorithmic Interview Structuring
Algorithmic interview structuring enhances assessment accuracy by implementing a structured interview format, which standardizes questions and evaluation criteria, reducing interviewer bias and improving predictive validity. Conversational interviews, while flexible, often lack consistent metrics, making them less reliable for algorithmic scoring and data-driven candidate comparisons.
Conversational Flow Mapping
Conversational Flow Mapping enhances the flexibility and depth of conversational interviews by allowing interviewers to adapt questions based on real-time responses, resulting in richer, more nuanced data compared to the rigid format of structured interviews. This dynamic approach improves candidate engagement and better assesses complex competencies through natural dialogue patterns.
Behavioral Event Interviewing (BEI)
Structured interviews, particularly Behavioral Event Interviewing (BEI), use standardized questions to systematically evaluate candidates' past behaviors and competencies, ensuring consistency and reliability in assessment. Conversational interviews offer flexibility and adaptability but may lack the rigorous framework BEI provides, potentially leading to variability in data quality and comparability across candidates.
Dynamic Prompt Engineering
Structured interviews utilize standardized questions to ensure consistency and reliability in candidate assessment, while conversational interviews allow for flexibility and adaptability in exploring responses, enhancing dynamic prompt engineering by tailoring follow-up questions based on real-time candidate input. Dynamic prompt engineering in interviews optimizes data quality by blending structured question frameworks with adaptive dialogue strategies, improving accuracy in evaluating candidate competencies and fit.
Semi-structured Dialogue Assessment
Semi-structured dialogue assessment combines the consistency of structured interviews with the flexibility of conversational approaches, allowing interviewers to explore topics in-depth while maintaining a clear evaluation framework. This method enhances the reliability and validity of candidate assessments by providing standardized questions alongside adaptive follow-ups tailored to the interviewee's responses.
Adaptive Interview Protocols
Structured interviews use predefined questions and scoring criteria to ensure consistent evaluation, while conversational interviews adapt dynamically to candidate responses, enhancing flexibility and depth. Adaptive interview protocols combine both methods by employing structured frameworks that guide follow-up questions based on real-time answers, improving assessment accuracy and candidate engagement.
Narrative Inquiry Technique
Structured interviews employ standardized questions ensuring consistency and reliability in assessment, while conversational interviews offer flexibility to explore participants' perspectives in depth; the Narrative Inquiry Technique aligns with conversational interviews by emphasizing personal storytelling to capture rich, contextualized data. This technique reveals nuanced insights and patterns through participants' narratives, enhancing qualitative understanding beyond rigid structured formats.
Unscripted Response Analysis
Structured interviews use predefined questions to ensure consistency and comparability, while conversational interviews emphasize unscripted response analysis to capture authentic candidate insights and adaptability. Assessing unscripted responses provides deeper evaluation of critical thinking, problem-solving, and interpersonal skills beyond standardized answer patterns.
Qualitative Conversation Mining
Structured interviews employ standardized questions to ensure consistency and comparability, making them ideal for quantitative data collection, while conversational interviews facilitate open-ended dialogue, enabling deeper insights through qualitative conversation mining by capturing nuanced participant perspectives and contextual information. Qualitative conversation mining leverages natural language processing techniques to analyze conversational data from unscripted interviews, uncovering themes, emotions, and patterns that structured formats may overlook.
Competency Anchoring
Structured interviews utilize competency anchoring by maintaining consistent, predefined questions mapped to specific skills, ensuring objective assessment and reducing interviewer bias. Conversational interviews offer flexibility but often lack standardized competency anchoring, potentially leading to subjective evaluations and inconsistent measurement of candidate abilities.
Structured interview vs conversational interview for assessment style. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com