An internship provides hands-on work experience by integrating students directly into a company's daily operations, often lasting several months and sometimes offering academic credit. Externships typically involve shorter, observational opportunities where participants shadow professionals to gain insight into a specific career without performing actual job tasks. Choosing between an internship and an externship depends on the desired level of engagement and the depth of real-world experience sought in a particular field.
Table of Comparison
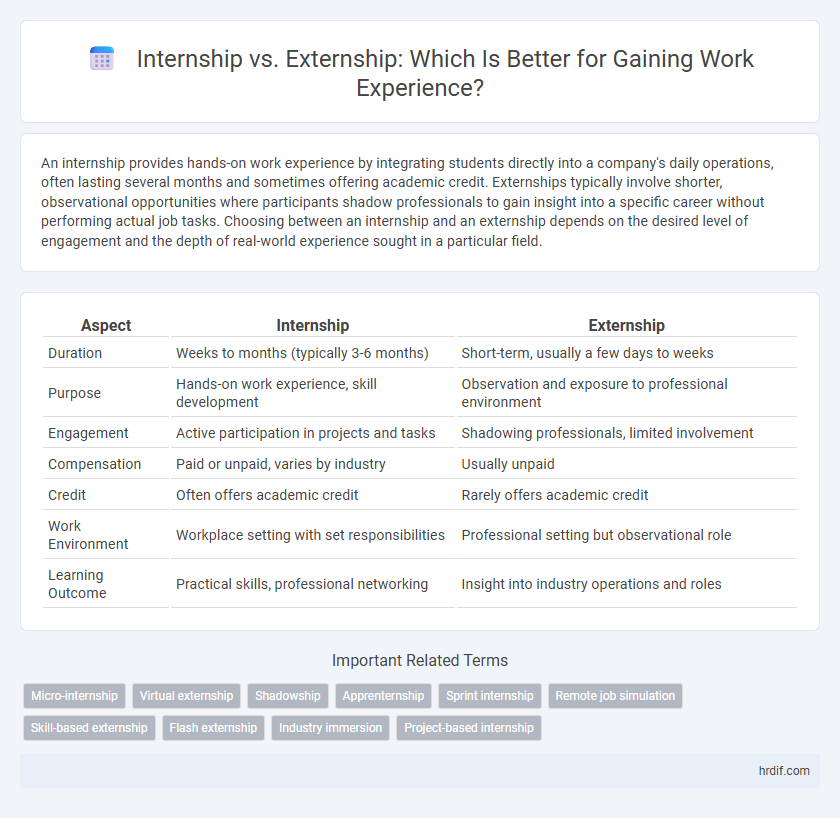
| Aspect | Internship | Externship |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Weeks to months (typically 3-6 months) | Short-term, usually a few days to weeks |
| Purpose | Hands-on work experience, skill development | Observation and exposure to professional environment |
| Engagement | Active participation in projects and tasks | Shadowing professionals, limited involvement |
| Compensation | Paid or unpaid, varies by industry | Usually unpaid |
| Credit | Often offers academic credit | Rarely offers academic credit |
| Work Environment | Workplace setting with set responsibilities | Professional setting but observational role |
| Learning Outcome | Practical skills, professional networking | Insight into industry operations and roles |
Understanding Internships and Externships
Internships offer hands-on work experience where individuals engage in specific projects and receive mentorship within a company over an extended period, typically weeks to months. Externships provide short-term observational opportunities, allowing participants to shadow professionals and gain insight into a particular career field without direct task involvement. Understanding these distinctions helps students and job seekers choose the best form of experiential learning based on their career goals and time availability.
Key Differences Between Internships and Externships
Internships involve hands-on work experience within a company over weeks or months, offering in-depth exposure to professional tasks and workplace culture. Externships are typically shorter, observational experiences lasting a few days to weeks, designed to provide a snapshot of a job or industry without direct work responsibilities. Internships often include structured learning objectives and mentorship, while externships prioritize shadowing and gaining broad insights.
Duration and Structure: Internship vs Externship
Internships typically last several weeks to months, offering a comprehensive, structured work experience with defined projects, training, and evaluations. Externships are shorter, often lasting a few days to a week, providing a brief, observational experience without the depth of responsibility or training found in internships. The structured nature of internships allows for skill development and practical application, while externships primarily offer exposure to the workplace environment and industry insights.
Learning Outcomes: Hands-on vs Observational Experience
Internships provide immersive, hands-on learning experiences that develop practical skills through direct participation in workplace projects. Externships emphasize observational learning, allowing individuals to shadow professionals and gain insights into industry operations and workflows. These distinct learning outcomes influence the depth of skill acquisition and real-world application during career preparation.
Eligibility and Application Process
Internship opportunities typically require candidates to be enrolled in a college or university program, with applications often submitted through formal channels such as company websites or university career services. Externships generally have more flexible eligibility criteria, often targeting high school or college students seeking short-term observational experiences, and applications may involve direct outreach to organizations or participation in structured externship fairs. Both programs demand tailored application materials emphasizing relevant skills and a clear understanding of the role's expectations.
Benefits of Internships in Career Development
Internships offer hands-on experience that directly enhances career development by allowing students to apply academic knowledge in real-world settings, build industry-specific skills, and expand professional networks. Unlike externships, which are typically shorter and observational, internships provide deeper engagement and often lead to job offers, mentoring relationships, and a stronger resume. These benefits make internships a critical stepping stone for gaining meaningful work experience and increasing employability after graduation.
Advantages of Externships for Career Exploration
Externships offer immersive, short-term work experiences that allow students to explore specific career fields without long-term commitments, enhancing practical understanding and networking opportunities. They provide direct exposure to industry environments and real-world tasks, helping individuals make informed career decisions while building valuable professional connections. Companies benefit from externships by identifying potential talent and fostering industry relationships with emerging professionals.
Choosing Between Internship and Externship
Choosing between an internship and an externship depends on the desired level of work experience and time commitment; internships typically offer longer, hands-on experience with specific projects, while externships provide short-term observational opportunities in a professional environment. Internships allow students to develop practical skills and build professional networks through direct involvement, whereas externships are ideal for exploring career fields and gaining insights without extensive time investment. Assessing personal career goals, availability, and the depth of experience needed is crucial in selecting the right program for meaningful industry exposure.
Industry Preferences: Where Each is Valued
Internships are highly valued in industries such as technology, finance, and healthcare for their extended duration and hands-on project involvement, offering deeper skill development. Externships, often preferred in legal, medical, and education fields, provide short-term observational experiences that allow students to gain insights into professional environments without long-term commitment. Companies in sectors emphasizing practical application and sustained contribution prioritize internships, whereas those seeking quick exposure and networking opportunities lean towards externships.
Tips for Maximizing Work Experience Opportunities
Prioritize roles that align closely with your career goals to gain relevant skills and industry knowledge. Actively seek feedback and network with professionals during both internships and externships to build valuable connections. Balance hands-on tasks with observation opportunities to maximize learning and showcase your adaptability to potential employers.
Related Important Terms
Micro-internship
Micro-internships offer short-term, project-based work experiences that differ from traditional internships and externships by providing flexible, skill-specific opportunities ideal for building a diverse portfolio. Unlike externships, which are typically observational and brief, micro-internships involve active contribution to real business tasks, enhancing practical job readiness and professional growth in condensed timeframes.
Virtual externship
Virtual externships offer flexible, remote work experience by allowing participants to observe professionals and gain industry insights without the hands-on responsibilities typical of internships. Unlike internships that involve active project contributions and skill application, virtual externships emphasize mentorship and job shadowing through online platforms.
Shadowship
Shadowship offers immersive observational learning by allowing interns to closely follow experienced professionals during their workday, providing real-time insights into job functions without direct task responsibility. Unlike externships, which typically last a few days or weeks, shadowships facilitate ongoing mentorship and detailed understanding of career paths, enhancing practical knowledge for future employment.
Apprenternship
Internships provide hands-on work experience over a fixed period, allowing participants to apply academic knowledge in real-world settings, while externships offer short-term observational opportunities without direct job responsibilities. Apprenticeships combine paid on-the-job training with classroom instruction, delivering a structured pathway to develop specialized skills and industry-recognized certifications.
Sprint internship
Sprint internships provide hands-on work experience through longer-term projects within a professional setting, allowing interns to develop practical skills and industry knowledge. Unlike externships, which are typically short-term observational experiences, Sprint internships emphasize active participation and direct contribution to company goals.
Remote job simulation
Internships offer immersive, long-term work experience often including remote job simulation to develop practical skills, while externships provide brief, observational opportunities with limited hands-on remote tasks. Remote internships enhance proficiency in digital collaboration tools and real-world project management, whereas externships mainly expose participants to virtual work environments without intensive engagement.
Skill-based externship
Skill-based externships provide targeted, hands-on experience in specific industries, allowing participants to rapidly develop practical competencies without the extended time commitment of internships. Unlike internships, which often combine learning with broader organizational exposure, skill-based externships focus intensely on mastering particular tasks and technical skills essential for career advancement.
Flash externship
Flash externships offer short-term, immersive work experiences designed to provide rapid exposure to industry-specific skills, making them ideal for students seeking concise yet impactful career insights. Unlike traditional internships, flash externships prioritize flexibility and a condensed timeline, enabling participants to quickly explore professional environments without long-term commitments.
Industry immersion
Internships provide comprehensive industry immersion through extended hands-on projects and professional networking opportunities, enhancing practical skills and workplace adaptability. Externships offer short-term observational experiences that allow students to gain insights into industry workflows and company culture without the deeper engagement of an internship.
Project-based internship
Project-based internships offer hands-on experience by allowing interns to complete specific assignments or projects that mirror real-world work challenges, enhancing practical skills and portfolio development. Unlike externships, which typically involve observational learning and short-term exposure, project-based internships provide deeper engagement and measurable outcomes essential for career growth.
Internship vs Externship for work experience. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com